Estimación del riesgo cardiovascular en pacientes con diabetes mellitus tipo 2
Resumen
Introducción: Las personas diabéticas tienen entre dos y tres veces más riesgo de morbilidad y mortalidad cardiovascular que aquellas que no padecen la enfermedad.
Objetivo: Estimar el riesgo cardiovascular en pacientes con diabetes mellitus tipo 2 atendidos en un Área de Salud.
Métodos: Se realizó un estudio descriptivo y trasversal de 103 pacientes con diabetes mellitus tipo 2, pertenecientes al Consultorio Médico de la Familia No. 23 del policlínico Carlos J Finlay, municipio Songo-La Maya en la provincia Santiago de Cuba, desde enero hasta diciembre de 2023. Se estudiaron variables cualitativas y cuantitativas (edad, año de diagnóstico y duración de la enfermedad); se estimó el riesgo cardiovascular según el modelo para la predicción del riesgo en personas con diabetes tipo 2.
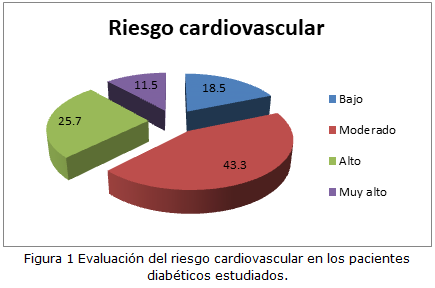
Resultados: Se observó predominio del sexo femenino (58,3 %). La mayoría de los pacientes tenían hipertensión arterial (76 %) y microalbuminuria (31,2 %). La edad media de los pacientes fue de 65,5 años y como promedio tenían un tiempo de evolución de la diabetes de 8,6 años. La evaluación del riesgo cardiovascular ubicó a 43,3 % de la población en un nivel moderado y 25,7 % con alto riesgo.
Conclusiones: Los pacientes diabéticos estudiados mostraron un riesgo de moderado a alto de presentar eventos cardiovasculares. Se hace necesario realizar intervenciones educativas en estos pacientes y sus familiares para lograr cambios favorables en los estilos de vida y mejorar el control de la enfermedad, previniendo así complicaciones y la ocurrencia de eventos fatales en los próximos años.
DeCS: DIABETES MELLITUS TIPO 2/complicaciones; FACTORES DE RIESGO DE ENFERMEDAD CARDÍACA; ATENCIÓN PRIMARIA DE SALUD; FACTORES DE RIESGO; INDICADORES DE SALUD.
Descargas
Citas
1. Organización Mundial de la Salud [Internet].Suiza: OMS; 2023 [actualizado 05 Abr 2023; citado 23 Nov 2023].Diabetes. Disponible en: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes
2. OPS/OMS [Internet]. Washington: OPS; 2023 [actualizado 19 Nov 2023; citado 20 Nov 2023].Diabetes. Disponible en: https://www.paho.org/es/temas/diabetes
3. International Diabetes Federation [Internet]. Bruselas: FID; 2023 [actualizado 22 Nov 2023; citado 23 Nov 2023]. Datos y cifras. Disponible en: https://idf.org/es/about-diabetes/diabetes-facts-figures/
4. Oficina Nacional de Estadística e Información. Anuario Estadístico de Cuba [Internet]. La Habana: ONEI; 2023 [citado 20 Nov 2023]. Disponible en: https://www.onei.gob.cu/sites/default/files/publicaciones/2023-08/19_salud_publica-_asistencia-social-2022-edicion-2023.pdf
5. Visseren FL, Mach F, Smulders YM, Carballo D, Koskinas KC, Bäck M, et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice. Eur Heart J [Internet]. 2021 [citado 20 Nov 2023];42:3227-337. Disponible en: https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/42/34/3227/6358713?login=true
6. Kengne AP, Patel A, Marre M, Travert F, Lievre M, Zoungas S, et al. Contemporary model for cardiovascular risk prediction in people with type 2 diabetes. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil [Internet]. 2011 [citado 20 Nov 2023];18(3) 393-8. Disponible en: https://academic.oup.com/eurjpc/article/18/3/393/5931558?login=true
7. Medina Fuentes G, Carbajales León E, Carbajales León A. Características clínicas epidemiológicas de la diabetes mellitus en pacientes de un consultorio médico. REMIJ [Internet]. 2020 [citado 19 Nov 2023];21(2):[aprox. 12 p.]. Disponible en: https://remij.sld.cu/index.php/remij/article/view/291/501
8. Rafael Heredia A, Iglesias Osores S. Factores asociados a diabetes mellitus tipo 2 en pacientes atendidos en un hospital amazónico de Perú. UMP [Internet]. 2020 [citado 23 Nov 2023];16(2). Disponible en: https://revgaleno.sld.cu/index.php/ump/article/view/493/pdf
9. Huaynatti Tejedo DM. Características clínicas–epidemiológicas en pacientes con diabetes mellitus tipo 2 en hospital central de la policía Luis N. Sáenz en el año 2020. [tesis]. Lima-Perú: Universidad privada San Juan Bautista; 2022 [citado 20 Nov 2023]. Disponible en: https://repositorio.upsjb.edu.pe/bitstream/handle/20.500.14308/4070/T-TPMC-HUAYNATTI%20TEJEDO%20DIEGO%20MAURICIO.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
10. Gutiérrez Jiméne I, López Aparicio LR, Flores Díaz AG. Perfil clínico-epidemiológico de pacientes diabéticos con hipoglucemia que ingresan a urgencias. Revista electrónica semestral en Ciencias de la Salud [Internet]. 2022 [citado 20 Nov 2023];13(1):[aprox. 13 p.]. Disponible en: https://revistas.uaz.edu.mx/index.php/ibnsina/article/view/1106/1137
11. Rodríguez Salvá A, Céspedes Hernández L, Díaz Piñera A, García Roche R, Balcindes Acosta S. Brechas en el manejo del paciente diabético tipo 2 en un área metropolitana de La Habana. Rev Finlay [Internet]. 2019 [citado 30 May 2023];9(2):[aprox. 14 p.]. Disponible en: https://revfinlay.sld.cu/index.php/finlay/article/view/638/1754
12. Touyz RM, Rios FJ, Alves R, Neves KB, Camargo LL, Montezano AC. Oxidative Stress: A Unifying Paradigm in Hypertension. Can J Cardiol Finlay [Internet]. 2020 [citado 30 May 2023];36(5):659-70. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7225748/
13. Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B, Woodward M, Billot L, et al. Effects of a fixed combination of perindopril and indapamide on macrovascular and microvascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (the ADVANCE trial): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet [Internet]. 2007 [citado 30 May 2023];370(9590):829-40. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17765963/
14. Buckley LF, Dixon DL, Wohlford GF, Wijesinghe DS, Baker WL, Van Tassell BW. Effect of intensive blood pressure control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus over 9 years of follow-up: A subgroup analysis of high-risk ACCORDION trial participants. Diabetes Obes Metab [Internet]. 2018 [citado 30 May 2023];20(6):1499-502. Disponible en: https://dom-pubs.pericles prod.literatumonline.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/dom.13248
15. Núñez Cortés JM, Botet JP. Dislipemia aterogénica: la otra pandemia, asociada a la diabesidad. Clin Investig Arterioscler [Internet]. 2021 [citado 30 May 2023];33(1):30-32. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7833629/
16. Valle Pimienta T, Gato Armas CA, Rodríguez López M, Hernández Gómez JR, Rosales Álvarez G, Lago Díaz Y. Riesgo cardiovascular en pacientes ingresados en un Centro de Atención al diabético. Arch méd Camagüey [Internet]. 2023 [citado 23 Dic 2023];27:e9479. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1025-02552023000100036&lng=es
17. American Diabetes Association. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care [Internet]. 2021 [citado 23 Dic 2023];44(suplem 1):125-50. Disponible en: https://diabetesjournals.org/care/article/44/Supplement_1/S125/30445/10-Cardiovascular-Disease-and-Risk-Management
18. Valdes Ramos E, Alvares Aleaga A. Índice predictivo de cardiopatía isquémica en personas con diabetes mellitus. Rev Cub Med Milit [Internet]. 2022 [citado 23 Oct 2023];51(4). Disponible en: https://revmedmilitar.sld.cu/index.php/mil/article/view/2190
19. Valente T, Arbex AK. Glycemic variability, oxidative stress, and impact on complications related to type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Diabetes Rev [Internet]. 2021 [citado 23 Oct 2023];17(7):1-11. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32674737/
20. Leal Ruiz E, Rodríguez Méndez L, Fusté M. Complicaciones crónicas en pacientes con diagnóstico reciente de diabetes mellitus tipo 2. Medicentro Electrónica [Internet]. 2019 [citado 23 Jun 2023];23(2):136-39. Disponible en: https://medicentro.sld.cu/index.php/medicentro/article/view/2758#:~:text=El%2080%20%25%20de%20los%20diagn%C3%B3sticos%20se%20realiz%C3%B3,enfermedades%20de%20la%20piel%20y%20esteatohepatitis%20no%20alcoh%C3%B3lica
21. Samaniego N. Características clínicas, epidemiológicas y complicaciones en pie diabético de pacientes con diabetes mellitus tipo 2 en el Hospital José Carrasco Arteaga, 2016-2018 [tesis]. Cuenca: Universidad Católica de Cuenca; 2020 [citado 20 Jun 2023]. Disponible en: https://dspace.ucacue.edu.ec/handle/ucacue/8517
22. Sánchez Delgado JA, Sánchez Lara NE. Epidemiología de la diabetes mellitus tipo 2 y sus complicaciones. Rev Finlay [Internet]. 2022 [citado 18 Dic 2023];12(2):[aprox. 8 p.]. Disponible en: https://revfinlay.sld.cu/index.php/finlay/article/view/1121/2114
23. Morales Carrasco AP, Rodríguez Conza D, Espinoza Diaz C, Vallejo Salazar J, Gaibor Ortiz A, Bravo Bohórquez G, et al. Características clínico-bioquímicas de pacientes diabéticos tipo2 del Instituto Ecuatoriano de Seguridad Social de Pastaza, Ecuador. Archivos Venezolanos de Farmacología y Terapéutica [Internet]. 2020 [citado 20 Nov 2023];39(4):251-55. Disponible en: https://www.revistaavft.com/images/revistas/2020/avft_4_2020/2_caracteristicas_psico_bioquimicas.pdf
24. Espinoza Murga G. Características clínicas y epidemiológicas de pacientes diabéticos tipo 2 del Servicio de Medicina del Hospital Eleazar Guzmán Barrón. Nuevo Chimbote, julio-diciembre 2019 [tesis]. Chimbote-Perú: Universidad Nacional Del Santa; 2020 [citado 23 Nov 2023]. Disponible en: https://repositorio.uns.edu.pe/bitstream/handle/20.500.14278/3534/85105.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
25. Arencibia Alvarez M de la C, Bell Castillo J, George Carrión W, Gallego Galano J,
George Bell MJ. Caracterización de los pacientes con diabetes mellitus tipo 2 atendidos en el Hospital General Docente Dr. Juan Bruno Zayas Alfonso. UMP [Internet]. 2020 [citado 20 Nov 2023];16(2). Disponible en: https://www.redalyc.org/journal/6382/638266622006/638266622006.pdf
26. Pomares Avalo AJ, Jorge González R, Alfonso Trujillo Y, Vázquez Núñez MA. Adherencia terapéutica y bienestar subjetivo en pacientes con diabetes mellitus tipo II. Finlay [Internet]. 2019 [citado 16 Jul 2023];9(3):[aprox. 4 p.]. Disponible en: http://revfinlay.sld.cu/index.php/finlay/article/view/672
27. Colom C, Rull A, Sanchez JL, Pérez A. Cardiovascular Disease in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Epidemiology and Management of Cardiovascular Risk. J Clin Med [Internet]. 2021 [citado 16 Jul 2023];10(8):1798. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33924265/
28. Gedebjerg A, Almdal TP, Berencsi K, Rungby J, Nielsen JS, Witte DR, et al. Prevalence of micro- and macrovascular diabetes complications at time of type 2 diabetes diagnosis and associated clinical characteristics: A cross-sectional baseline study of 6958 patients in the Danish DD2 cohort. J Diabetes Complications [Internet]. 2018 [citado 16 Jul 2023];32(1):34-40. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29107454/
29. Martín Rioboó E, Brotons Cuixart C, Ruiz García A, Villafañe Sanz F, Frías Vargas M, Moyá Amengual A, et al. Luces y sombras de la Guía Europea ESC-2021 de Prevención de la Enfermedad Cardiovascular en la Práctica Clínica. Rev Esp Salud Pública [Internet]. 2023 [citado 20 Dic 2023];97. Disponible en:https://www.sanidad.gob.es/biblioPublic/publicaciones/recursos_propios/resp/revista_cdrom/VOL97/C_ESPECIALES/RS97C_202308064.pdf
30. Zamora Fung R, Blanc Márquez A, García Gázquez J, Borrego Moreno Y, Fundora Gonzales C. Estimación del riesgo cardiovascular en pacientes con diabetes mellitus tipo 2 en un consultorio médico. Univ Med Pinareña [Internet]. 2020 [citado 02 Ene 2023];16(1). Disponible en: https://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/revunimedpin/ump-2020/ump201j.pdf
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2024 Meibis Poll-Cabrera, Naifi Hierrezuelo-Rojas, Yarisbel Soto-Bell, Jorge Emilio Begó-Godínez, Irina Velazquez-Cedeño, Daymara Acosta-Montero

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 4.0.
La Revista Archivo Medico Camagüey, ofrece de forma inmediata después de ser indexada en el Proyecto SciELO; acceso abierto al texto completo de los artículos bajo el principio de hacer disponible y gratuita la investigación para favorecer el intercambio del conocimiento global y coadyuvar a una mayor extensión, publicación, evaluación y uso extensivo de los artículos que se exponen pudiendo ser utilizados, sin fines comerciales, siempre y cuando se haga referencia a la fuente primaria.
Carta De Declaración De Autoría u Derechos De Autor(a)
Conflictos de intereses: los autores deberán declarar de forma obligatoria la presencia o no de conflictos de intereses en relación con la investigación presentada. (Descargar Plantilla para declarar confictos de intereses)
La Revista Archivo Médico Camagüey se encuentra bajo una
Licencia Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial 4.0 International (CC BY NC 4.0).
Esta licencia permite a otros distribuir, mezclar, ajustar y construir a partir de su obra, incluso con fines comerciales, siempre que le sea reconocida la autoría de la creación original. Esta es la licencia más servicial de las ofrecidas. Recomendada para una máxima difusión y utilización de los materiales sujetos a la licencia. La licencia completa puede consultarse en: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/











