The expression of Ki67 and its correlation with classic prognostic value factors
Abstract
Introduction: Ki67 is a regulatory protein of cellular cycle which is associated to the proliferation of tumoral cells. Its expression has always had an important role at the tumor classification and it is one of the prognostic and predictive factors in breast carcinoma.
Objective: To determine the relationship between the expression of Ki67 and other classic prognostic factors used in breast cancer.
Methods: A cross-sectional, analytic and descriptive study was carried out at the Teaching Clinic-Surgical Hospital Celestino Hernández, Villa Clara, from January 2017 to June 2019. It was included 286 women with diagnosis of infiltrating breast carcinoma, whose biopsies were studied by immunohistochemistry. The Ki-67 cell marker expression was categorized as low (Ki-6720 %). It was analyzed the relationship between level of expression of Ki67 and other classical prognostic and predictive factors.
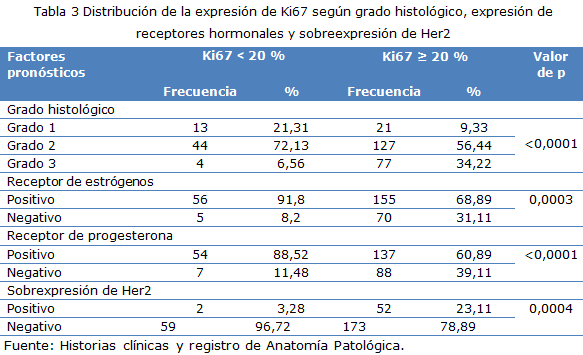
Results: The no special histological type (ductal carcinoma) was the type more often reported. High expression level of Ki67 was associated with the high histological grade (grade 3) and the overexpression of Her2. Low expression of Ki-67.
Conclusions: The levels of expression of Ki67 showed significant association with several predictive and prognostic factors of breast carcinoma.
DeCS: KI67; CELLULAR PROLIFERATION; PROGNOSTIC FACTORS; IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY STUDY; BREAST CANCER.
Downloads
References
1. Valle-Solís AE, Miranda-Aguirre AP, Mora-Pérez J, Pineda-Juárez JA, Gallardo-Valencia LE, Santana L, et al. Supervivencia en cáncer de mama por subtipo mediante inmunohistoquímica: Un estudio retrospectivo. Gac Med Mex [Internet]. 2019 [citado 01 Mar 2022];155(Suppl 1):S50-S55. Disponible en: https://www.gacetamedicademexico.com/files/gmm_s1_19_s50-s55.pdf
2. Martínez Navarro J, Socorro Castro C. Inmunohistoquímica en el cáncer de mama. Herramienta necesaria en la actualidad. Medisur [Internet]. 2018 Ene-Feb [citado 02 Feb 2022];16(1):209-13. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1727-897X2018000100016
3. Ministerio de Salud Pública. Anuario Estadístico 2020. La Habana: Dirección Nacional de Registros Médicos y Estadísticas de Salud; 2021.
4. Panal Cusati M, Herrera de la Muela M, Hardisson Hernaez D, Choqueneira Dionisio M, Román Guindo A, de Santiago García FJ. Correlación entre la expresión de Ki67 con factores clásicos pronósticos y predictivos en el cáncer de mama precoz. Rev Senol Patol Mamar [Internet]. 2014 [citado 02 Mar 2022];27(4):163-9. Disponible en: https://www.elsevier.es/es-revista-revista-senologia-patologia-mamaria--131-pdf-S0214158214000565
5. Programa Argentino de Consensos de Enfermedades Oncológicas. Factores pronósticos y predictivos en cáncer de mama temprano. Consenso Nacional Inter-Sociedades. Revista Argentina de Mastología [Internet]. 2016 [citado 03 Mar 2022];36(128):12-33. Disponible en: https://www.revistasamas.org.ar/revistas/2016_v36_n128/4.pdf
6. Nielsen TO, Leung SCY, Rimm DL, Dodson A, Acs B, Badve S, et al. Assessment of Ki67 in Breast Cancer: Undated Recommendations From the International Ki67 in Breast Cancer Working Group. J Natl Cancer Inst [Internet]. 2021 Jul [citado 04 Feb 2022];113(7):808-19. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8487652/
7. Mayanga Sausa SL. Características clínico patológicas del cáncer de mama asociadas a la expresión del marcador celular Ki-67 en el Hospital Nacional Edgardo Rebagliati Martins, 2013-2017. An Fac med [Internet]. 2019 [citado 04 Feb 2022];80(4):427-31. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.pe/pdf/afm/v80n4/a03v80n4.pdf
8. Li FY, Wu S, Zhou JG, Sun JY, Lin Q, Lin HX, et al. Prognostic Value of Ki-67 in Breast Cancer Patients with Positive Axillary Lymph Nodes: A Retrospective Cohort Study. PLoS ONE [Internet]. 2014 [citado 03 Mar 2022];9(2):e87264. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3911937/
9. Mannell A. The role of Ki67 in breast cancer. S Afr j surg [Internet]. 2016 Jun [citado 03 Mar 2022];54(2). Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.za/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0038-23612016000200004
10. Davey MG, Hynes SO, Kerin MJ, Miller N, Lowery AJ. Ki67 as a Prognostic Biomarker in Invasive Breast Cancer. Cancers [Internet]. 2021 Sep [citado 03 Mar 2022];13(17):4455. doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174455.
11. Untch M, Gerber B, Harbeck N, Jackisch C, Marschner N, Möbus V, et al. 13th St. Gallen International Breast Cancer Conference 2013: Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer Evidence, Controversies, Consensus- Opinion of a German Team of Experts (Zurich 2013). Breast Care [Internet]. 2013 Jun [citado 05 Mar 2022];8(3):221-9. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3728634/
12. Coates AS, Winer EP, Goldhirsch A, Gelber RD, Gnant M, Piccart-Gebhart M, et al. Tailoring therapies--improving the management of early breast cancer: St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2015. Ann Oncol [Internet]. 2015 Ago [citado 05 Mar 2022];26(8):1533-46. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4511219/
13. Cserni G. Histological type and typing of breast carcinomas and they WHO classification changes over time. Pathologica [Internet]. 2020 Mar [citado 04 Feb 2022];112(1):25-41. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8138497/
14. Alcaide Lucena M, Rodríguez González CJ, de Reyes Lartategui S, Gallart Aragón T, Sánchez Barrón MT, García Rubio J, et al. Clasificación actual del cáncer de mama. Implicación en el tratamiento y pronóstico de la enfermedad. Cir Andal [Internet]. 2021 [citado 02 Feb 2022];32(2):155-59. Disponible en: https://www.asacirujanos.com/admin/upfiles/revista/2021/Cir_Andal_vol32_n2_09.pdf
15. Kumar V, Abbas AK, Aster JC. Robbins Basic Pathology. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2013.
16. Aman NA, Doukoure B, Koffi KD, Koui BS, Traore ZC, Kouyate M, et al. Her2 overexpression and correlation with other significant clincopathologic parameters in Ivorian breast cancer women. BMC Clin Pathol [Internet]. 2019 [citado 03 Feb 2022];19:1. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6335844/
17. Gamarra Manrique RR. Evaluación de la sobre-expresión molecular del receptor HER2/neu (Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2/Neuro Glioblastoma) en cáncer de mama humano, mediante inmunohistoquímica por anticuerpos monoclonales, y su correlación pronóstica con el sistema de estadiaje TNM [tesis doctoral]. Arequipa: Universidad Nacional de San Agustín de Arequipa; 2018 [citado 02 Mar 2022]. Disponible en: http://repositorio.unsa.edu.pe/bitstream/handle/UNSA/5995/BIDgamarr.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
18. Galve Agudo B. Valor pronóstico y predictivo del índice de proliferación Ki67 en el carcinoma infiltrante de mama [tesis doctoral]. Zaragoza: Universidad de Zaragoza; 2017 [citado 02 Mar 2022]. Disponible en: https://zaguan.unizar.es/record/60868/files/TESIS-2017-024.pdf
19. Yao Y, Cao M, Fang H, Xie J. Breast cancer in 30-year-old or younger patients: clinicopathologic characteristic and prognosis. World J Surg Oncol [Internet]. 2015 Feb [citado 08 Jul 2022];13:38. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25889848/
20. Ramírez-Torres N, Maycotte-González P, Rivas-Ruiz R. Evaluación de la clasificación molecular por inmunohistoquímica en cáncer de mama avanzado tratado con epirubicina y docetaxel: diferencias clínicas, patológicas, terapéuticas y pronósticas. Gac Mex Oncol [Internet]. 2018 [citado 03 Mar 2022];17:15-27. Disponible en: https://biblat.unam.mx/hevila/Gacetamexicanadeoncologia/2018/vol17/no1/2.pdf
21. Pérez Sánchez VM, Vela Chávez TA, Mora Tiscareño A. Diagnóstico Histopatológico y Factores Pronóstico en Cáncer Infiltrante de Glándula Mamaria. Cancerología 3 [Internet] 2008 [citado 20 Abr 2021];7-17. Disponible en:
22. Awadelkarim KD, Mariani-Costantini R, Osman I, Barberis MC. Ki-67 Labeling Index in Primary Invasive Breast Cancer from Sudanese Patients: A Pilot Study. ISRN Pathology. 2012;6. doi.org/10.5402/2012/232171.
23. Thangarajah F, Enninga I, Malter W, Hamacher S, Markiefka B, Richters L, et al. A Retrospective analysis of Ki-67 Index and its prognostic significance in over 800 primary breast cancer cases. Anticancer Res [Internet]. 2017 Abr [citado 03 May 2022];37(4):1957-64. Disponible en: https://ar.iiarjournals.org/content/37/4/1957
24. Makar W, Lasheen S. Assessment of the Prognostic Role of Ki-67 and Optimal Cutoff Value in Early Breast Cancer: A Retrospective Analysis. Res Oncol [Internet]. 2020 Dic [citado 20 May 2022];16(2):35-41. Disponible en: https://resoncol.journals.ekb.eg/article_105973.html
25. Larios León JE. El estado de los receptores hormonales como factor pronostico en pacientes con cáncer de mama HER2 positivos metastásicos recientemente diagnosticados en el Hospital Almanzor Aguinaga Asenjo durante el periodo 2016-2017 [tesis]. Lambayeque: Universidad Nacional Pedro Ruiz Gallo; 2019 [citado 03 Mar 2022]. Disponible en: https://repositorio.unprg.edu.pe/bitstream/handle/20.500.12893/4926/BC-3734%20LARIOS%20LEON.pdf?sequence=3&isAllowed=y
26. Kamranzadeh H, Ardekani RM, Kasaeian A, Sadighi S, Maghsudi S, Jahanzad I, et al. Association between Ki-67 expression and clinicopathological features in prognosis of breast cancer: a retrospective cohort study. J Res Med Sci [Internet]. 2019 [citado 22 May 2022];24:30. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6521610/
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Raisel García-Pérez, Llanuris Llanes-García, María del Carmen Agüero-Arboláez, Disney Borrego-Gutiérrez, Yunexy Aguado-Besú, Carmen Patricia Alfonso-González

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025