Nutritional anthropometry in children from one to six years old mal nourished by excess
Abstract
Background: obesity is one of the commonest chronic disorders in childhood, with a prevalence that increases rapidly and continuously.
Objective: to describe some of the anthropometric features in children from one to six year old who present malnourishment by excess.
Methods: an observational, descriptive and transversal study was conducted in the Human Anatomy Department at the School of Medicine in Camaguey from March 2015 to May 2016. The universe was composed of 482 children who belong to the nurseries in Vertientes municipality. The sample was 101 children who are malnourished by excess. The variables studied were: age, weight, height, BMI, brachial perimeter, tricipital, bicipital, subscapular and suprailiac skinfolds. Statistical analysis was carried out using the SPSS program. Anthropometric technique was performed and nutritional tables were used by physicians at primary health care nowadays to evaluate the nutritional condition.
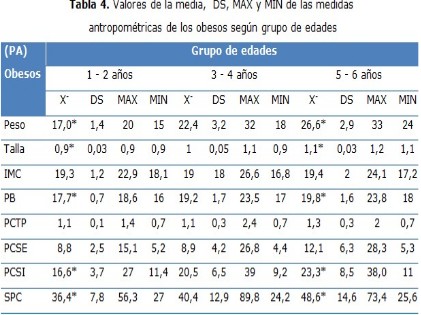
Results: predominance of obesity and overweight with a remarkable incidence for all groups of age, where the greater incidence was for males with the biggest percentages.
Conclusions: significant figures in weight and BMI were found, with more impact in obese male than in females. For the last ones the frequency was greater in all the skin folds. There were significant differences in terms of weight and height between the three groups of age, meanwhile the brachial perimeter was different between extreme groups of age and between the one to two year age group with three to four year age group.
DeCS: BODY WEIGHTS AND MEASURES; OBESITY; OVERWEIGHT; CHILD; EPIDEMIOLOGY, DESCRIPTIVE.
Downloads
References
1. Gahagan S. Sobrepeso y obesidad. En: Kliengman RM, Stanton B, St. Geme J, Schor N, Behrman R, editors. Nelson. Tratado de Pediatría. Vol 2. 19ma ed. Barcelona, España: ELSEVIER; 2013. p. 191-200.
2. Kaufer Horwitz M, Tavano Colaizzi L, Ávila Rosas H. Obesidad en el adulto. En: Casanueva E, Kaufer Horwitz M, Pérez Lizaur AB, Arroyo P, editores. Nutriología Médica. Ciudad de la Habana: ECIMED; 2006. p. 283-310.
3. Jiménez Acosta SM, Rodríguez Suárez A. Evolución del sobrepeso en preescolares cubanos en un período de diez años. Rev Cub Pediatr [Internet]. Jun 2013 [citado 22 Jun 2016];85(4):[aprox. 10 p.]. Disponible en: http://scieloprueba.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S003475312013000400003&lng=es&nrm=iso
4. Santos Beneit G, Sotos Prieto M, Stuart P, Redondo J, Fuster V, Peñalvo JL. Asociación entre antropometría y presión arterial alta en una muestra representativa de preescolares de Madrid. Rev Esp Cardiol [Internet]. Jun 2015 [citado 22 Jun 2016];68(6):[aprox. 8 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.clinicalkey.es/service/content/pdf/watermarked/1-s2.0-S0300893214004977.pdf?locale=es_ES
5. Piñeiro Lamas R. Obesidad en la infancia y la adolescencia. La Habana: Editorial Científico-Técnica; 2014.
6. Ferrer Arocha M. Persistencia del sobrepeso desde la niñez. Implicaciones en la salud del adulto. En: Piñeiro Lamas R, editor. Obesidad en la infancia y la adolescencia. La Habana: Editorial Científico-Técnica; 2014. p. 32-36.
7. Gloria Santos B, Mercedes Soto P, Stuart P, Redondo J, Fuster V, Peñalvo JL. Asociación entre antropometría y presión arterial alta en una muestra representativa de escolares en Madrid. Rev Esp Cardiol [Internet]. Jun 2015 [citado 22 Jun 2016];68(6):[aprox. 8 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.clinicalkey.es/service/content/pdf/watermarked/1-s2.0-S0300893214004977.pdf?locale=es_ES
8. Cabal Giver MA, Hernández Oviedo G, Torres Díaz G, Guerra Marín M. Alteraciones del estado nutricional y la tensión arterial como señales tempranas de ateroesclerosis. Rev Cubana Med Gen Integr [Internet]. Jun 2010 [citado 22 Jun 2016];26(2):[aprox. 4 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S086421252010000200005&lng=es
9. Cossio Bolaños M, Vidal Espinosa R, Lagos Luciano J, Gómez Campos M. Perfil antropométrico en función del estado nutricional de niños con discapacidad intelectual. Rev Chil Pediatr [Internet]. 2015 [citado 22 Jun 2016];86(1):[aprox. 7 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.clinicalkey.es/service/content/pdf/watermarked/1-s2.0-S0370410615000054.pdf?locale=es_ES
10. Carrillo Selles M, Pita Rodríguez G, Díaz ME, Mercader O, Wong I. Evaluación nutricional de niños de 10 a 14 meses de edad. Rev Cubana Pediatr [Internet]. 2009 [citado 22 Jun 2016];81(3):[aprox. 7 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttex&pid=s0034-75312009000300003&ing=es&mn=iso
11. Jiménez Acosta S M, Rodríguez Suárez A. Evolución del sobrepeso en preescolares cubanos en un período de diez años. Rev Cubana Pediatr [Internet]. Jun 2013 [citado 22 Jun 2016];85(4):[aprox. 10 p.]. Disponible en: http://scieloprueba.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S003475312013000400003&lng=es&nrm=iso
12. Puente Perpiñán M, Ricardo Falcón T R, Fernández Díaz R R. Factores de riesgo relacionados con la obesidad en niñas y niños menores de 5 años. MEDISAN [Internet]. Jun 2013 [citado 22 Jun 2016];17(7):[aprox. 9 p.]. Disponible en: http://scieloprueba.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S102930192013000700 006&lng=es&nrm=iso
13. Álvarez Gómez JL, Ondina Terrero E, Díaz Novás J, Ferrer Arocha M. Exceso de peso corporal e hipertensión arterial en adolescentes de secundaria básica. Rev Cubana Med Gen Integr. 2010;26(1):39-46.
14. Ávila Rosas H, Tejero Barrera E. Evaluación del estado de nutrición. En: Casanueva E, Kaufer Horwitz M, Pérez Lizaur AB, Arroyo P, editores. Nutriología Médica. Ciudad de la Habana: ECIMED; 2006. p. 593-672.
15. Hernández Fernández M, Plasencia Concepción D, Jiménez Acosta S, Martín González I, González Pérez T. Evaluación del estado nutricional. En: Hernández Fernández M, Plasencia Concepción D, Jiménez Acosta S, Martín González I, González Pérez T, editores. Temas de Nutrición básica. La Habana: ECIMED; 2008. p. 77-100.
16. Santana Porbén S, Barreto Penié J, González Pérez TL. Mediciones antropométricas. En: Santana Porbén S, Barreto Penié J, González Pérez TL, editores. Programa de Intervención Alimentario, Nutrimental y Metabólico para Hospitales Pediátricos. La Habana: ECIMED; 2009. p. 46-85.
17. Artiles Visbal L, Otero Iglesias J, Barrios Osuna I. Ética de la investigación científica. En: Artiles Visbal L, Otero Iglesias J, Barrios Osuna I, editores. Metodología de la investigación para las ciencias de la Salud. La Habana: ECIMED; 2009. p. 79-102.
18. González Hermida AE, Vila Díaz J, Guerra Cabrera CE, Quintero Rodríguez O, Dorta Figueredo M, Danilo Pacheco J. Estado nutricional en niños escolares. Valoración clínica, antropométrica y alimentaria. MediSur [Internet]. 2010 [citado 22 Jun 2016];8(2):[aprox. 6 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?pid=S1727897X2010000200004&script=sci_arttext&tlng=es
19. González Sánchez R, Llapar Milian R, Rubio Olivares D. Caracterización de la obesidad en adolescentes. Rev Cubana Pediatr [Internet]. Jun 2009 [citado 22 Jun 2016];81(2):[aprox. 7 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php
20. Pineda Pérez S, González Hernández DI, Zayas Torriente GM, Domínguez Aillón Y, Herrera Arguelles X. La obesidad infantil y del adolescente: un problema pediátrico y un desafío para la prevención. Rev Cubana Pediatr. 2009;81(supl):102-7.
21. Gotlhelf S, Jubany L. Comparación de tablas de referencias en el diagnóstico antropométrico de niños y adolescentes obesos. Arch Argentinos de Pediatr [Internet]. Jun 2009 [citado 22 Jun 2016];103(2):[aprox. 6 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.ar/scielo.php
22. Torre Montejo E de la, Pelayo González Posada EJ. Obesidad. En: Amador García M, Peña Escobar M, Hermelo Treche M, Martínez González A, editores. Pediatría. T I. La Habana: ECIMED; 2006. p. 264-76.
23. Esquivel Lauzurique M, González Fernández C. Excess weight and adiposity in children and adolescents in Havana, Cuba: Prevalence and trends, 1972 to 2005. MEDICC Review [Internet]. Jun 2010 [citado 22 Jun 2016];12(2):[aprox. 11 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.medicc.org/mediccreview/index.php?issue=12&id=146&a=vhtml
24. Jiménez Acosta S, Rodríguez Martínez O, Gómez Machado LM. La prevención y tratamiento de la obesidad desde la niñez es una estrategia para disminuir las enfermedades. En: Jiménez Acosta S, Roque P, Rodríguez Martínez O, Gómez Machado LM, editores. Folleto sobre Manejo práctico del sobrepeso y la obesidad en los niños y niñas. La Habana: UNICEF-Cuba; 2006. p. 1-2.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2017 Dioneski Quesada Molina, Iris S. Bacallao Cabreras, Carmen Labrada Salvat, Yolexis Prieto Cordovés, Luisa M. Serrano González, Vivian Garcés Ortiz

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025