Antimicrobial Resistance in Latin America in the last 5 years, Narrative Review
Abstract
Introduction: Antibiotics were discovered in the 20th century. Antimicrobial resistance is defined as the ability of a microorganism to resist the effects of antibiotics, which endangers global priorities and harms human development.
Objective: To analyze the scientific evidence available in relation to antimicrobial resistance in the last 5 years in Latin America.
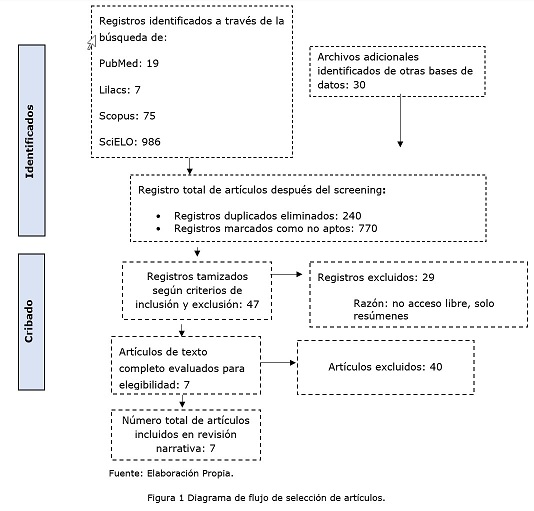
Methods: A narrative review was carried out. The research was carried out from August 2023 to July 2024, the included texts were only in Spanish. Four databases were used: Pubmed, SciELO, Scopus and Dialnet.
Results: 7 articles were found: 3 Ecuadorian, 2 Mexican, 1 from Colombia and 1 from Peru.
Conclusions: Antimicrobial resistance itself is a global problem, it represents an urgent challenge for human, animal and environmental health, the narrative points less to clinical aspects and more dimensioned in socioeconomic problems generated by it, overuse of antibiotics, free sale prescriptions uncontrolled, lack of education, overuse in livestock farming generating large financial costs for governments and its consequent effect on public policies where common regulations are lacking. Alexander Fleming remains present as a historical figure as a prophet who predicted possible consequences of antimicrobial resistance. Strategies for addressing this problem are proposed: improving administration programs and surveillance systems at the hospital level, implementing public policies with regulatory effects at the international level, education at all levels from pharmaceutical companies to the community, including clinical staff, regulations on the prevailing technology, greater research development, and finally the creation of vaccines with prophylactic effects.
DeCS:DRUG RESISTANCE, MICROBIAL; ANTI-INFECTIVE AGENTS; ANTI-BACTERIAL AGENTS; DRUG RESISTANCE, MULTIPLE, BACTERIAL; ANTIMICROBIAL STEWARDSHIP
Downloads
References
1.- ACS, Chemistry for life. Descubrimiento y desarrollo de la penicilina 1928-1945. [Internet]. London: American Chemical Society; 1999. Disponible en: http://www.acs.org/content/acs/en/education/whatischemistry/landmarks/historia-quimica/ descubrimiento-desarrollo-penicilina.html
2.Giono-Cerezo S, Santos-Preciado JI, Rayo Morfín-Otero M, Torres-López FJ, Alcántar-Curiel MD. Resistencia antimicrobiana. Importancia y esfuerzos por contenerla. Gac Méd Méx [Internet]. 2020 [citado 4 abr 2023]; 156(2): 172-180. Disponible en: https://www.scielo.org.mx/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0016-38132020000200172
3.Isaías-Camacho JO, Salinas-Lezama E, Rodríguez-Weber FL, Díaz-Greene E. Prescripción racional de antibióticos: una conducta urgente. Med interna Méx [Internet] 2018 [citado 8 Abr 2023];34(5):762-770. Disponible en: https://www.scielo.org.mx/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0186-48662018000500012
4.World Health Organization. 10 global health issues to track in 2021 [Internet]. 2020. [citado 15 Abr 2024] Disponible en:
https://www.who.int/news-room/spotlight/10-global-health-issues-to-track-in-2021
5.World Health Organization. Antimicrobial resistance [Internet].2023 [citado 15 Abr 2024] Disponible en:
https://www.who.int/news-room/factsheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance
6.Abushaheen MA, Muzaheed M, Fatani AJ, Alosaimi M, Mansy W, George M; et al. Antimicrobial resistance, mechanisms and its clinical significance. Dis Mon [Internet]. 2020 [citado 16 Abr 2023];66(6). Disponible en: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S001150292030033X?via%3Dihub
7.Instituto de Salud Pública. Resistencia Antimicrobiana [internet]. 2024 [citado 9 Ago 2024]. Disponible en:
https://www.ispch.gob.cl/biomedico/resistencia-antimicrobiana/
8. Valdés AM. La resistencia microbiana en el contexto actual y la importancia del conocimiento y aplicación en la política antimicrobiana. Rev haban cienc méd[internet]. 2017 [citado 6 Oct 2023]; 16(3): 402-419. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_abstract&pid=S1729519X2017000300011&lng=es&nrm=iso&tlng=es
9.Baker E, Thomson N, Weill FX, Hollt K. Genomic insights into the emergence and spread of antimicrobial-resistant bacterial pathogens. J Science [Internet]. 2020 [citado 24 Abril 2023]; 360 (6390): 733–738. Disponible en: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.aar3777
10. World Health Organization. Interagency Coordination Group on Antimicrobial Resistance. No podemos esperar: asegurar el futuro contra las infecciones farmacorresistente [Internet]. 2019 [citado 24 Abril 2023]. Disponible en: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/antimicrobial-resistance/amr-gcp-tjs/iacg/iacg-final-report-es.pdf?sfvrsn=d5acc002_8
11. Karakonstantis S, Kalemaki D. Antimicrobial overuse and misuse in the community in Greece and link to antimicrobial resistance using methicillin-resistant S. aureus as an example. J Infect Public Health [Internet]. 2019 [citado 6 May 2023]; 12 (4): 460-464. Disponible en: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1876034119301261?via%3Dihub
12.Mancuso G, Midiri A, Gerace E, Biondo C. Bacterial antibiotic resistance: the most critical pathogens. Pathogens [Internet]. 2021 [citado 6 May 2023]; 10(10): 1310. Disponible en: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8541462/
13.Manohar P, Loh B, Leptihn S. Will the overuse of antibiotics during the Coronavirus pandemic accelerate antimicrobial resistance of bacteria? Infect Microbes Dis [Internet]. 2020 [citado 6 May 2023]; 2(3). Available in: https://journals.lww.com/imd/fulltext/2020/09000/will_the_overuse_of_antibiotics_during_the.1.aspx
14.Almagor J, Temkin E, Benenson I, Fallach N, Carmeli Y. The impact of antibiotic use on transmission of resistant bacteria in hospitals: insights from an agent-based model. PLoS One [Internet]. 2018 [citado 3 Jun 2023];13(5). Disponible en: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0197111
15.Dadgostar P. Antimicrobial Resistance: Implications and Costs. Infection and drug Resistance [Internet]. 2019 [citado 3 Jun 2023]; 12: 3903-3010. Disponible en: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6929930/
16.Rochford C, Sridhar D, Woods N, Saleh Z, Hartenstein L, Ahlawat H; Global governance of antimicrobial resistance. Lancet [Internet]. 2018 [citado 3 Jun 2023]; 391 (10134): 1976-1978. Disponible en: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(18)31117-6/abstract
17.Chandler CIR. Cuentas actuales de la resistencia a los antimicrobianos: estabilización, individualización y antibióticos como infraestructura. Comunidad Palgrave [Internet]. 2019 [citado 6 jul 2023]; 5(53): 1-13. Disponible en: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41599-019-0263-4
18.Okeke IN, de Kraker MEA, Van Boeckel TP, Kumar CK, Schmitt H, Gales AC, et al. The scope of the antimicrobial resistance challenge. Lancet [Internet].2024 [citado 3 Jun 2023]; 403 (10442): 2426-2438. Disponible en: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(24)00876-6/abstract
19.Walsh TR, Gales AC, Laxminarayan R, Dodd PC. Antimicrobial Resistance: Addressing a Global Threat to Humanity. PLoS Med [Internet]. 2023 [citado 3 Jun 2023]; 20 (7): e1004264. Disponible en: https://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1004264
20.Sarkar S, Bhatia G. Writing and appraising narrative reviews. Journal of Clinical and Scientific Research [Internet]. 2021[citado 3 Jun 2023]; 10(3): 169-172. Disponible en: https://journals.lww.com/jcsr/fulltext/2021/10030/writing_and_appraising_narrative_reviews.8.aspx
21.Molina-Arias M. La importancia de no menospreciar las palabras clave. Rev Pediatr Aten Primaria [Internet]. 2019 [citado 8 Ago 2023]; 21(83): 313-318. Disponible en: http://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1139-76322019000300024&lng=es.
22. Arksey H, O´Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol [Internet]. 2003 [citado 16 Ago 2023]; 8(1): 19-32. Disponible en: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/1364557032000119616
23.Yáñez-Baeza C, Aguilera-Eguía R, Fuentes-Barria H, Roco-Videla A. Importancia de la directriz PRISMA. Nutr Hosp [Internet] 2023 [citado 23 Ago 2023]; 40(3): 670-675. Disponible en: https://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0212-16112023000400028
24.The EQUATOR Network. Enhancing the QUAlity and Transparency Of Health Research. [Internet]. [citado 3 Sep 2023]. Disponible en:
https://www.equator-network.org/
25.Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine, Oxford. CEBM. OCEBM Levels of Evidence. [Internet] 2019 [citado 15 sep 2023]; Disponible en: https://www.cebm.ox.ac.uk/resources/levels-of-evidence/ocebm-levels-of-evidence
26.Quino-Sifuentes W, Alvarado-Guerrero JI. La resistencia antimicrobiana en el Perú: Un problema de salud pública. Alpha Centauri [Internet]. 2021 [citado 2 Oct 2023];2(3):15-22. Disponible en: https://www.journalalphacentauri.com/index.php/revista/article/view/38/39
27.Vanegas-Múnera JM, Jiménez-Quiceno JN. Resistencia antimicrobiana en el siglo XXI: ¿hacia una era postantibiótica?. Fac Nac Salud Pública [Internet]. 2020 [citado 16 Oct 2023];38(1):e337759. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.co/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0120386X2020000100105
28.Montero- Espina L, Gutiérrez González JP. Resistencia Antimicrobiana; futuro de la medicina. Discover Medicine [Internet]. 2020 [citado 2 Nov 2023]; 4(1): 59-62. Disponible en: https://revistascientificas.una.py/index.php/DM/article/view/3025
29.Da Silva JB Jr, Espinal M, Ramón-Pardo P. Resistencia a los antimicrobianos: tiempo para la acción. Panam Salud Publica [Internet]. 2020 [citado 17 Nov 2023]; 44: e122. Disponible en: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/345024154_Resistencia_a_los_antimicrobianos_tiempo_para_la_accion
30.García Balda HA, Palacios M. Resistencia Antimicrobiana en el Contexto Actual. Pentaciencias [Internet]. 2022 [citado 26 Nov 2023]; 4(3): 610-621. Disponible en: https://www.editorialalema.org/index.php/pentaciencias/article/view/142/263
31.- Rivera-Ullauri MV, Quintana-Hernández H. Resistencia antimicrobiana. HJCA [Internet]. 2021 [citado 4 Dic 2023]; 13(1): 11-14. Disponible en: https://revistamedicahjca.iess.gob.ec/ojs/index.php/HJCA/article/view/642
32.Mendieta-Condado E, Márquez-Aguirre AL. Superbacterias y análisis genómico de la Resistencia antimicrobiana. Biociencias [Internet]. 2021 [citado 8 Ene 2024]; 9: e1088. Disponible en: https://www.scielo.org.mx/pdf/revbio/v9/2007-3380-revbio-9-e1088.pdf
33.Murugaiyan J, Kumar PA, Rao GS, Iskandar K, Hawser S, Hays JP; et al. MBM. Progress in Alternative Strategies to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance: Focus on Antibiotics. Antibiotics (Basel) [Internet]. 2022 [citado 22 marzo 2024]; 11(2): 200. Disponible en: https://www.mdpi.com/2079-6382/11/2/200
34. Aljeldah MM. Antimicrobial Resistance and Its Spread Is a Global Threat. Antibiotics [Internet]. 2022 [citado 22 marzo 2024]; 11(8): 1082. Disponible en: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9405321/
35. Tamayo-Trujillo VR, Guevara-Ramírez AP, Cadena-Ullauri SA, Paz-Cruz EA, Ruiz -Pozo VA, Zambrano-Espinosa AK. Estudio de revisión: Genes involucrados con resistencia antimicrobiana en hospitales del Ecuador. Cambios [Internet]. 2022 [citado 28 Mar 2024]; 21 (2): 2-7. Disponible en: https://revistahcam.iess.gob.ec/index.php/cambios/article/view/863/668
36. Majumder MAA, Rahman S, Cohall D, Bharatha A, Singh K, Haque M, et al. Antimicrobial Stewardship: Fighting Antimicrobial Resistance and Protecting Global Public Health. Infect Drug Resist. [Internet]. 2020 [citado 02 abr 2024]; 13: 4713-4738. Disponible en: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/373094655_Antimicrobial_stewardship_program_Fighting_antimicrobial_resistance_in_India
37. Camacho-Silvas LA. Resistencia bacteriana, una crisis actual [Bacterial resistance, a current crisis.]. Rev Esp Salud Publica. [Internet]. 2023 [citado 17 abr 2024]; 97: e202302013. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10541255/
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Alejandro Antonio Hernández-Díaz, José Ignacio Villagra-Savaria, Michele Abigail Hernández-Hernández, Carolina Adriana Placencia-Acuña

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025