Método fácil para la medición de las deformidades angulares de la rodilla
Resumen
Fundamento: las deformidades angulares de la rodilla son muy frecuentes en pacientes con artrosis, existen varios métodos de medición clínicos y radiográficos, con características propias.
Objetivo: proponer un método de medición para la desviación angular de la rodilla que sea fácil y rápido.
Métodos: la búsqueda y revisión de la información se realizó en un periodo de cuatro meses (primero de abril de 2018 al 30 de junio de 2018) y se emplearon las siguientes palabras: knee angular deformities, measurement of knee deformities, measures and knee angular deformities, a partir de la información obtenida se realizó una revisión bibliográfica de un total de 213 artículos publicados en las bases de datos PubMed, Hinari, SciELO y Medline mediante el gestor de búsqueda y administrador de referencias EndNote, de ellos se utilizaron 32 citas seleccionadas para realizar la revisión, 29 de los últimos cinco años.
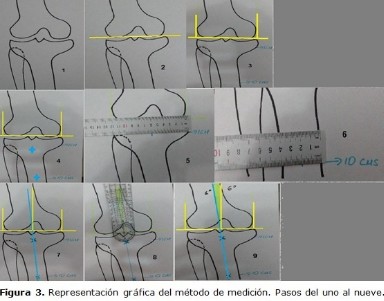
Desarrollo: se describen las características clínicas y radiográficas de los pacientes con desviación angular de la rodilla. En caso de las radiografías se hace referencia a la vista específica para la medición de esta deformidad. Se mencionan las ventajas y desventajas de los métodos de medición del eje mecánico y anatómico. Basados en la revisión de este tema, se propone un método de medición que puede ser llevado a cabo en radiografías digitales y películas.
Conclusiones: el método propuesto es aplicable a nuestro medio y puede ser llevado a cabo en radiografías digitales y películas radiográficas.
DeCS: RODILLA/anomalías; RODILLA/diagnóstico por imagen; OSTEOARTRITIS DE LA RODILLA/diagnóstico por imagen; MEDICIONES, MÉTODOS Y TEORÍAS; INTENSIFICACIÓN DE IMAGEN RADIOGRÁFICA.
Palabras clave
Referencias
Birmingham TB, Moyer R, Leitch K, Chesworth B, Bryant D, Willits K, et al. Changes in biomechanical risk factors for knee osteoarthritis and their association with 5-year clinically important improvement after limb realignment surgery. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017 Dec;25(12):1999-2006.
Huang TL, Wang CC, Yang KC, Wu CC. Reliability of roentgenographic knee alignment measurements in gonarthrosis. J Knee Surg. 2018 Apr;31(4):302-5.
Fryzowicz A, Dworak LB, Koczewski P. Prophylaxis of medial compartment gonarthrosis in varus knee current state of knowledge. Arch Med Sci. 2018 Mar;14(2):454-9.
Lazennec JY, Chometon Q, Folinais D, Robbins CB, Pour AE. Are advanced three-dimensional imaging studies always needed to measure the coronal knee alignment of the lower extremity? Int Orthop. 2017 May;41(5):917-24.
Yazdanpanah O, Mobarakeh MK, Nakhaei M, Baneshi MR. Comparison of double and single leg weight-bearing radiography in determining knee alignment. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2017 May;5(3):174-80.
Cavallo M, Sayyed Hosseinian SH, Parma A, Buda R, Mosca M, Giannini S. Combination of high tibial osteotomy and autologous bone marrow derived cell implantation in early osteoarthritis of knee: a preliminary study. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2018 Mar;6(2):112-8.
Martay JL, Palmer AJ, Bangerter NK, Clare S, Monk AP, Brown CP, et al. A preliminary modeling investigation into the safe correction zone for high tibial osteotomy. Knee. 2018 Mar;25(2):286-95.
Clément J, Toliopoulos P, Hagemeister N, Desmeules F, Fuentes A, Vendittoli PA. Healthy 3D knee kinematics during gait: Differences between women and men, and correlation with x-ray alignment. Gait Posture. 2018 Jul;64:198-204.
Jamali AA, Meehan JP, Moroski NM, Anderson MJ, Lamba R, Parise C. Do small changes in rotation affect measurements of lower extremity limb alignment? J Orthop Surg Res. 2017 May;12(1):77-8.
Wang JH, Shin JM, Kim HH, Kang SH, Lee BH. Discrepancy of alignment in different weight bearing conditions before and after high tibial osteotomy. Int Orthop. 2017 Jan; 41(1):85-92.
Akamatsu Y, Kobayashi H, Kusayama Y, Kumagai K, Saito T. Opening wedge high tibial osteotomy using combined computed tomography-based and image-free navigation system. Arthrosc Tech. 2017 Jul;6(4):e1145-e1151.
Webb M, Dewan V, Elson D. Functional results following high tibial osteotomy: a review of the literature. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2018 May;28(4):555-63.
Krackow KA. The measurement and analysis of axial deformity at the knee. Bufalo: Homer Stryker Center;2008.
Black MS, d'Entremont AG, McCormack RG, Hansen G, Carr D, Wilson DR. The effect of wedge and tibial slope angles on knee contact pressure and kinematics following medial opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2018 Jan; 51:17-25.
ImageJ-Official Site [Internet]. New York: Image Processing and Analysis in Java; c1995-2002 [actualizado 15 de Abr 2015; citado 20 de septiembre 2018]. University of Wisconsin Madison [aprox. 1 p]. Disponible en: https://imagej.net/Welcome
Lee OS, Ahn S, Ahn JH, Teo SH, Lee YS. Effectiveness of concurrent procedures during high tibial osteotomy for medial compartment osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018 Feb;138(2):227-36.
Ma JB, He Q. Is high tibial osteotomy superior to unloader brace treatment in patients with varus malaligned medial knee osteoarthritis? Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018 Jun;26(6):e1-e2.
Tipton SC, Sutherland J, Schwarzkopf R. Using the anatomical axis as an alternative to the mechanical axis to assess knee alignment. Orthopedics. 2015 Dec; 38(12):e1115-20.
Kim YC, Yang JH, Kim HJ, Tawonsawatruk T, Chang YS, Lee JS, et al. Distal femoral varus osteotomy for valgus arthritis of the knees: systematic review of open versus closed wedge osteotomy. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2018 Mar;30(1):3-16.
Gibson K, Sayers SP, Minor MA. Measurement of varus/valgus alignment in obese individuals with knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care & Research. 2010 May;62(5):690-6.
Orellana Reta C, Valdez Jiménez LA. Functional results of open wedge osteotomies in lower limb angular deformities in teenagers. Acta Ortop Mex. 2017 May-Jun;31(3):141-4.
Buda R, Castagnini F, Gorgolini G, Baldassarri M, Vannini F. Distal femoral medial closing wedge osteotomy for degenerative valgus knee?: mid-term results in active patients. Acta Orthop Belg. 2017 Mar;83(1):140-5.
van Outeren MV, Waarsing JH, Verhaar JAN, Reijman M, Brouwer RW, Bierma-Zeinstra SMA. Response to the Letter to the Editor: 'Is a high tibial osteotomy superior to non-surgical treatment in patients with varus malaligned medial knee osteoarthritis?' Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018 Jun;26(6):e3-e4.
Lo GH, Merchant MG, Driban JB, Duryea J, Price LL, Eaton CB, et al. Knee alignment is quantitatively related to periarticular bone morphometry and density, especially in patients with osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018 Feb;70(2):212-21.
Iranpour Boroujeni T, Li J, Lynch JA, Nevitt M, Duryea M. A new method to measure anatomic knee alignment for large studies of OA: data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014 Oct;22(10):1668-74.
Blackburn J, Ansari A, Porteous A, Murray J. Reliability of two techniques and training level of the observer in measuring the correction angle when planning a high tibial osteotomy. Knee. 2018 Jan;25(1):130-4.
El-Alfy BS. Hemi-wedge osteotomy in the management of large angular deformities around the knee joint. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2016 Aug; 26(6):639-45.
Lee OS, Kwon O, Lee YS. Comparison of the outcome between unilateral and bilateral open wedge high tibial osteotomy in the bilateral varus knees. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018 Mar;138(3):307-16.
Liu B, Chen W, Zhang Q, Yan X, Zhang F, Dong T, et al. Proximal fibular osteotomy to treat medial compartment knee osteoarthritis: preoperational factors for short-term prognosis. PLoS One. 2018 May;13(5):e0197980.
Xie W, Zhang Y, Qin X, Song L, Chen Q. Ground reaction vector re-adjustment-the secret of success in treatment of medial compartment knee osteoarthritis by novel high fibular osteotomy. J Orthop. 2018 Jan;15(1):143-5.
Niemeyer P, Stöhr A, Köhne M, Hochrein A. Medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2017 Aug;29(4):294-305.
Monllau JC, Erquicia JI, Ibañez F, Ibañez M, Gelber PE, Masferrer-Pino A, et al. Open-wedge valgus high tibial osteotomy technique with inverted L-shaped configuration. Arthrosc Tech. 2017 Nov;6(6):e2161-e2167.
Enlaces refback
- No hay ningún enlace refback.

Esta obra está bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0 Internacional.















 10 julio 2025
10 julio 2025 La Revista está: Certificada por el CITMA
La Revista está: Certificada por el CITMA Acreditados como: "Web de Interés Sanitario"
Acreditados como: "Web de Interés Sanitario"
