Morbilidad en pacientes hemodializados
Palabras clave:
Morbilidad, Hemodiálisis, Factores ambientales.Resumen
Fundamento: cada día se incrementa el número de enfermos con una enfermedad renal crónica, tributarios de hemodiálisis, procedimiento que no está exento de producir complicaciones por la complejidad de su realización, en la que intervienen el ambiente y condiciones de la unidad de hemodiálisis, la calidad del agua empleada y el buen funcionamiento de la planta de tratamiento de esta agua.
Objetivo: caracterizar la morbilidad infecciosa de los pacientes con enfermedad renal crónica.
Métodos: se realizó un estudio observacional, descriptivo, transversal. La población de estudio estuvo constituida por 85 pacientes con enfermedad renal crónica que fueron atendidos en el servicio de hemodiálisis del Hospital General Provincial Universitario Camilo Cienfuegos de Sancti Spíritus durante el período comprendido entre el 1ro de Octubre de 2016 al 31 de Marzo de 2018.
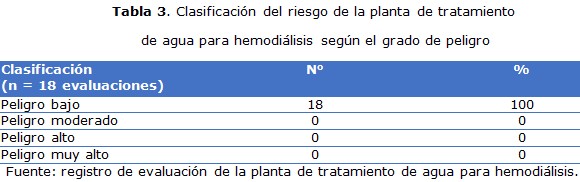
Resultados: la mayor cantidad de casos hemodializados se correspondió con el grupo de edad mayor de 60 años del género masculino. Los factores ambientales y microbiológicos indicaron que la calidad del agua utilizada en el proceso de atención de pacientes hemodializados fue satisfactoria y el peligro de riesgo en la planta de tratamiento, en la categoría de bajo riesgo. El tipo de acceso vascular de los pacientes que con mayor frecuencia se utilizó y el de mayor morbilidad infecciosa fue el catéter transitorio.
Conclusiones: la mayoría de los enfermos eran hombres en la sexta década de la vida, la calidad del agua utilizada fue adecuada, con escaso riesgo en la planta de tratamiento y el catéter transitorio mostró mayor proporción de infecciones asociadas.
DeCS: DIÁLISIS RENAL/métodos; INSUFICIENCIA RENAL CRÓNICA/complicaciones; DISPOSITIVOS DE ACCESO VASCULAR; CATETERISMO VENOSO CENTRAL; ESTUDIO OBSERVACIONAL.
Descargas
Citas
1. Ángel Zahira E, Duque Castaño GA, Tovar Cortes DL. Cuidados de enfermería en el paciente con enfermedad renal crónica en hemodiálisis: una revisión sistemática. Enferm Nefrol [Internet]. Sep 2016 [citado 07 Mar 2020];19(3):202-213. Disponible en: http://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2254-28842016000300003&lng=es
2. Northwestern Memorial Hospital. Insuficiencia Renal: Elección del Tratamiento [Internet]. Chicago: NMH; 2019 [citado 03 Ene 2020]:[aprox. 11 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=2ahUKEwjyvr-2yJjqAhUiWN8KHcegDnYQFjAAegQIARAB&url=https%3A%2F%2
Fwww.nm.org%2F-%2Fmedia%2FNorthwestern%2FResources%2Fpatients-and-visitors%2Fpatient-education-espanol-spanish%2Fnorthwestern-medicine-insuficiencia-renal-eleccion-del-tratamiento-kidney-failure-treatments.pdf%3Fla%3Den&usg=
AOvVaw2QXIcFmBVJTyQhztAq8bsf
3. Pinares Astete F, Meneses Liendo V, Bonilla Palacios J, Ángeles Tacchino P, Cieza Zevallos J. Supervivencia a largo plazo en pacientes con enfermedad renal crónica estadio 5 tratada por hemodiálisis en Lima, Perú. Acta méd Peru [Internet]. 2018 [citado 01 Mar 2020];35(1):20-27. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.pe/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1728-59172018000100004&lng=es
4. Pérez Escobar MM, Herrera Cruz N, Pérez Escobar E. Comportamiento de la mortalidad del adulto en hemodiálisis crónica. Arch méd Camagüey [Internet]. Feb 2017 [citado 06 Feb 2020];21(1):773-786. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1025-02552017000100004&lng=es
5. Sanabria Arenas M, Paz Wilches J, Laganis Valcarcel S, Muñoz Porras F, López Jaramillo P, Vesga Gualdrón J, et al. Inicio de diálisis y mortalidad en una población con enfermedad renal crónica en Colombia. Rev Fac Med. 2015;63(2):209-16.
6. Huidobro JP, Vega J. Función renal al fallecimiento según causa de muerte en trasplantados renales. Rev méd Chile [Internet]. 2016 [citado 24 Feb 2020];144(7):853-861. Disponible en: https://scielo.conicyt.cl/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-98872016000700005&lng=es
7. Cuevas-Budhart MÁ, Saucedo García RP, Romero Quechol G, García Larumbe JA, Hernández Paz y Puente A. Relación entre las complicaciones y la calidad de vida del paciente en hemodiálisis. Enferm Nefrol [Internet]. 2017 [citado 02 Mar 2020];20(2):112-119. Disponible en: http://scielo.isciii.es/pdf/enefro/v20n2/2255-3517-enefro-20-02-00112.pdf
8. Pérez García R, García Maset R, González Parra E, Solozábal Campos C, Ramírez Chamond R, Martín-Rabadán P. Guía de gestión de calidad del líquido de diálisis (LD). Rev Soc Esp Nefrol [Internet]. 2016 [citado 02 Mar 2020];36(3):1–52. Disponible en: https://reader.elsevier.com/reader/sd/pii/S0211699516000047?token=3A8B6F40C859AFB4782DB839163A5AE0B42C8E4EF22EFBC271B751EB56BB7252D70353 AAFC806D309BCFA6F0A4886B79
9. García Melián M, González González MI, Mariné Alonso MÁ. Criterios para la vigilancia de la calidad química y microbiológica del agua para hemodiálisis. Rev Cubana Hig Epidemiol [Internet]. Ago 2013 [citado 02 Mar 2020];51(2):192-202. Disponible en: http://scieloprueba.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1561-32013000200008&lng=es
10. Ojeda M, Fretes S. Calidad de agua para hemodiálisis utilizada en un Hospital de Asunción, Paraguay. Rev Cient UCSA [Internet]. Dic 2016 [citado 24 Mar 2020];3(2):12-17. Disponible en: http://scielo.iics.una.py/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2409-87522016000200012&lng=es&nrm=iso
11. Zúñiga Carrasco IR, Caro Lozano J. Importancia de la limpieza y la desinfección en el área hospitalaria para el control de infecciones nosocomiales. J Medicine [Internet]. 2019 [citado 02 Mar 2020];8(1):20-26. Disponible en: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333149293_Importancia_de_la_limpieza_y_la_desinfeccion_en_el_area_hospitalaria_para_el_control_de_infecciones_nosocomiales/link/5cddb614299bf14d959f682e/download
12. Vijayan A, Boyce JM. 100 % Use of Infection Control Procedures in Hemodialysis Facilities. CJASN [Internet]. 2018 [citado 02 Mar 2020];13(4):671-673. Disponible en: https://cjasn.asnjournals.org/content/13/4/671
13. Rodríguez Pérez AU. Infecciones asociadas a la asistencia sanitaria. Instrumento técnico-metodológico para la vigilancia microbiológica selectiva en áreas críticas. Hig Sanid Ambient. 2018;18(4):1669-1674.
14. Vega de la Torre M, de la Torre Rosés M, Diéguez Velázquez D, Nicó García M, Valenciano García Y. Infecciones relacionadas con el acceso vascular en pacientes con insuficiencia renal crónica terminal en hemodiálisis. Rev inf cient [Internet]. 2015 [citado 22 Mar 2020];90(2):[aprox. 12 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.revinfcientifica.sld.cu/index.php/ric/article/view/243
15. Vento Valdés I, Toraño Peraza G, Del Sol González AC, Piquero Lazo EM. Bacteriemia relacionada con catéter por Staphylococcus aureus resistente a meticilina en pacientes con enfermedad renal crónica avanzada. Rev cubana med trop [Internet]. 2019 [citado 22 Mar 2020];71(2):[aprox. 7 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.revmedtropical.sld.cu/index.php/medtropical/article/view/427/258
16. Ramírez Felipe LC, Martínez Cuéllar YN, González Cárdenas Y, Santos Treto Y. Caracterización clínico epidemiológico de los pacientes con enfermedad renal crónica avanzada. AMC [Internet]. 2016 [citado 22 Mar 2020];10(3):10-18. Disponible en: https://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/medicadelcentro/mec-2016/mec163b.pdf
17. Hinostroza Morales M. Insuficiencia renal crónica terminal (IRCT) en hemodiálisis en el hospital Nacional Ramiro Prialé de Huancayo 2011-2015 [Internet]. 2016 [citado 22 Mar 2020]. Disponible en: http://repositorio.uncp.edu.pe/handle/UNCP/444
18. Torrijos Gil JJ. Prevalencia y características clínicas de la Insuficiencia Renal Crónica en el ámbito hospitalario [Tesis Doctoral]. España: Universitat de les Illes Balears; 2018 [citado 22 Mar 2020]:[aprox. 152 p.]. Disponible en: http://hdl.handle.net/11201/4440
19. Gutiérrez Rufín M, Polanco López C. Enfermedad renal crónica en el adulto mayor. Rev Finlay [Internet]. Mar 2018 [citado 24 Mar 2020];8(1):1-8. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2221-24342018000100001&lng=es
20. Franco Pérez N, Rodríguez Hung S, Telemaque H. Comportamiento de las fístulas arteriovenosas para hemodiálisis en pacientes con insuficiencia renal crónica. Rev Cubana Angiol Cir Vasc [Internet]. Jun 2015 [citado 24 Mar 2020];16(1):3-8. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1682-00372015000100002&lng=es
21. Pereira Feijoo M, Concepción Bretaña VN, Prada Monterrubio N, Fernández León S, González Parada O. Seguridad del paciente en la práctica clínica de una unidad de hemodiálisis. Enferm Nefrol [Internet]. 2015 [citado 24 Mar 2020];18(Suppl1):132-132. Disponible en: http://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2254-28842015000500103&lng=es
22. Pérez García R, García Maset R, González Parra E, Solozábal Campos C, Ramírez Chamond R, Martín Rabadán P, et al. Guía de gestión de calidad del líquido de diálisis (LD). Nefrología [Internet]. 2016 [citado 24 Mar 2020];36(3):[aprox. 52 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.nefrologiaaldia.org/es-articulo-guias-gestion-calidad-del-liquido-132
23. Rodríguez Pérez AU, Delgado Pérez M, Dujarric Martínez MD. Vigilancia químico-bacteriológica de las aguas de sistemas de hemodiálisis en instituciones seleccionadas. Rev Cubana Hig Epidemiol [Internet]. Dic 2007 [citado 24 Mar 2020];45(3):[aprox. 5 p.]. Disponible en: http://scieloprueba.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1561-30032007000300006&lng=es
24. Tirado-Gómez LL, Durán-Arenas JL, Rojas-Russell ME, Venado-Estrada A, Pacheco-Domínguez RL, López-Cervantes M. Las unidades de hemodiálisis en México: una evaluación de sus características, procesos y resultados. Salud pública Méx [Internet]. 2011 [citado 24 Mar 2020];53(Suppl4):491-498. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.mx/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0036-36342011001000013&lng=es
25. Sosa Vázquez OR. Fístulas arterio-venosas trombosadas para hemodiálisis y su tratamiento. Rev Cubana Angiol Cir Vasc [Internet]. 2017 [citado 02 Mar 2020];18(2):192-201. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1682-00372017000200006&lng=es
26. Böhlke M, Uliano G BF. Hemodialysis catheter-related infection: Prophylaxis, diagnosis and treatment. J Vasc Access. 2015;16(5):347–55.
27. Álvarez Villarreal M, Chocarro González L, Velarde García JF, Palacios Ceña D. La experiencia de ser portador de un catéter venoso central para hemodiálisis: estudio cualitativo. Enferm Nefrol [Internet]. Jun 2018 [citado 24 Mar 2020];21(2):146-154. Disponible en: http://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2254-28842018000200006&lng=es
28. Cerdán Urrutia E, Mena Mayayo MC, Catalán Beloqui L. ¿Qué sabemos de la seguridad del paciente en hemodiálisis? Enferm Nefrol. 2015;18(1):101-137.
29. Andreu Périz D, Hidalgo Blanco MA, Moreno Arroyo C. Eventos infecciosos en pacientes en hemodiálisis. Enferm Nefrol [Internet]. 2015 [citado 02 Mar 2020];18(1):54-56. Disponible en: http://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2254-28842015000100008&lng=es
30. Gómez J, Pimienta L, Pino R, Hurtado M, Villaveces M. Prevalencia de infección asociada a catéter de hemodiálisis en el Hospital Universitario Clínica San Rafael. Rev Colomb Nefrol. 2018;5(1):17-25.
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2020 Dayana Bárbara González-Coca, René Rafael Bonachea-Peña, Dayana Cardoso-García, Reinaldo Gómez-Pacheco, Ania Cecilia Reyes-Roque, María Obdulia Benítez-Pérez

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 4.0.
La Revista Archivo Medico Camagüey, ofrece de forma inmediata después de ser indexada en el Proyecto SciELO; acceso abierto al texto completo de los artículos bajo el principio de hacer disponible y gratuita la investigación para favorecer el intercambio del conocimiento global y coadyuvar a una mayor extensión, publicación, evaluación y uso extensivo de los artículos que se exponen pudiendo ser utilizados, sin fines comerciales, siempre y cuando se haga referencia a la fuente primaria.
Carta De Declaración De Autoría u Derechos De Autor(a)
Conflictos de intereses: los autores deberán declarar de forma obligatoria la presencia o no de conflictos de intereses en relación con la investigación presentada. (Descargar Plantilla para declarar confictos de intereses)
La Revista Archivo Médico Camagüey se encuentra bajo una
Licencia Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial 4.0 International (CC BY NC 4.0).
Esta licencia permite a otros distribuir, mezclar, ajustar y construir a partir de su obra, incluso con fines comerciales, siempre que le sea reconocida la autoría de la creación original. Esta es la licencia más servicial de las ofrecidas. Recomendada para una máxima difusión y utilización de los materiales sujetos a la licencia. La licencia completa puede consultarse en: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/











