Correlation between initial clinical assessment, SOFA score, and severity of sepsis in children
Abstract
Introduction: The initial clinical evaluation, the adequate stratification of sepsis in children, according to the severity of the disease and the score achieved when applying the SOFA scale are essential to define the behavior and prognosis.
Objective: To identify the correlation between the initial clinical evaluation, the clinical stage and the score obtained when applying the SOFA scale in children admitted for sepsis.
Methods: Clinical exploratory study, at the Guillermo Luis Fernández-Baquero General Hospital in the Moa municipality, Holguín province in the period from January 2021 to December 2022. The population under study was 72 patients with a diagnosis of sepsis. The statistics used were absolute frequency, percentage (%) and arithmetic average. To measure the association, the Chi square test (p
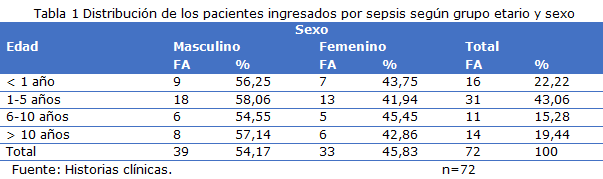
Results: The average age was 4.75 years; 54.17 % belonged to the male sex. When correlating the initial clinical estimate with the clinical stage of sepsis, X2p=26.043 > X2c=16.812 (VC= 0.404). When associating the initial clinical evaluation and the SOFA scale score at admission, it was obtained that X2p=44.253 > X2c=16.812 (VC= 0.826). Between the clinical stage of sepsis and the score achieved when applying the SOFA scale at admission, it was evidenced that X2p=28.557 > X2c=13.277 (VC= 0.623).
Conclusions: There was an association between the data obtained when performing the initial clinical evaluation of the patients, the clinical stage of sepsis on admission and the score achieved on the SOFA scale.
DeCS: SEPSIS/diagnosis; PROGNOSIS; CHILD; ORGAN DYSFUNCTION SCORES; EARLY DIAGNOSIS.
Downloads
References
1. Cruces P. Sepsis desde la perspectiva de países de medianos y bajos ingresos. Andes pediatr [Internet]. 2021 [citado 16 Jun 2023];92(6):829-30. Disponible en: https://www.revistachilenadepediatria.cl/index.php/rchped/article/view/4122
2. Liu L, Oza S, Hogan D, Chu Y, Perin J, Zhu J, et al. Global, regional, and national causes of under-5 mortality in 2000-15: an updated systematic analysis with implications for the Sustainable Development Goals. Lancet [Internet]. 2016 [citado 16 Jun 2023];388(10063):3027-3035. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5161777/
3. Fleischmann Struzek C, Goldfarb DM, Schlattmann P, Schlapbach LJ, Reinhart K, Kissoon N. The global burden of paediatric and neonatal sepsis: a systematic review. Lancet Respir Med [Internet]. 2018 [citado 11 Jun 2023];6(3):223-30. Disponible en: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2213-2600(18)30063-8
4. Weiss SL, Fitzgerald JC, Pappachan J, Wheeler D, Jaramillo Bustamante JC, Salloo A, et al. Global epidemiology of pediatric severe sepsis: the sepsis prevalence, outcomes, and therapies study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med [Internet]. 2015 [citado 12 Jun 2023];191(10):1147-57. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4451622/.
5. Paredes P, Aguayo Escobar A, Espinoza Barbosa A, Bravo Paredes A. Sepsis en Pediatría. Eventos moleculares y consideraciones actuales. Mediciencias UTA [Internet]. 2017 [citado 14 Jun 2023];1(3):10-24. Disponible en: https://revistas.uta.edu.ec/erevista/index.php/medi/article/view/1651
6. Jabornisky R, Sáenz SS, Capocasa P, Jaen R, Moreno RP, Landry L, et al. Epidemiological study of pediatric severe sepsis in Argentina. Arch Argent Pediatr [Internet]. 2019 [citado 16 Sep 2020];117(Suppl 3):135-156. Disponible en: https://www.sap.org.ar/docs/publicaciones/archivosarg/2019/v117n3a35se.pdf.
7. Rodríguez Heredia O, Martín Díaz G, Cabrera Domínguez S, Castañeda Barberán D, Castellanos Aguilera M. Comportamiento de la sepsis en el Hospital Pediátrico Provincial Eduardo Agramonte Piña. Arch méd Camagüey [Internet]. 2022 [citado 15 Jul 2023];26. Disponible en: https://revistaamc.sld.cu/index.php/amc/article/view/9130
8. Baique Sánchez PM. Sepsis en pediatría: nuevos conceptos. An Fac Med [Internet]. 2017 [citado 22 Jun 2023];78(3):333-342. Disponible en: http://dx.doi.org/10.15381/anales.v78i3.13769.
9. Sánchez Díaz JI, de Carlos Vicente JC, Gil Antón J. Diagnóstico y tratamiento del shock séptico y de la sepsis asociada a disfunción orgánica. Protoc diagn ter pediatr [Internet]. 2021 [citado 10 Jun 2023];1:585-610. Disponible en: https://www.aeped.es/sites/default/files/documentos/42_shock_septico_disfuncion_organica.pdf
10. Montalván González G. Sobreviviendo la sepsis. Rev Cuban Pediatr [Internet]. 2007 [citado 22 Jun 2023];79(1). Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-75312007000100010&lng=es.
11. Goldstein B, Giroir B, Randolph A. International Consensus Conference on Pediatric Sepsis. International pediatric sepsis consensus conference: definitions for sepsis and organ dysfunction in pediatrics. Pediatr Crit Care Med [Internet]. 2005 [citado 222 Jun 2023];6(1):2-8. Disponible en: https://www.cpccrn.org/documents/PUD_CQI_definitions.pdf.
12. Velasco Zúñiga R. Triángulo de Evaluación Pediátrica. Pediatr Integral [Internet]. 2014 [citado 12 Jun 2023];XVIII(4):320-323. Disponible en: https://www.pediatriaintegral.es/publicacion-2014-06/triangulo-de-evaluacion-pediatrica/
13. Horeczko T, Enriquez B, McGrath NE, Gausche Hill M, Lewis RJ. The Pediatric Assessment Triangle: accuracy of its application by nurses in the triage of children. J Emerg Nurs [Internet]. 2013 [citado 9 Jun 2023];39(2):182-9. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4318552/.
14. Matics TJ, Sanchez Pinto LN. Adaptation and Validation of a Pediatric Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Score and Evaluation of the Sepsis-3 Definitions in Critically Ill Children. JAMA Pediatr [Internet]. 2017 [citado 11 Jun 2023];171(10):e172352. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6583375/
15. Schlapbach LJ, Straney L, Bellomo R, MacLaren G, Pilcher D. Prognostic accuracy of age-adapted SOFA, SIRS, PELOD-2, and qSOFA for in-hospital mortality among children with suspected infection admitted to the intensive care unit. Intensive Care Med [Internet]. 2018 [citado 10 Jun 2023];44:179-188. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmid/29256116/.
16. Torres Molina A, Fuentes Lambert J, Rodríguez Góngora Y, Navarro Caboverde Y, Calzadilla Columbie C. Aplicación del SOFA score a pacientes con sepsis en Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos Pediátricos. Correo cient méd [Internet]. 2021 [citado 22 Jun 2023];25(2). Disponible en: https://revcocmed.sld.cu/index.php/cocmed/article/view/3529.
17. Uriarte Méndez AE, Cardoso Armas R, Cruz Pérez NR, Valladares Vilches M. Comportamiento de la sepsis en pacientes atendidos en el Hospital Pediátrico Paquito González (2009-2019). Medisur [Internet]. 2021 [citado 20 Jun 2023];19(2):198-207. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1727-897X2021000200198&lng=en&nrm=iso
18. González Ramírez Y, Almaguer Boch JR. Caracterización clínico epidemiológica de pacientes pediátricos con sepsis atendidos en el municipio Puerto Padre. Rev electrón Dr Zoilo E Marinello Vidaurreta [Internet]. 2019 [citado 20 Jun 2023];44(5).Disponible en: http://revzoilomarinello.sld.cu/index.php/zmv/article/view/1930
19. Rodríguez Peña RB. Validación de la Escala Pediátrica de Fallo Multiorgánico Secuencial (pSOFA) para el diagnóstico de sepsis en la Unidad de Cuidado Intensivo Pediátrico del Hospital General de la Plaza de la Salud [tesis]. Santo Domingo: Universidad Iberoamericana (UNIBE); 2021 [citado 20 Jun 2023]. Disponible en: https://repositorio.unibe.edu.do/jspui/handle/123456789/827.
20. Fernández Arribas JL. Aproximación y estabilización inicial del niño enfermo o accidentado. Triángulo de evaluación pediátrica. ABCDE. Protoc diagn ter pediatr [Internet]. 2020 [citado 10 Jun 2023];1:15-26. Disponible en: https://www.aeped.es/sites/default/files/documentos/02_tep_abcde.pdf.
21. Gómez Cortés B. Sepsis. Protoc diagn ter pediatr [Internet]. 2020 [citado 10 Jun 2023];1:153-166. Disponible en: https://www.aeped.es/sites/default/files/documentos/12_sepsis.pdf.
22. Cristobo Bravo T, Quirós Viqueira O, Rodríguez Bencomo D. Actualización en la detección y manejo de la sepsis en el menor de un año. Arch méd Camagüey [Internet]. 2015 [citado 01 Nov 2023];19(5):512-527. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1025-02552015000500011&lng=es
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Alexander Torres-Molina

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025