Satisfacción con la introducción del nuevo procedimiento de evaluación de riesgo biológico en laboratorios clínicos
Abstract
Introduction: The evaluation of satisfaction regarding the change introduced in the biological risk assessment procedure provides elements to assess its effectiveness.
Objective: To evaluate through the Ladov technique the level of satisfaction as a user of the biological risk assessment procedure in clinical laboratories with a focus on defense in depth.
Methods: A descriptive cross-sectional study was carried out in the period from July to December 2021. The universe consisted of the 82 clinical laboratories of primary health care in Havana and a non-probabilistic sample of 3 laboratories with a total of 37 workers; based on the inclusion criteria: being a laboratory worker and agreeing to participate in the research, as exclusion criteria: personnel from other centers providing services and students in training. The empirical research method (survey) was used and the percentage analysis was used as a statistical method. The processing of the information was carried out using the V.A. Iadov.
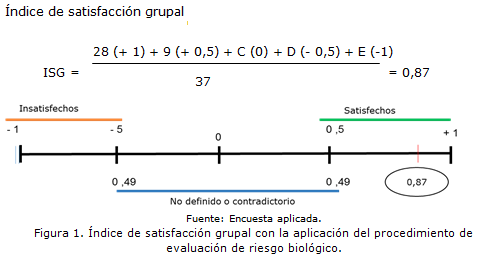
Results: The satisfaction survey revealed that 78.6% of the sample expressed maximum satisfaction, 24.3% more satisfied than dissatisfied. The open questions (2 and 4 of the survey) identified as the aspect that they liked the most, the purpose and interest of improving the risk assessment and management stage, the successive stages of the procedure that allow obtaining detailed information on the state of biosafety y and among the aspects that they did not like, the mathematical analysis is described. The group satisfaction index obtained was 0.87.
Conclusions: The group satisfaction index of clinical laboratory workers where the biological risk assessment procedure was applied was high, reflecting acceptance of the proposal and recognition of its relevance in the biological risk assessment process.
DeCS: HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCES; RISK ASSESSMENT; RISK ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES; LABORATORIES, CLINICAL; JOB SATISFACTION.
Downloads
References
1. Organización Panamericana de la Salud. Atención Primaria de Salud. Principios y métodos. 2da ed [Internet]. Washington, D.C: OPS; 1992 [citado 04 Jul 2022]. Disponible en: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/primary-health-care
2. Espín-Arguello A. Análisis de la bioseguridad frente la pandemia covid-19 y el impacto psicológico en profesionales de enfermería. Rev Pol Con [Internet]. 2020 [citado 26 Feb 2022];53(5):29-38. Disponible en: http://polodelconocimiento.com/ojs/index.php/es
3. Rodríguez Méndez M, Echemendía Tocabens B. La prevención en salud: posibilidad y realidad. Rev cuba hig epidemiol [Internet]. 2011 Ene-Abr [citado 28 Jul 2022];49(1):135-150. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1561-30032011000100015&lng=es
4. Cobos Valdés D. Bioseguridad en el contexto actual. Rev cuba hig epidemiol [Internet]. 2021 [citado 26 Feb 2022];58. Disponible en: https://revepidemiologia.sld.cu/index.php/hie/article/view/192
5. Perdomo Ojeda M. Métodos semicuantitativos avanzados para la seguridad y fiabilidad de la industria nuclear y otras prácticas riesgosas [tesis doctoral]. La Habana: Editorial Universitaria; 2016 [citado 27 Feb 2022]. Disponible en: https://buscadorinfo.unan.edu.ni/Record/ELB90931/UserComments
6. Raggi N. Defensa en profundidad: cómo implementar esta estrategia de ciberseguridad [Internet]. 2021 [citado 27 Feb 2022]. Disponible en: https://www.welivesecurity.com/la-es/2021/03/26/defensa-profundidad-que-es-como-implementar-estrategia-ciberseguridad/
7. Valdés Fernández M, Escalante Quintero I, Perdomo Ojeda M, Salomón Llanes J. Evaluación del nivel de seguridad en tres laboratorios clínicos de atención primaria de salud. Rev cuban salud trabajo [Internet]. 2021 [citado 08 Jun 2022];22:[aprox. 11 p.]. Disponible en: https://revsaludtrabajo.sld.cu/index.php/revsyt/article/view/222
8. Fernández Sotelo A, Vanga Arvelo M. Satisfacción o insatisfacción con la introducción de resultados científicos. ¿Cómo valorarla? SATHIRI [Internet]. 2015 Ene-Jun [citado 08 Jun 2022];8:180-194. Disponible en: https://revistasdigitales.upec.edu.ec/index.php/sathiri/article/view/405
9. Mena Silva P, Condemaita Quilligana KD, Caicedo Reyes M. Medidas de bioseguridad durante la pandemia de COVID 19 en los servicios odontológicos en ecuador. Estrategia educativa. Revista Conrado [Internet]. 2022 Jun [citado 08 Jun 2022];18(S2):68-76. Disponible en: https://conrado.ucf.edu.cu/index.php/conrado/article/view/2443
10. Zueck Enriquez M, Ramírez García A, Rodríguez Villalobos J, Irigoyen Gutiérrez H. Satisfacción en las clases de Educación Física y la intencionalidad de ser activo en niños del nivel de primaria. Retos [Internet]. 2020 [citado 10 Mar 2022];37:33-40. Disponible en: https://recyt.fecyt.es/index.php/retos/article/view/69027
11. Mateu López L, Sedeño Argilagos C, Estrada Senti V, Pérez Arrazcaeta S, Cuba Venereo MM. Estrategia de gestión del conocimiento para la formación de competencias de los profesionales farmacéuticos cubanos. Anales de la ACC [Internet]. 2021 Sep-Dic [citado 29 Ago 2022];11(3). Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2304-01062021000300015
12. Tinajero Jiménez M, Catota Mesías VD, Catota Mesías E. La técnica de Iadov. Niveles de satisfacción del cliente en RM Latacunga–Maltería Plaza año 2019. Rev Ciencias Administrativas Económicas [Internet]. 2021 [citado 29 Ago 2022];4(1):110-120. Disponible en: http://investigacion.utc.edu.ec/revistasutc/index.php/prospectivasutc/article/viewFile/317/270
13. López Rodríguez A, González Maura V. La técnica de Iadov. Una aplicación para el estudio de la satisfacción de los alumnos por las clases de educación física. Rev Digital-Buenos Aires [Internet]. 2022 Abr [citado 29 Ago 2022];8(47). Disponible en: https://www.efdeportes.com/efd47/iadov.htm
14. Triana Velázquez Y, Boligan Expósito M, Díaz Pérez M. Comprobación de la usabilidad y consistencia lógica de un procedimiento de gestión del conocimiento. Universidad Sociedad [Internet]. 2020 Sep-Oct [citado 20 Mar 2022];12(5):196-202. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2218-36202020000500196
15. Roque Herrera Y, Alonso García S, Maldonado León AE. Nivel de satisfacción con la estrategia de investigación científica en una facultad de la Universidad Nacional De Chimborazo, Ecuador. IE Rev de Investigación Educativa de la REDIECH [Internet]. 2019 [citado 29 Ago 2022];10(18):177-91. Disponible en: https://www.redalyc.org/journal/5216/521658238012/html/
16. World Medical Association. Declaration of Helsinki–Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects [Internet]. 2018 [citado 10 Sep 2021]. Disponible en: https://www.wma.net/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/DoH-Oct2008.pdf
17. Laguna Ávila D, Escalona Fernández Y, Leyva Gómez H, Flores Saldeño GE. Procedimiento para la implementación del aprendizaje por proyecto a productores del sector vegas del hoyo. Revista Dilemas Contemporáneos: Educación, Política y Valores [Internet]. 2019 Ago [citado 20 Mar 2022];36(3). Disponible en: https://dilemascontemporaneoseducacionpoliticayvalores.com/index.php/dilemas/article/view/1809/1938
18. Triana Velázquez Y, Boligan Expósito M, Díaz Pérez M. Comprobación de la usabilidad y consistencia lógica de un procedimiento de gestión del conocimiento. Rev Universidad y Sociedad [Internet]. 2020 [citado 20 Mar 2022];12(5);196-202. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2218-36202020000500196&Ing=es&tIng=es
19. Arias Verdecia L, Valdés Pérez L, Benítez Méndez OG, Váldes Corsos M. Índice de Satisfacción por la Estrategia Didáctica para la utilización de Recursos Educativos Abiertos en la disciplina Historia de Cuba a través de la técnica Iadov. IV Conferencia Cientifica Internacional UCIENCIA [Internet]. 2021 [citado 29 Ago 2022]. Disponible en: https://repositorio.uci.cu/jspui/bitstream/123456789/9789/1/UCIENCIA_2021_paper_148.pdf
20. Hernández-Pérez R, Ávila-S? nchez M, Espinosa Aguilar A, Hernández-Núñez A, Lemus-Lima E. Satisfacción del profesional de Enfermería con una intervención de cuidados como vía para la gestión del conocimiento. Rev cuba enferm [Internet]. 2022 [citado 29 Ago 2022];38(2). Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0864-03192022000200007
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Miriam Virginia Valdés-Fernández

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025