Anatomical variations of the lienal or splenic artery in the human being
Abstract
Background: the spleen is one of the best vascularized organs in the body, irrigated by the lienal artery.
Objective: to characterize from the point of view of the anatomical variations of the lienal or splenic artery in the human being.
Methods: an observational and descriptive study in the Human Anatomy Department of the School of Medicine in Camaguey from November 2015 to February 2016. It was dissected the arterial splenic system in 15 anatomical preparations: five human blocks and ten fetuses between 20 to 29 weeks of development using a direct macroscopic methods and a binocular magnifying glass. These specimens were rinsed with pipe water and immersed in a formalin 5% solution; the study variables were: origin, trajectory, collateral branches and termination. Descriptive statistics, frequencies, and percentages were used.
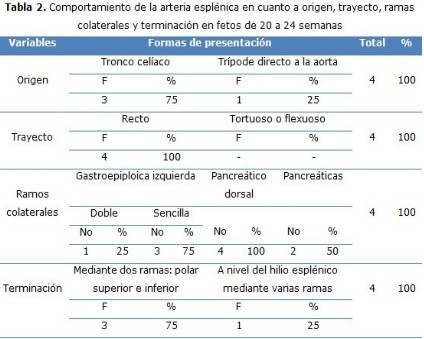
Results: the origin of the vessel from the celiac trunk with a tortuous trajectory and direction to the superior border of the pancreas in relation with the splenic vein, anterior aspect of the left kidney and suprarenal gland; giving off collateral branches: dorsal pancreatic, pancreatic arteries and left gastroepiploica with variations in number and origin in fetuses; the form of terminations in two terminal branches: superior and inferior polar arteries, or to the level of the splenic hilum dividing in various branches.
Conclusions: predominance of the origin from the celiac trunk, tortuous and rectilinear trajectory in fetuses. Variant collateral branches of the gastroepiploica in a double or single form with predominance of the doubles in fetuses. Dichotomized termination in superior and inferior polar arteries.
DeCS: SPLENIC ARTERY/anatomy & histology; ANATOMIC VARIATION; SPLEEN/blood supply; FETUS; EPIDEMIOLOGY, DESCRIPTIVE.
Downloads
References
1. Mckinley M P, O´Loughlin V D. Human Anatomy. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2006.
2. Shier D, Butler J, Lewis R. Human Anatomy and Physiology. 10th ed. New York: McWraw-Hill; 2004.
3. Melone S, Merrera N, Rodríguez M, Antonetti C. Contribución de la Arteria Esplénica en la irrigación del bazo. Revista de la Facultad de Medicina. 2008 dic 25; 31(2): 284-7.
4. Price M, Patino M, Sahani D. Computed Tomography Angiography of the Hepatic, Pancreatic, and Splenic Circulation. Am N Radiol Clin [Internet]. 2016 Jun [citado 2016 Jul 22];54:[about 3 p.]. Available from: https://www.clinicalkey.es/service/content/pdf/watermarked/1-s2.0-S0033838915001633.pdf?locale=es
5. Borley N R. Bazo. In: Standring S, editor. Anatomy. The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 39th ed. London: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2011. p. 1239-44.
6. Snell R S. Clinical Anatomy by regions. 9th ed. New York: Lippincontt Wiliams and Wilkins; 2012.
7. Thomas S D, Abraham M. Textbook of gastrointestinal Radiology. 4th ed. London: Elsevier; 2011.
8. Leyendecker J. Solución de problemas en imagen abdominal. España: Elsevier; 2011.
9. Shelton J, Molzman MD. Tratado de Cirugía. España: Elsevier; 2013.
10. Kumar N, Patil J, Swamy RS, Guru A, Nayak SB. A typical arterial supply to the spleen by polar branches of splenic artery and accessory splenic artery. J Clin Diagn Res [Internet]. 2014 Aug [citado 2016 Jul 22];8(8):[about 1 p.]. Available from: https://www.clinicalkey.es/#!/content/medline/2-s2.0-25302184
11. Paluetto R, Mieres J, Incaborne A, García A, Sanatera O. Exclusión de aneurisma esplénico gigante con técnica de catéteres mother-in-child en paciente de alto riesgo quirúrgico. Rev Cardionagiol de Argentina. 2013 Sept 11;4(1):62-65.
12. Drake L R, Vogl W, Mitchel A W. Anatomy for Students. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2005.
13. Sankar K D, Branw P S, Susan P G. Variación anatómica del tronco celiaco y sus ramas. N Engl J Med. 2011 Jun 22;29(8):581-84.
14. Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AM. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 7th ed. USA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2014.
15. Díaz Mesa J, Domínguez Cordovés J, González Sosa Gl, Madrigal Batista G, Gómez Quintero R, Collera Rodríguez S, et al. Aneurisma de la arteria esplénica. Rev Cubana Cir [Internet]. 2008 Jun [citado 24 Jul 2016];47(2):[aprox. 2 p.]. Disponible en: http://scieloprueba.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-74932008000200010&lng=es
16. Netter FH. Atlas de Anatomía Humana. 5ta ed. USA: Elsevier; 2011.
17. Jáuregui E. Anatomía de la arteria esplénica. Rev Fac de Ciencias Méd Córdoba. 2012;56(21):41.
18. Vanhoenacker FM, Op de Beeck B, de Schepper AM, Salgado R, Snoeckx A, Parizel PM. Vascular disease of the spleen. ClinicalKey [internet]. 2007 Feb [citado 2016 Jun 22];28:[about 2 p.]. Available from: https://www.clinicalkey.es/service/content/pdf/watermarked/1-s2.0-S0887217106000904.pdf?locale=es_ES
19. Romero García JA, Murie JM. Anatomía Humana. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2005.
20. Espinosa Quirós D, Milán Companioni D, Buliés de Armas S, Rubal Lorenzo N. Vasos arteriales y venosos de la circulación sistémico. En: Castillo Guerrerop LM, González Aguilar V, Espinosa Quirós D, González Jardínez D, Núñez López N, Milán Companioni D, et al, editores. Morfofisiología. T III. 2da ed. La Habana: ECIMED; 2015. p. 140-61.
21. Pardo Gómez G, García Gutíerrez A. Temas de Cirigía. T II. La Habana: ECIMED; 2010.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2017 Iris S. Bacallao Cabreras, Dioneski Quesada Molina, Virgen Fong Rodríguez, Luisa M. Serrano González, Olga L. Cuba Yordi, Carmen Almaguer Rodríguez

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025