Buschke-Lowenstein tumor: presentation of the case
Abstract
Background: the Buschke-Löwenstein tumor is a giant acuminate condyloma larger than 10 cm, more frequent in men, so the treatment of choice must always be surgical.
Objective: to describe a case of giant acuminate condylomata.
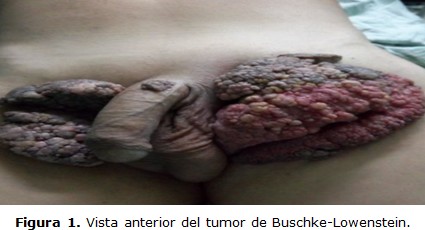
Case report: 54-year-old white male patient, who came with papillomatosis formations with soft and moist consistency of cauliflower, in both inguinal regions; on the right side of 13 centimeters in diameter and 19 centimeters on the left and at the root of the penis and perianal region of 2 centimeters, associated with pain of slight intensity in the lower limbs and occasional fetidity. Preoperative studies including non-reactive serology and HIV were performed. He underwent surgery, performing excision and closure with abdominal skin flap. He evolved clinically stable, although he presented an infection of the surgical wound where Escherichia Coli, gentamicin sensitive, was reported; he complied with treatment and left without further complications.
Conclusions: Buschke-Löwenstein tumor is currently considered as a form of verrucous carcinoma, it does not present cellular atypia, described as benign, but one third of the cases can be maligne. Despite frequent recurrences, some authors consider it as a malignant tumor. Despite the existence of several treatments, the surgical treatment is the one with the best results.
DeCS: BUSCHKE-LOWENSTEIN TUMOR; CONDYLOMATA ACUMINAT/surgery; CARCINOMA, VERRUCOUS/surgery; CASE REPORTS; MEN.
Downloads
References
1. Montoya M, Morón W, Pontillo H, Poggiolli O. Condiloma acuminado gigante (Tumor de Buschke Lowenstein). Rev Venez Oncol [Internet]. 2013 [citado 30 Mar 2019];25(1):[aprox. 5 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/3756/375634875006.pdf
2. Ganem NS, Silva BC, Nascimento M LFO, Tibúrcio AS, Lyra LMR, Mesquita RB, et al. Condiloma anal Gigante. DST-J bras Doenças Sex Transm [Internet]. 2011 [citado 30 Mar 2019];22(4):[aprox. 3 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.academia.edu/download/41192204/Condiloma_anal_gigante_relato_de_caso20160114-26324-1hc7n65.pdf20160115-19908-q95on5.pdf
3. Beltrán Pérez I, Reyes Argudín MA, Navarro Garvey Y, Rodríguez Pérez S, Suárez Rivera JJ. Condiloma acuminado gigante. Rev Cub Cirug [Internet]. 2014 [citado 30 Mar 2019];53(3):269-302. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S003474932014000300009&lng=es
4. Montaña CN, Labra WA, Schiappacasse FG. Condiloma acuminado gigante (Tumor de Buschke Lowenstein). Rev Chilena Radiol [Internet]. 2014 [citado 30 Mar 2019];20(2):57-63. Disponible en: http://dx.doi.org/10.4067/S0717-93082014000200005
5. Pupo Ricardo A, Roca Socarras A, Rodríguez Crespo A, González Sánchez M. Tumor de Buschke Löwenstein. Correo Científico Médico [Internet]. 2016 [citado 30 Mar 2019];20(1):204-11. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?pid=S1560-43812016000100020&script=sci_arttext&tlng=pt
6. Rosales Rocha GE, Torres Medina E, Peña Rodríguez A, Aragón Tovar A. Condiloma acuminado gigante (tumor de Buschke-Löwenstein). Rev Mex Urol [Internet]. 2010 [citado 30 Mar 2019];70(6):370-372. Disponible en: http://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/uro/ur-2010/ur106f.pdf
7. Rozas Llerena R, Sebastián Ayala R. Condiloma viral en lengua: presentación de un caso clínico y revisión bibliográfica. Rev Fac Med Hum [Internet]. 2019 [citado 30 Mar 2019];19(1):105-107. Disponible en: http://revistas.urp.edu.pe/index.php/RFMH/article/download/1799/1728
8. Valdés González JL, Solís Cartas U, Valdés González EM, Muñoz Balbín M. Condiloma gigante o tumor de Buschke-Löwenstein. Rev Cub Ped [Internet]. 2017 [citado 30 Mar 2019];89(1):[aprox. 5 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/revcubped/cup-2017/cup171h.pdf
9. Haider M, Nabeel Shafqat M, Chamizo Cabrera MG. Caracterización clínico- epidemiológica de la infección por condiloma acuminado Policlínico Universitario Marta Abreu. Abril 2011-diciembre 2012. Rev Fac Ciencias Salud [Internet]. 2018 [citado 30 Mar 2019];12(1):31-41. Disponible en:https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Miqdad_Haider/publication/329413625_Caracterizacion_clinicoepidemiologica_de_la_infeccion_por_condiloma_acuminado_Policlinico_Universitario_Marta_Abreu_Abril_2011diciembre_2012/links/5c073f08a6fdcc315f9de045/Caracterizacion-clinico-epidemiologica-de-la-infeccion-por-condiloma-acuminado-Policlinico-Universitario-Marta-Abreu-Abril-2011-diciembre-2012.pdf
10. Benavides Yánez BE, Franco Carrasco MA, Tuesca Armijos RJ, Taiano Espinoza MK. Enfermedades de trasmisión sexual en niños y adolescentes, contagio por el virus de papiloma humano. RECIMUNDO [Internet]. 2018 [citado 30 Mar 2019];2(3):410-21. Disponible en: http://recimundo.com/index.php/es/article/view/300
11. Rivera Rivadulla R, Lazo Herrera LA, Ordóñez Álvarez LY. Tumor de Buschke-Löwenstein. Rev Inform Científica [Internet]. 2018 [citado 30 Mar 2019];97(4):851-859. Disponible en: http://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/revinfcie/ric-2018/ric184o.pdf
12. Laís Diefenthäler V, Schneider Cardoso MA, Pavan Zanella JF, Ricardo Moreira P, Coser J. Anal lesion caused by human papillomavirus in a woman living with HIV/AIDS. Scientia Medica [Internet]. 2017 [citado 30 Mar 2019];27(3):[aprox. 4 p.]. Disponible en: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/descarga/articulo/6137845.pdf
13. Rodríguez Pastoriza R. Condiloma genital gigante o Tumor de Buschke-Löwenstein. Rev Cub Urol [Internet]. 2017 [citado 30 Mar 2019];6(1):61-66. Disponible en: http://www.revurologia.sld.cu/index.php/rcu/article/viewFile/271/332
14. Mandu Fonseca MS, Cardoso L, Morón Munhoz M, Martínez T, Miolode Carvalho E, Christian Silveira M, et al. Condiloma gigante de Buschke-Lowenstein: um relato de caso. Rev Fac Cienc Méd Sorocaba [Internet]. 2016 [citado 30 Mar 2019];18(3):169-172. Disponible en: https://revistas.pucsp.br/RFCMS/article/download/26302/pdf
15. Bustamante Sigarroa N, Bustamante Salazar N, García Jordán M, Ordaz Fuentes Y. Condiloma acuminado de Buschke y Lowenstein del pene. Rev Cubana Urol [Internet]. 2018 [citado 30 Mar 2019];7(2):53-59. Disponible en: http://www.revurologia.sld.cu/index.php/rcu/article/download/433/467
16. Guerrero Putz MD, Maya Epelstein A, García-Galaviz R, Olvera Posada D. Lesiones por virus del papiloma humano en pacientes urológicos. Rev Mex Urol Hum [Internet]. 2018 [citado 30 Mar 2019];78(6):463-73. Disponible en: http://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/uro/ur-2018/ur186j.pdf
17. Ríos Hernández MA, Hernández Menéndez M, Aguilar Vela de Oro FO, Aguilar Fabré K, Amigó de Quesada M, Silveira Pablos M, et al. Condiloma gigante (tumor de Buschke-Löwenstein) de la vulva. Rev Cubana Ginecol Obst [Internet]. 2014 [citado 30 Mar 2019];40(2):258-264. Disponible en: http://revista.fecolsog.org/index.php/rcog/article/download/369/402
18. Parapar I, Taboada N. Exéresis quirúrgica radical como único tratamiento del condiloma acuminado gigante: a propósito de un caso. Colomb Med [Internet]. 2007 [citado 30 Mar 2019];38(2):142-148. Disponible en: http://www.redalyc.org/comocitar.oa?id=28338207
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2020 Yarima Estrada-Brizuela, Raudel Méndez-León, Luis Ernesto Quiroga-Meriño, Manuel Hernández-Agüero

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025