Fractura de Hoffa
Palabras clave:
Fractura del extremo distal del fémur, Fractura de Hoffa, Reducción asistida por artroscopia, Tomografía computarizadaResumen
Introducción: Las fracturas del extremo distal del fémur son lesiones invalidantes. Entre ellas la fractura de Hoffa es una afección infrecuente de difícil diagnóstico y tratamiento.
Objetivo: Actualizar sobre los elementos más importantes de esta enfermedad traumática.
Métodos: La búsqueda y análisis de la información se realizó en un periodo de 60 días (primero de noviembre al 30 de diciembre de 2020) y se emplearon las siguientes palabras claves: Hoffa's fracture AND distal femur fracture a partir de la información obtenida se realizó una revisión bibliográfica de un total de 529 artículos publicados en las bases de datos PubMed, Hinari, SciELO y Medline mediante el gestor de búsqueda y administrador de referencias EndNote, de ellos se utilizaron 37 citas seleccionadas para realizar la revisión, 35 de los últimos cinco años.
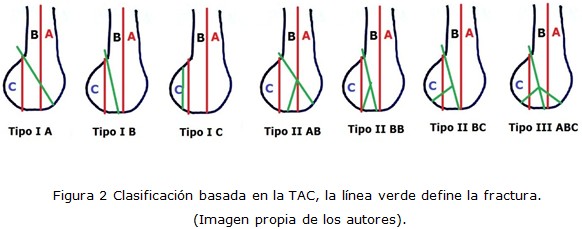
Resultados: Se menciona el mecanismo de producción de alta y baja energía. Se hace referencia a las clasificaciones basadas en la radiografía simple y la tomografía axial computarizada. Se exponen las principales enfermedades asociadas a la fractura de Hoffa. Con relación al tratamiento se mencionan las modalidades conservadoras y quirúrgicas, en esta última, las vías de abordaje según la localización y tipo de fractura, con especial énfasis en la cirugía artroscópica.
Conclusiones: La fractura de Hoffa es una lesión infrecuente provocada por un mecanismo de producción de alta energía y asociada en ocasiones a otras enfermedades traumáticas. El tratamiento de esta afección es por lo general de tipo quirúrgico y la modalidad a emplear está basada en la configuración geométrica de la fractura.
DeCS: FRACTURAS DEL FÉMUR/clasificación; FÉMUR/lesiones; ARTROSCOPÍA/métodos; TOMOGRAFÍA COMPUTARIZADA POR RAYOS X; LITERATURA DE REVISIÓN COMO ASUNTO.
Descargas
Citas
1. Collinge CA, Wiss DA. Distal femur fractures. En: Tornetta P, Ricci WM, Court Brown CM, McQueen MM, Heckman JD, editors. Rockwood and Green's Fractures in Adults. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health;2015.p.2229-66.
2. Egol KA, Broder K, Fisher N, Konda SR. Repair of displaced partial articular fracture of the distal femur: the Hoffa fracture. J Orthop Trauma [Internet]. 2017 Ago [citado 07 Ene 2021];31(Suppl 3):S10-S11. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28697072/.
3. Patel PB, Tejwani NC. The Hoffa fracture: Coronal fracture of the femoral condyle a
review of literature. J Orthop [Internet]. 2018 Jun [citado 07 Ene 2021];15(2):726-731. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5990301/.
4. Jordan MC, Bittrich LA, Fehske K, Meffert RH, Jansen H. A rare case of Hoffa fracture combined with lateral patellar dislocation. Trauma Case Reports [Internet]. 2017 [citado 07 Ene 2021];9:13-16. Disponible en: https://d-nb.info/1155098226/34
5. Kapoor C, Merh A, Shah M, Golwala P. A Case of Distal Femur Medial Condyle Hoffa Type II(C) Fracture Treated with Headless Screws. Cureus [Internet]. 2016 Sep [citado 07 Ene 2021];8(9):e802. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5081261/
6. Trikha V, Das S, Gaba S, Agrawal P. Analysis of functional outcome of Hoffa fractures: a
retrospective review of 32 patients. J Orthop Surg [Internet]. 2017 Jul [citado 07 Ene 2021];25(2):1-7. Disponible en: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/2309499017718928
7. Chandrabose R, Saha S, Kumar H, Tapadiya N, Hd B. A computed tomography-based classification of Hoffa fracture: surgical treatment considerations and prognostic outcome with assessment of reproducibility. J Orthop [Internet]. 2019 Dic [citado 07 Ene 2021];20:21-27. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32021051/
8. Xie X, Zhan Y, Dong M, He Q, Lucas JF, Zhang Y, et al. Two and three-dimensional CT mapping of Hoffa fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am [Internet]. 2017 Nov [citado 07 Ene 2021];99(21):1866-1874. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29088042/.
9. Pires RE, Giordano V, Fogagnolo F, Yoon RS, Liporace FA, Kfuri M. Algorithmic treatment of Busch-Hoffa distal femur fractures: a technical note based on a modified Letenneur classification. Injury [Internet]. 2018 Ago [citado 07 Ene 2021];49(8):1623-1629. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29885965/
10. Hill BW, Cannada LK. Hoffa fragments in the geriatric distal femur fracture: myth
or reality? Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil [Internet]. 2017 Dic [citado 07 Ene 2021];8(4):252-255. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5755847/.
11. Joseph CM, Rama-Prasad YS, Boopalan PRJVC, Jepegnanam TS. Long term follow-up of an open bicondylar Hoffa fracture with a disrupted extensor mechanism: a case report. Malays Orthop J [Internet]. 2019 Jul [citado 07 Ene 2021];13(2):59-62. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6702977/.
12. Harna B, Dwivedi DD, Pippal HK, Sabat D. Bicondylar conjoint Hoffa's fracture with patella entrapped in the fracture: a rare case report. J Clin Orthop Trauma [Internet]. 2018 Jun [citado 07 Ene 2021];9(Suppl 2):S35-S38. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6008609/.
13. Kumar P, Agarwal S, Kumar D, Rajnish RK, Jindal K. Rim plating for a rare variant of posteromedial tibial condyle fracture; partial coronal split, akin to Hoffa's fracture, associated with multi-ligament injuries and central depression. Trauma Case Rep [Internet]. 2019 [citado 07 Ene 2021];20. Disponible en: https://doaj.org/article/51646e92291246a5a7927d8d58a9a713
14. Coo MS, Best BJ. Distal femur fractures [Internet]. 2021 Ago [citado 07 Ene 2021]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551675/.
15. Yao SH, Su WR, Hsu KL, Chen Y, Hong CK, Kuan FC. A biomechanical comparison of two screw fixation methods in a Letenneur type I Hoffa fracture. BMC Musculoskelet Disord [Internet]. 2020 Jul [citado 07 Ene 2021];21:497. Disponible en: https://bmcmusculoskeletdisord.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12891-020-03527-4
16. Zhou Y, Pan Y, Wang Q, Hou Z, Chen W. Hoffa fracture of the femoral condyle: Injury mechanism, classification, diagnosis, and treatment. Medicine [Internet]. 2019 Feb [citado 07 Ene 2021];98(8):14633. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30813201/.
17. Bagaria V, Sharma G, Waghchoure C, Chandak RM, Nemade A, Tadepelli K, et al. A proposed radiological classification system of Hoffa's fracture based on fracture configuration and consequent optimal treatment strategy along with the review of literature. SICOT J [Internet]. 2019 [citado 07 Ene 2021];5:18. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6557153/.
18. Somford MP, Nieuwe Weme RA, Hoornenborg D, Wiegerinck JI, van Raay JJAM, Brouwer RW, et al. Biographical background and origin of common eponymous terms in orthopedic surgery: anatomy and fractures in knee surgery. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol [Internet]. 2018 Ene [citado 07 Ene 2021];28:79-84. Disponible en: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00590-017-2005-x
19. Gammon L, Hansen E, Cheatham S. Technique for reduction and fixation of a Hoffa fracture with ipsilateral patella dislocation from low-energy trauma, a rare injury: a case report. JBJS Case Connect [Internet]. 2020 Ene-Mar [citado 07 Ene 2021];10(1):e0250. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32224673/
20. Liu Q, Wang W, Fan W, Zhu W. Hoffa fracture associated with tibial shaft fracture and
multiple ligament avulsion fractures: a case report. Trauma Case Rep [Internet]. 2020 Ene [citado 07 Ene 2021];26:100277.Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31989015/.
21. Pathak S, Salunke A, Karn S, Ratna HVK, Thivari PS, Sharma S, et al. Hoffa's fracture wih associated injuries around the knee joint: an approach to a rare injury. Cureus [Internet]. 2020 Abr [citado 07 Ene 2021];12(4):e7865. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7255537/.
22. Goos JAC, Emmink BL, Nieuwenhuis D, Bosman WM. Hoffa fracture accompanied by dissection of the popliteal artery. BMJ Case Rep [Internet]. 2019 Dic [citado 07 Ene 2021];12(12):e232348. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31818893/.
23. Giotikas D, Nabergoj M, Krkovic M. Surgical management of complex intra-articular distal femoral and bicondylar Hoffa fracture. Ann R Coll Surg Engl [Internet]. 2016 Nov [citado 07 Ene 2021];98(8):e168-e170. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5392877/.
24. Xu Y, Li H, Yang HH, Pan ZJ. A comparison of the clinical effect of two fixation methods on Hoffa fractures. Springerplus [Internet]. 2016 Jul [citado 07 Ene 2021];5(1):1164. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27512623/.
25. Xu Y, Li H, Yang HH. [Intercondylar fossa screw with plate fixation for Letenneur type III Hoffa fractures]. Zhongguo Gu Shang [Internet]. 2016 Dic [citado 07 Ene 2021];29(12):1146-1149. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29292892/.
26. Singh R, Singh RB, Mahendra M. Functional outcome of isolated Hoffa fractures treated with cannulated cancellous screw. Malays Orthop J [Internet]. 2017 Jul [citado 07 Ene 2021];11(2):20-24. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5630046/.
27. Lian X, Zeng YJ. Meta plate and cannulated screw fixation for treatment of type Letenneur III lateral Hoffa fracture through posterolateral approach. Zhongguo Gu Shang [Internet]. 2018 Mar [citado 07 Ene 2021];31(3):267-271. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29600680/.
28. Zhao LL, Tong PJ, Xiao LW. Internal fixation with lag screws plus an anti-sliding plate
for the treatment of Hoffa fracture of the lateral femoral condyle. Zhongguo Gu Shang [Internet]. 2016 Mar [citado 07 Ene 2021];29(3):266-9. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27149799/.
29. Lu B, Zhao S, Luo Z, Lin Z, Zhu Y. Compression screws and buttress plate versus compression screws only for Hoffa fracture in Chinese patients: a comparative study. J Int Med Res [Internet]. 2019 Ene [citado 07 Ene 2021];47(1):142-151. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6384458/.
30. Onay T, Gülabi D, Çolak İ, Bulut G, Gümüştaş SA, Çeçen GS. Surgically treated Hoffa Fractures with poor long-term functional results. Injury [Internet]. 2018 Feb [citado 07 Ene 2021];49(2):398-403. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29198374/.
31. Orapiriyakul W, Apivatthakakul T, Buranaphatthana T. How to determine the surgical approach in Hoffa fractures? Injury [Internet]. 2018 Dic [citado 07 Ene 2021];49(12):2302-2311. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30526925/.
32. Maheshwari V, Sharma SL, Goyal D, Qureshi P, Hussain Z. Clinical experience with management of Hoffa fractures using headless compression screw and headed screw. J Clin Orthop Trauma [Internet]. 2019 Sep-Oct [citado 07 Ene 2021];10(5):934-940. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6739431/.
33. Sun H, He QF, Huang YG, Pan JF, Luo CF, Chai YM. Plate fixation for Letenneur type I Hoffa fracture: a biomechanical study. Injury [Internet]. 2017 Jul [citado 07 Ene 2021];48(7):1492-1498. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28390685/.
34. Tham WW, Khor YP, Chee YH. Deformity correction using the "Sandwich" technique for a non-union Hoffa fracture. Ann Acad Med Singapore [Internet]. 2019 Feb [citado 07 Ene 2021];48(2):63-66. Disponible en: https://annals.edu.sg/pdf/48VolNo2Feb2019/V48N2p63.pdf
35. Ercin E, Baca E, Kural C. Arthroscopic treatment of isolated Hoffa fractures. J Knee Surg [Internet]. 2017 Oct [citado 07 Ene 2021];30(8):842-848. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28219089/.
36. Goel A, Sabat D, Agrawal P. Arthroscopic-assisted fixation of Hoffa fracture: a case report and description of technique. J Clin Orthop Trauma [Internet]. 2016 Ene-Mar [citado 07 Ene 2021];7(1):61-65. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4735559/.
37. Xiao K, Chen C, Yang J, Yang D, Liu J. An attempt to treat Hoffa fractures under arthroscopy: a case report. Chin J Traumatol [Internet]. 2018 Oct [citado 07 Ene 2021];21(5):308-310. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30340980/.
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
La Revista Archivo Medico Camagüey, ofrece de forma inmediata después de ser indexada en el Proyecto SciELO; acceso abierto al texto completo de los artículos bajo el principio de hacer disponible y gratuita la investigación para favorecer el intercambio del conocimiento global y coadyuvar a una mayor extensión, publicación, evaluación y uso extensivo de los artículos que se exponen pudiendo ser utilizados, sin fines comerciales, siempre y cuando se haga referencia a la fuente primaria.
Carta De Declaración De Autoría u Derechos De Autor(a)
Conflictos de intereses: los autores deberán declarar de forma obligatoria la presencia o no de conflictos de intereses en relación con la investigación presentada. (Descargar Plantilla para declarar confictos de intereses)
La Revista Archivo Médico Camagüey se encuentra bajo una
Licencia Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial 4.0 International (CC BY NC 4.0).
Esta licencia permite a otros distribuir, mezclar, ajustar y construir a partir de su obra, incluso con fines comerciales, siempre que le sea reconocida la autoría de la creación original. Esta es la licencia más servicial de las ofrecidas. Recomendada para una máxima difusión y utilización de los materiales sujetos a la licencia. La licencia completa puede consultarse en: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












