External fixation due to complex pelvic fracture with hemodynamic instability
Keywords:
fijación, pelvis, inestabilidad.Abstract
Background: one of the main causes of death in hospitals in the first hours after a pelvic trauma therefore, a multidisciplinary and early management is required.
Objective: to report a case of severe pelvic fracture and moderate bleeding treated with external fixation.
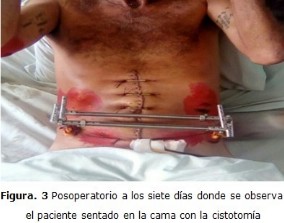
Clinical case: a forty-six-year-old male patient who suffered from severe pelvic traumatism, which provoked a pelvic fracture hemodynamically unstable and posterior urethral rupture, therefore he had to go through surgery since hemodynamic stability was not achieved with regular methods wich are non-invasive. Exploratory laparotomy, urethrostomy and external fixation of the pelvis were indicated.
Conclusions: the first procedure to interrupt bleeding is the stabilization of the fracture through external fixation and in most cases it becomes the only necessary procedure.
DeCS: PELVIS/injuries; FRACTURE FIXATION; JOINT INSTABILITY; ADULT; CASE REPORTS.
Downloads
References
1.Angulo Tabernero M, Fernández Letamendi T, Hidalgo Mendía B, Ungría Murillo J, Gros Bañeres B, Fernández Letamendi N, et al. Fracturas osteoporóticas de ramas pélvicas: ¿Son una lesión benigna? Rev Cubana Ortop Traumatol [Internet]. Jul-Dic 2016 [citado 5 Ene 2018];30(2):[aprox. 12 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0864-215X2016000200004
2.ArvieuxC,Vendrell A, BouzatP,AbbaJ,VoiglioE.Generalidades. Técnica de tratamiento de las hemorragias de los traumatismos pélvicos cerrados. EMC Técnicas Quirúrgicas-Aparato Digestivo [Internet]. Feb 2017 [citado 5 Ene 2018];33(1):[aprox. 10 p.]. Disponible en: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1282-9129(16)81972-8Get rights and content
3.Agri F, Bourgeat M, Becce F, Moerenhout K, Pasquier M, Borens O, et al. Association of pelvic fracture patterns, pelvic binder use and arterial angio-embolization with transfusion requirements and mortality rates; a 7-year retrospective cohort study. BMC Surg [Internet]. 2017 Nov [cited 2018 Jan 5];17(1):[about 8 p.]. Available from: https://preview.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29121893
4.Nasef H, Elhessy A, Abushaban F, Alhammoud A. Pelvic fracture instability-associated L5 transverse process fracture, fact or myth? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol [Internet]. 2017 Dec 7 [cited 2018 Jan 5]:[about 9 p.]. Available from: https://preview.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29218648
5.Zhang W. Forensic Analysis of the Characteristics of Pelvic Fracture in 65 Road Traffic Accident Death Cases. Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi [Internet]. 2016 Dec [cited 2018 Ene 5];32(6):[about 10 p.]. Available from: https://preview.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29205969
6.Skitch S, Engels PT. Acute Management of the Traumatically Injured Pelvis. Emerg Med Clin North Am [Internet]. 2018 Feb [cited 5 Jan 2018];36(1):[about 13 p.]. Available from: https://preview.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29132575
7.Chana-Rodríguez F, Cuervas-Mons M, Rojo-Manaute J, Mora F, Arnal J, Vaquero-Martín J. Ultrasound-guided supra-acetabular pin placement in pelvic external fixation: description of a surgical technique and results. Injury [Internet]. 2017 Nov [cited 2018 Ene 5];48(supl 6):[about 8 p.]. Available from: https://preview.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29162245
8.Sagawa K, Sawano M. A case series of pelvic fracture patients who developedlo werurinary tract symptoms after transarterial embolization of bilateral internal iliac arteries. Acute Med Surg [Internet]. 2017 May [cited 2018 Jan 5];4(3):[about 10 p.]. Available from: https://preview.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29123891
9.Martin MP, Rojas D, Mauffrey C. Reduction and temporary stabilization of Tile C pelvic ring injuries using a posteriorly based external fixation system.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol [Internet]. 2017 Dec 5 [cited 2018 Jan 5]:[about 12 p.]. Available from: https://preview.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29209809
10.Bi C, Wang Q, Wu J, Zhou F, Zhang F, Liang H, et al. Modified pedicle screw-rod fixation versus anterior pelvic external fixation for the management of anterior pelvic ring fractures: a comparative study. J Orthop Surg Res [Internet]. 2017 Dec [cited 2018 Jan 5];12(1):[about 11 p.]. Available from: https://preview.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29191213
11.Moskowitz EE, Burlew CC, Moore EE, Pieracci FM, Fox CJ, Campion EM et al. Preperitoneal pelvic packing is effective for hemorrhage control in open pelvic fractures.Am J Surg [Internet]. 2018 Abr [cited 2018 Jan 5];215(4):[about 3 p.]. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0002-9610(17)30772-9
12.Li Q, Dong J, Yang Y, Wang G, Wang Y, Liu P, et al. Retroperitoneal packing or angioembolization for haemorrhage control of pelvic fractures-Quasi-randomized clinical trial of 56 haemodynamically unstable patients with Injury Severity Score ≥33. Injury [Internet]. 2016 Feb [cited 2018 Jan 5];47(2):[about 6 p.]. Available from: http://www.injuryjournal.com/article/S0020-1383%2815%2900587-2/pdf
13.Yoshikawa S, Shiraishi A, Kishino M, Honda M, Urushibata N, Sekiya K, et al. Predictive ability and interobserver reliability of computed tomography findings for angioembolization in patients with pelvic fracture.J Trauma Acute Care Surg [Internet]. 2018 Feb [cited 5 Jan 2018];84(2):[about 6 p.]. Available from: https://preview.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29140949
14.Ramasamy B, Thewlis D, Moss MJ, Fraysse F, Rickman M, Solomon LB. Complications of trans arterial embolization during the resuscitation of pelvic fractures. Injury [Internet]. 2017 Dec [cited 2018 Jan 5];48(12):[about 10 p.]. Available from: https://preview.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29096928
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2018 Yosvani Sánchez Pérez, Osmany Mario Maestre Ramos, Luis Andrés Guibert Adolfo, Edel Cabreja Mola, Mario Alain Riverón Basulto, Paul Valverde Hernández

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025