Los campos electromagnéticos de frecuencia extremadamente baja y su influencia en la salud humana: un tema polémico
Palabras clave:
campos electromagnéticos, salud ambiental, límites permisibles, control de la exposición a la radiación, humanosResumen
Fundamento: en todas las áreas de la vida moderna, está presente de forma creciente la exposición a campos electromagnéticos de frecuencia muy baja, su influencia sobre la salud de los seres humanos constituye un tema de debate a nivel mundial por considerarse como posibles carcinógenos humanos.
Objetivo: realizar un análisis crítico del tema basado en los valores de exposición a los campos electromagnéticos de frecuencia baja, propuestos en las directrices de la comisión internacional para la protección contra las radiaciones no ionizantes y la bibliografía existente consultada.
Métodos: se realizó una revisión bibliográfica con el método de análisis bibliográfico a través de una búsqueda realizada entre los años 1979 al 2016, donde se consultaron bases de datos especializadas y se seleccionaron 28 publicaciones científicas sobre el tema.
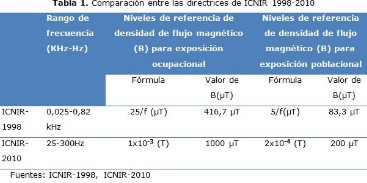
Desarrollo: la comisión internacional para la protección contra las radiaciones no ionizantes publicó directrices de exposición en 1998 y 2010, de manera que superó por margen muy amplio los valores de la segunda respecto a la primera, lo que no se justifica de acuerdo a los numerosos estudios publicados sobre el tema que relacionan la aparición de leucemia con inducciones magnéticas mayores de 0,4 µT.
Conclusiones: los sistemas biológicos sufren la influencia de la inducción magnética de los campos electromagnéticos de frecuencia muy baja antropogénicos. Existe la necesidad de que la proyección mundial sobre este tema esté dirigida a la protección inmediata de las personas con regulaciones sanitarias de carácter legal.
DeCS: CAMPOS ELECTROMAGNÉTICOS; SALUD AMBIENTAL; CONTROL DE LA EXPOSICIÓN A LA RADIACIÓN; HUMANOS; LITERATURA DE REVISIÓN COMO ASUNTO.
Descargas
Citas
1.Reiter RJ. A review of Neuroendocrine and Neurochemical Changes Associated with Static and Extremely Low Frequency Electromagnetic Field Exposure. Int Physiol Behav Science. 1993;28(1):57-75.
2.Knave B. Radiation, non-ionizing. En: Stellman JM, editor. Encyclopaedia of Occupational Health and Safety. VII. 4th ed. Geneva: International Labour Office; 1998. p. 49.1-49.31.
3. García SI. La Salud Humana y los Campos electromagnéticos de frecuencia extremadamente baja (CEM-FEB) [Internet]. Buenos Aires: Asociación Toxicológica Argentina; 2005 [citado 6 Jul 2016]. Disponible en: http://www.adeera.com.ar/archivos/INFORME%20DE%20ATA%20Version%20final.pdf
4.Revueltas Agüero M. Contaminación magnética de frecuencia extremadamente baja en instalaciones eléctricas y sus vecindades. La Habana, 2013-2015 [tesis Maestria]. La Habana: INHEM; 2015.
5. Spruijt P, Knol AB, Petersen AC, Lebret E. Different roles of electromagnetic field experts when giving policy advice: an expert consultation. Environmental Health [Internet]. 2015 [citado 2016 Jul 12];14(7):[about 8 p.]. Available from: https://ehjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1476-069X-14-7
6.Organización Mundial de Salud. Campos electromagnéticos (CEM). El Proyecto Internacional CEM [Internet]. Ginebra: OMS; c2016 [citado 19 Jul 2016]. Disponible en: http://www.who.int/peh-emf/project/es/.
7.Johansen C. Electromagnetic fields and health effects–epidemiologic studies of cancer and arrhythmia-related heart disease. Scand J Work Environ Heath [Internet]. 2004 [citado 2016 Jul 12];30(Suppl 1):[about 80 p.]. Available from: http://www.sjweh.fi/download.php?abstract_id=792&file_nro=1
8.International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection. Guidelines for limiting exposure to time-varyng electric, magnetic, and electromagnetic fields (Up to 300GHz). Health Physics [Internet]. 1998 [citado 2016 Jul 12];74(4):[about 28 p.]. Available from: http://www.icnirp.org/cms/upload/publications/ICNIRPemfgdl.pdf
9.International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection. Guidelines for limiting exposure to time-varyng electric, magnetic, and electromagnetic fields (1Hz to 100 kHz) Health Phys [Internet]. 2010 Dec [citado 2016 Jul 12];99(6):[about 18 p.]. Available from: http://www.icnirp.org/cms/upload/publications/ICNIRPLFgdl.pdf
10.World Health Organization. Extremely low frequency fields [Internet]. Ginebra: WHO; 2007 [citado 2016 Jul 14]. Available from: http://www.who.int/peh-emf/publications/Complet_DEC_2007.pdf
11.Koifman RJ, Echenique Mattos I. Campos electromagnéticos de freqüência extremadamente baixa (50-60Hz) e cáncer: Revisao comentada da literatura. Rio de Janeiro: Escola Nacional de Saúde Pública; 1996.
12.Organización Mundial de Salud. Campos electromagnéticos (CEM).Campos electromagnéticos y la salud pública. Exposición a campos de frecuencia extremadamente bajas [Internet]. Ginebra: OMS; c2016. Nota descriptiva No.322; Jun 2007 [citado 12 Jul 2016]. Disponible en: http://www.who.int/peh-emf/publications/facts/fs322/es/.
13.Heredia Rojas JA, Rodríguez Flores L, Santoyo Stephano M, Castañeda Garza E, Rodríguez De la Fuente A. Los campos electromagnéticos: ¿un problema de salud pública? Respyn [Internet]. 2003 [citado 6 Feb 2015];4(1):[aprox. 25 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.respyn.uanl.mx/iv/1/ensayos/campos.html
14.Upton A. Radiación. En: Frumkin H, editor. Salud Ambiental de lo global a lo local. Washington, DC: McGraw-Hill Interamericana; 2010. p. 776-8.
15.Panagopoulos DJ, Johansson O, Carlo GL. Polarization: A key difference between man-made and natural electromagnetic fields, in regard to biological activity. Nature.com. Scientific Reports [Internet]. 2015 Oct [citado 2016 Jul 23];(5):[about 25 p.]. Available from: http://www.nature.com/articles/srep14914
16.Markov MS, Pilla AA. Weak static magnetic field modulation of myosin phosphorylation in a cell free preparation: calcium dependence. Biolectr Bionerg. 1997;43(2):233-8.
17.Feychting M, Ahlbom A. Magnetic fields and cancer in children residing near swedish high-voltage power lines. Am J Epidemiol. 1993;138(7):467-81.
18.Wertheimer N, Leeper E. Electrical Wiring Configurations and Childood Cancer. Am J Epidemiol [Internet]. 1979 [citado 2016 Jul 23];109(3):[aprox. 12 p.]. Available from: http://aje.oxfordjournals.org/content/109/3/273.full.pdf
19.Kheifets L, Ahlbom A, Crespi CM, Draper G, Hagihara J, Lowenthal RM, et al. Pooled analysis of recent studies on magnetic fields and childhood leukaemia. Br J Cancer [Internet]. 2010 Sep 28 [citado 2016 Jul 12];103(7):[aprox. 8 p.]. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2965855/.
20.Khail AM, Qassem W, Amoura F. Citogenetic changes in human lymphocytes from workers occupationally exposed to high-voltage electromagnetic fields. Electro magnetobiol [Internet]. 1993 [citado 2016 Jul 12];12(1):[aprox. 9 p.]. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/15368379309012859
21.Barceló Pérez C, Guzmán Piñeiro R, Taureaux Díaz N. Campos electromagnéticos de baja frecuencia y leucemia infantil en Ciudad de la Habana. Rev Cub Hig Epidemiol [Internet]. 2005 [citado 7 Jul 2016];43(3):[aprox. 20 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?pid:5O864-03001997000100006&script=sci_arttext&tlng=pt
22.Guzmán Piñeiro R, Barceló Pérez C, Taureaux Díaz N, Reyes Secades G, Moncada Rodríguez I. Estudio caso-control sobre factores de riesgo de la leucemia infantil en Ciudad de la Habana. Rev Cubana HigEpidemiol [Internet]. Abr 2007 [citado 14 Jul 2016];45(1):[aprox. 11 p. ]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?scrpt=sci_arttext&pid=S1561-30032007000100006&1ng=es
23.Reyes Secades G, Barceló Pérez C, Moncada Rodríguez I. Leucemia infantil aguda y campos electromagnéticos en municipios de Ciudad de La Habana: Estudio de casos y controles. Rev Cubana Hig Epidemiol [Internet]. Abr 2006 [citado 14 Jul 2016];44(1):[aprox. 26 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1561-30032006000100002&1ng=es
24.The Bioinitiative Report 2012. A Rationale for Biologically-based Exposure Standards for Low-Intensity Electromagnetic Radiation [Internet]. California, (USA): Bioinitiative Report; c2006-2014 [citado 2016 Jul 12]. Available from: http://bioinitiative.info/bioInitiativeReport2012.pdf
25.Yang Y, Jin X, Yan Ch, Tian Y, Tang J, Shen X. Case-only study of interactions between DNA repair genes (hMLH1, APEX1, MGMT, XRCC1 and XPD) and low-frequency electromagnetic fields in childhood acute leukemia. Leukemia & Lymphoma [Internet]. 2008 Dec [citado 2016 Jul 9];49(12):[about 17 p.]. Available from: http://hinari-gw.who.int/whalecominformahealthcare.com/whalecom0/doi/pdf/10.1080/10428190802441347
26.Marcilio I, Gouveia N, Pereira Filho ML, Kheifets L. Adult mortality from leukemia, brain cancer, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and magnetic fields from power lines: a case-control study in Brazil. Rev bras epidemiol [Internet]. 2011 Dec [citado 2016 Jul 24];14(4):[about 8 p.]. Available from: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1415-790X2011000400005&lng=en
27.Asamblea Parlamentaria del Consejo de Europa (APCE). Consejo de Europa pide que se tomen medidas frente a la radiación [Internet]. España: Consejo de Europa; 2011 [citado 12 Jul 2016]. Disponible en: http://www.next_up.org/Newsoftheworld/2011.pdf
28.Grellier J, Ravazzani P, Cardis E. Potential health impacts of residential exposures to extremely low frequency magnetic fields in Europe. Environ Int [Internet]. 2014 [citado 2016 Jul 16];62:[about 9 p.]. Available from: http://public-files.prbb.org/publicacions/4260f5d0-9ada-0131-59d5-525400e56e78.pdf
29.Schüz J, Dasenbrock C, Ravazzani P, Röösli M, Schär P, Bounds PL, et al. Extremely Low-Frequency Magnetic Fields and Riskof Childhood Leukemia: A Risk Assessment by the ARIMMORA Consortium Bioelectromagnetics [Internet]. 2016 [citado 2016 Aug 23];37(3):[about 7 p.]. Available from: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/bem.21963/full
30.Alonso Fustel E, Garcia Vázquez R, Onaindia Olalde C. Campos electromagnéticos y efectos en salud [Internet]. Bizkaia (España): Subdirección de Salud Pública de Bizkaia; 2012 [citado 2 Jul 2016]. Disponible en: http://www.osakidetza.euskadi.eus/contenidos/informacion/cem_salud/es_cem/adjuntos/cem.pdf
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2017 Moura Revueltas Agüero, Tania Gutiérrez Soto

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 4.0.
La Revista Archivo Medico Camagüey, ofrece de forma inmediata después de ser indexada en el Proyecto SciELO; acceso abierto al texto completo de los artículos bajo el principio de hacer disponible y gratuita la investigación para favorecer el intercambio del conocimiento global y coadyuvar a una mayor extensión, publicación, evaluación y uso extensivo de los artículos que se exponen pudiendo ser utilizados, sin fines comerciales, siempre y cuando se haga referencia a la fuente primaria.
Carta De Declaración De Autoría u Derechos De Autor(a)
Conflictos de intereses: los autores deberán declarar de forma obligatoria la presencia o no de conflictos de intereses en relación con la investigación presentada. (Descargar Plantilla para declarar confictos de intereses)
La Revista Archivo Médico Camagüey se encuentra bajo una
Licencia Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial 4.0 International (CC BY NC 4.0).
Esta licencia permite a otros distribuir, mezclar, ajustar y construir a partir de su obra, incluso con fines comerciales, siempre que le sea reconocida la autoría de la creación original. Esta es la licencia más servicial de las ofrecidas. Recomendada para una máxima difusión y utilización de los materiales sujetos a la licencia. La licencia completa puede consultarse en: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/











