Polyostotic fibrous displasia
Abstract
Introduction: Fibrous dysplasia is a skeletal disease characterized by the replacement of normal bone by fibrous bone tissue. The disease can most commonly affect any bones in the skull and face.
Objective: To present an 8-year-old patient who was offered the surgical modality as therapy due to polyostotic fibrous dysplasia with morphological-functional and aesthetic disorders.
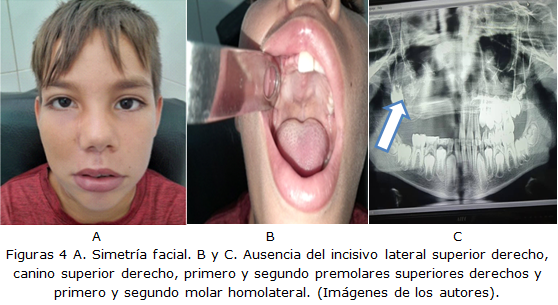
Case report: A white male patient, 8 years old, came to the clinic due to nasal obstruction, increased volume of the nasolabial region, and pain in the right upper hemiarch. On physical examination, medial displacement of the lateral wall of the right nostril, deformity of the inferior turbinate, and occlusion of the nostril was observed. In oropharyngoscopy: mixed block dentition of the upper right hemiarch, increased volume of the vestibule, up to the occlusal surfaces of the teeth. Facial asymmetry with increased volume of stony consistency and pain in the right hemifacial region. On intraoral examination, mixed dentition, with blocky mobility of the upper right hemiarch, and increased volume in the vestibule to the occlusal surfaces of the teeth. Imaging studies showed a mixed lytic and sclerotic area, in ground glass, in the right upper maxillary hemiarch, maxillary sinus, orbital floor, pterygopalatine fossa and nasal septum. Considering the compressive, cosmetic, and functional oculonasosinusal manifestations, surgical treatment was performed using a Weber Ferguson incision, to expose the lower anterior, internal and orbital wall of the upper jaw.
Conclusions: Fibrous dysplasia can affect any bone in the body. Many patients have symptoms due to deformity and displacement of structures adjacent to the injuries. The indicated surgery can correct deformities, eliminate symptoms and functional and aesthetic alterations.
DeCS: FIBROUS DYSPLASIA, POLYOSTOTIC/diagnosis; FIBROUS DYSPLASIA, POLYOSTOTIC/surgery; CHILD; NASAL OBSTRUCTION; CRANIOFACIAL FIBROUS DYSPLASIA.
Downloads
References
1. Von Recklinghausen F. Die fibrose oder deformierende ostitis,die osteomalacie und die osteoplastische carcinose in ihren gegenseitigen beziehungen [Internet]. Berlin: Festschr, Rudolf Virchow; 1891 [citado 17 Abr 2024]. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=1.%09Von+Recklinghausen+F.+Die+fibrose+oder+deformierende+ostitis%2Cdie+osteomalacie+und+die+osteoplastische+carcinose+in+ihren+gegenseitigen+beziehungen
2. McCune DJ. Osteitis fibrosa cystica. The case of a nine year old girl who also exhibitis precoucius puberty, multiple pigmentation of the skin and hyperthyroidism. Am J Dis Child [Internet] 1936 [citado 17 Abr 2024];52:743-5. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=2.%09McCune+DJ.+Osteitis+fibrosa+cystica.+The+case+of+a+nine+year+old+girl+who+also+exhibitis+precoucius+puberty%2C+multiple+pigmentation+of+the+skin+and+hyperthyroidism.+Am+J+Dis+Child.+1936
3. Albright F, Butler AM, Hampton AO, Smith P. Syndrome characterized by osteítis fibrosa disseminata, áreas of pigmentation and endocrine dysfunction with precocious puberty in females. N Engl J Med [Internet]. 1937 [citado 17 Abr 2024];216:727-9. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=3.%09Albright+F%2C+Butler+AM%2C+Hampton+AO%2C+Smith+P.+Syndrome+characterized+by+oste%C3%ADtis+fibrosa+disseminata%2C+%C3%A1reas+of+pigmentation+and+endocrine+dysfunction+with+precocious+puberty+in+females.+N+Engl+J+Med.1937%3B216%3A+727-
4. Lictenstein L. Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia. Arch Surg [Internet]. 1938 [citado 17 Abr 2024];36:874. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=4.%09Lictenstein+L.+Polyostotic+fibrous+dysplasia.+Arch+Surg.1938%3B36%3A874&sort=date&show_snippets=off&filter=simsearch1.fha
5. Perdigão PF, Pimenta FJ, Castro WH, De Marco L, Gomez RS. Investigation of the GSalpha gene in the diagnosis of fibrous dysplasia. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg [Internet]. 2004 [citado 17 Abr 2024];33(5):498-501. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15183415/
6. Weinstein LS. G(s)alpha mutations in fibrous dysplasia and McCune-Albright syndrome. J Bone Miner Res [Internet]. 2006 [citado 17 Abr 2024];21 Suppl 2:120-4. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17229000/
7. Jiménez C, Schneider P, Baudrand R, García H, Martínez A, Mendoza C, et al. Caracterización clínica de pacientes chilenos con displasia fibrosa/síndrome de McCune-Albright. Rev Med Chil [Internet]. 2022 [citado 17 Abr 2024];150(10):1275-1282. Disponible en: https://www.scielo.cl/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-98872022001001275
8. Schwartz DT, Alpert M. The malignant transformationof fibrosus displasia. Am J Med Sci [Internet]. 1964 [citado 21 Mar 2024];247:1-20. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14106874/
9. Díaz de Miguez N. Tratamiento antireabsortivo-eficacia bifosfonatos. Rev Venez Endocrinol Metab [Internet]. 2007 [citado 21 Mar 2024];5(2):26-28. Disponible en: http://ve.scielo.org/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1690-31102007000200009&lng=es
10. Adetayo OA, Salcedo SE, Borad V, Richards SS, Workman AD, Ray AO. Fibrous dysplasia: an overview of desease process, indicationsfor surgicalmanagement, and a case report. Eplasty [Internet]. 2015 [citado 21 Mar 2024];15. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25848443/
11. Guzmán Menco E, López Aparicio E, Harris Ricardo J. Displasia fibrosa: parámetros para la decisión quirúrgica. Rev habanera cienc méd [Internet]. 2018 [citado 21 Mar 2024];17(3):451-461. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1729-519X2018000300451
12. Valentini V, Cassoni A, Terenzi V, Monaca M, Fadda MT, Zadeh R, et al. Our experience quirugical management of craneofacial fobrous displasia: hhat have change in the last 10 years? Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital [Internet]. 2017 [citado 21 Mar 2024];37(5):436-443. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5720872/
13. Tuñón Álvarez MT, Ruiz Calleja A, Pérez de Nanclares G. The enigma of Henry IV's disease: Did he suffer from McCune-Albright syndrome/fibrous dysplasia? Rev Esp Patol [Internet]. 2023 [citado 21 Mar 2024];56(4):243-251. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37879821/#:~:text=Conclusion%3A%20We%20suggest%20that%20Henry%20IV%20may%20have,due%20to%20gain-of-function%20mutations%20in%20the%20GNAS%20gene
14. Gun ZH, Arif A, Boyce AM. Fibrous dysplasia in hildren and its management. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes [Internet]. 2024 Feb 01 [citado 21 Mar 2024];31(1):60-66. Disponible en: https://journals.lww.com/co-endocrinology/abstract/2024/02000/fibrous_dysplasia_in_children_and_its_management.10.aspx
15. Rienzi T, Silveri C, Risso M, Mendoza B, Bianchi G. Displasia fibrosa poliostótica - síndrome de McCune-Albright: reporte de un caso. Rev Méd Urug [Internet]. 2021 Mar [citado 29 Jun 2024];37(1):e701. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.edu.uy/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1688-03902021000102701&lng=es
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Jorge Santana-Álvarez, Yuslaidy de Los Ángeles López-Consuegra, Reynier Ramírez-Suárez, Rachel Peña-Reyes

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025