External fixation in distal femur fractures: a case report
Keywords:
EDF- Extremo distal del fémur FE- Fijación externa LISS- Less Invasive Stabilization SystemAbstract
Background: fractures of the distal femur are frequent lesions and are generally treated by surgery as: AO plates, nails and occasionally external fixation.
Objective: show a patient with fractures of the distal femur treated by means of external fixation.
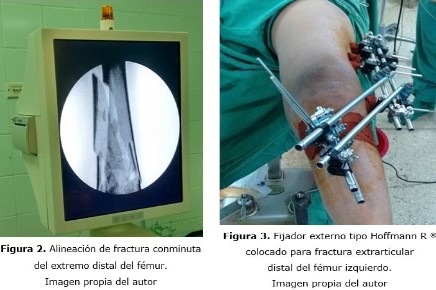
Clinical case: a 59 year old white, woman. The patient was taken to the Orthopedic Emergency Department because of left thing pain after falling at home. On inspection swelling, shortening and external rotation were found. Palpation revealed crepitus and abnormal mobility of the fracture site. Anteroposterior and lateral X rays showed a comminuted fractures of the distal femur. The patient was placed in a skeletal traction by a Braun frame with 12 kilograms of weight. Surgical treatment was carried out six days after admission by a Hoffmann R ® external fixator.
Conclusions: external fixation is a useful method as a transitory and definitive treatment in patients with fractures of the distal femur, the advantages of the method include: short surgical time (less than one hour), few blood lost, control of reduction and a faster indication for rehab.
DeCS: EXTERNAL FIXATORS; FEMORAL FRACTURES; ORTHOPEDIC PROCEDURES; ADULT; CASE REPORTS.
Downloads
References
1. Egol KA, Koval KJ, Zuckerman JD. Handbook of fractures. 5 th ed. New York; Wolkers Kluwer Health; 2015.
2. Collinge CA, Wiss DA. Distal femur fracture. En: Bucholz RW, Heckman JD, Court Brown CM, Tornetta P, editors. Rockwood and Green's Fractures in Adults. 7 th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2010. p. 1719-51.
3. Seligson D, Mauffrey C, Roberts CS. External fixation in Orthopedic Traumatology. London: Springer Verlag; 2012.
4. Lindvall EM, Infante AF, Sanders R. Distal femur fractures. En: Scott WN, editor. Insall & Scott Surgery of the Knee. 5 th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2012. p. 762-72.
5. Jahangir AA, Ricci WM. Distal femur fracture. En: Sethi MK, editor. Orthopedic Traumatology: an evidence based approach. New York: Springer; 2013. p. 247-59.
6. Rudloff MI. Fractures of the lower extremity. En: Canale ST, Beaty JH, editors. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. 12 th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2013. p. 2690-2701.
7. Iyer KM. The Knee Joint. En: Iyer KM, editor. Trauma Management in Orthopedics. London: Springer; 2013. p. 103-14.
8. Refaat M, Coleman S, Meehan JP, Jamali AA. Periprosthetic supracondylar femur fracture treated with spanning external fixation. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2015 Feb;44(2):90-3.
9. Qu H, Knabe C, Radin S, Garino J, Ducheyne P. Percutaneous external fixator pins with bactericidal micron-thin sol-gel films for the prevention of pin tract infection. Biomaterials. 2015 Sep;62:95-105.
10. Beltran MJ, Gary JL, Collinge CA. Management of distal femur fractures with modern plates and nails: state of the art. J Orthop Trauma. 2015 Apr;29(4):165-72.
11. Massoud EI. Fixation of distal femoral fractures: Restoration of the knee motion. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2015 May;21(3):197-203.
12. Bedes L, Bonnevialle P, Ehlinger M, Bertin R, Vandenbusch E, Piétu G. External fixation of distal femoral fractures in adults' multicenter retrospective study of 43 patients. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014 Dec;100(8):867-72.
13. Smith JR, Halliday R, Aquilina AL, Morrison RJ, Yip GC, McArthur J, et al. Distal femoral fractures: The need to review the standard of care. Injury. 2015 Jun;46(6):1084-8.
14. Carroll EA, Koman LA. External fixation and temporary stabilization of femoral and tibial trauma. J Surg Orthop Adv. 2011 Spring;20(1):74-81.
15. Pawasuttikul C, Chantharasap T. Open biological reduction and a locking compression plate for distal femoral fractures: a review of 40 cases. J Med Assoc Thai. 2014 Dec;97(12):1325-31.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2017 Alejandro Alvarez López, Yenima García Lorenzo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025