Therapeutic approach of diabetes mellitus type 2 in Primary Care in special situations
Abstract
Introduction: There is an urgent need to individualize each diabetes mellitus type 2 treatment according to the special situations of each patient diagnosed with the disease.
Objective: To describe the therapeutic approach of patients with diabetes type 2.
Methods: A descriptive and cross-sectional study was carried out in 96 patients diagnosed with diabetes mellitus type 2, belonging to the Camilo Torres Restrepo polyclinic, in the period from January to December 2021. Variables such as age, sex, type of treatment, individualized treatment, metabolic control and adherence to treatment were studied. Descriptive statistical techniques were used, such as absolute frequency and percentage for qualitative variables, as well as measures of central tendency for quantitative variables.
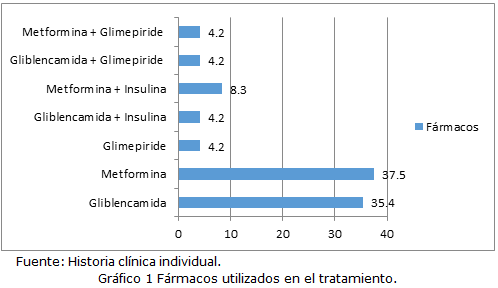
Results: There was a predominance of older ages (over 60 years) with 72.9 % of the casuistry and females (58.3 %). 97.0 % of the participants received pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatment, and 21.8% required more than one drug. Metformin was the most used drug (37.5 %). Treatment of diabetic patients in special situations was inadequate, except in overweight and obese patients, and patients who adhered to treatment achieved better metabolic control of the disease (48%).
Conclusions: The therapeutic approach in the studied patients was inadequate. The treatment of diabetes mellitus type 2 must be individualized, from a comprehensive basis of the baseline condition of each patient, taking into account their comorbidities to achieve comprehensive actions at the primary level of prevention.
DeCS: DIABETES MELLITUS, TYPE 2/drug therapy; TREATMENT ADHERENCE AND COMPLIANCE; METFORMIN/therapeutic use; AGED; PRIMARY HEALTH CARE.
Downloads
References
1. International Diabetes Federation. Atlas de la Diabetes de la FID. 9na ed [Internet]. Bruselas: FID; 2019 [citado 12 Mar 2021]. 169 p. Disponible en: https://www.diabetesatlas.org/upload/resources/material/20200302_133352_2406-IDF-ATLAS-SPAN-BOOK.pdf
2. Arnold Y, Licea ME, Hernández J. Contribución de la Epidemiología al estudio de la diabetes mellitus. Rev Cubana Hig Epidemiol [Internet]. 2017 [citado 14 Mar 2021];55(2):[aprox. 4 p]. Disponible en: http://www.revepidemiologia.sld.cu/index.php/hie/article/view/116
3. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes -2018. Diabetes Care [Internet]. 2017 [citado 24 Mar 2021];41(Suppl 1):S1–S2. Disponible en: https://diabetesjournals.org/care/article/41/Supplement_1/S1/29751/Introduction-Standards-of-Medical-Care-in-Diabetes
4. World Health Organization. World health statistics 2017: monitoring health for the SDGs, Sustainable Development Goals [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization;2017 [citado 12 Abr 2021]. Disponible en: https://www.apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/255336/1/9789241565486-eng.pdf
5. Ministerio de Salud Pública. Anuario Estadístico 2020 [Internet]. La Habana: Dirección Nacional de Registros Médicos y Estadísticas de Salud; 2021 [citado 24 Abr 2021]. Disponible en: https://files.sld.cu/bvscuba/files/2021/08/Anuario-Estadistico-Espa%C3%B1ol-2020-Definitivo.pdf
6. Organización Mundial de la Salud. Informe Mundial sobre la Diabetes [Internet]. Ginebra: OMS; 2016 [citado 15 May 2021]. 86 p. Disponible en: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/254649/9789243565255-spa.pdf
7. Saldarriaga Betancur S. Enfoque terapéutico de la Diabetes Mellitus tipo 2 en adultos. Más allá de una meta glucémica. Med UPB [Internet]. 2018 Ene-Jun [citado 25 May 2021];37(1):36-46. Disponible en: https://revistas.upb.edu.co/index.php/medicina/article/view/918
8. Tschöpe D, Hanefeld M, Meier JJ, Gitt AK, Halle M, Bramlage P, et al. The role of co-morbidity in the selection of antidiabetic pharmacotherapy in type-2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol [Internet]. 2013 [citado 26 Nov 2021];12:62. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3664601/
9. Figueroa Villa K, Gafas González C, Pérez Rodríguez M, Brossard Peña E, García Rios CA, Valdiviezo Maygua MA. Dimensiones de calidad de vida afectadas en pacientes diabéticos. Rev cuba enferm [Internet]. 2020 [citado 27 May 2021];36(1). Disponible en: http://www.revenfermeria.sld.cu/index.php/enf/article/view/2610
10. American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2009. Diabetes Care [Internet]. 2009 Ene [citado 28 Dic 2021];32(Suppl 1):S13-S61. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2613589/
11. Pomares AJ, Jorge R, Alfonso Y, Vázquez MA. Adherencia terapéutica y bienestar subjetivo en pacientes con diabetes mellitus tipo II. Rev Finlay [Internet]. 2019 [citado 27 May 2021];9(3):[aprox. 4 p]. Disponible en: http://revfinlay.sld.cu/index.php/finlay/article/view/672
12. Yanes Quesada M, Perich Amador P, Gonzales Suárez R, Yánez Quesada MA, Cruz Hernández J, Vázquez Díaz GJ. Factores clínicos relacionados con la hipertensión arterial en pacientes con trastornos de tolerancia a los carbohidratos. Rev cuban med gen integ [Internet]. 2017 [citado 12 Ago 2021];23(4). Disponible en:
http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0864-21252007000400005
13. Arencibia-Alvarez MC, Bell-Castillo J, George-Carrión W, Gallego-Galano J, George-Bell MJ. Caracterización de los pacientes con diabetes mellitus tipo 2 atendidos en el Hospital General Docente Dr. Juan Bruno Zayas Alfonso. Univ Méd Pinareña [Internet]. 2020 May-Ago [citado 12 Jun 2021];16(2):e516. Disponible en: https://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/revunimedpin/ump-2020/ump202f.pdf
14. Estrada Vaillant A, Hernández Hernández R, Izada Carnesoltas LT, González Gil A, Quiñones Cabrera D, Cabrera Dorta T. Características clínico-epidemiológicas de la Diabetes Mellitus tipo 2 en el Policlínico Milanés. Municipio Matanzas. Rev méd electrón [Internet]. 2017 [citado 14 Jun 2021];39(5):1084-1093. Disponible en:
http://scielo.sld.cu/pdf/rme/v39n5/rme080517.pdf
15. Rodríguez Salvá A, Céspedes Hernández L, Díaz Piñera A, García Roche R, Balcindes Acosta S. Brechas en el manejo del paciente diabético tipo 2 en un área metropolitana de La Habana. Rev Finlay [Internet]. 2019 [citado 30 May 2021];9(2):[aprox. 14 p.]. Disponible en: http://revfinlay.sld.cu/index.php/finlay/article/view/638/1753
16. Arteaga Noriega A, Cogollo Jiménez R, Muñoz Monterroza D. Apoyo social y control metabólico en la diabetes mellitus tipo 2. Rev Cuid [Internet]. 2017 [citado 25 May 2021];8(2):1668-76. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.co/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2216-09732017000201668
17. Bello Escamilla NV, Montoya Cáceres PA. Adherencia al tratamiento farmacológico en adultos mayores diabéticos tipo 2 y sus factores asociados. Gerokomos [Internet]. 2017 Jun [citado 25 Jun 2021];28(2):73-77. Disponible en: https://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1134-928X2017000200073&lng=es&tlng=es
18. Rincón MK, Torres C, Corredor KA. Adherencia terapéutica en personas con diabetes mellitus tipo 2. Rev ciencia y cuidado [Internet]. 2017 [citado 2020 Jun 2021];14(1):40-59. Disponible en: file:///C:/Users/Dr/Downloads/Dialnet-AdherenciaTerapeuticaEnPersonasConDiabetesMellitus-5817723.pdf
19. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). Lancet [Internet]. 1998 [citado 22 Oct 2021];352:854-65. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9742977/
20. Boussageon R, Supper I, Bejan-Angoulvant T, Kellou N, Cucherat M, Boissel JP, et al. Reappraisal of metformin efficacy in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. PLoSMed [Internet]. 2012 [citado 27 Oct 2021];9:e1001204. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3323508/
21. Trujillo G, Vicente B, Rivas E, Costa M. Caracterización de los pacientes diabéticos tipo 2 ingresados en el Centro de Atención al Diabético de Cienfuegos. Rev Finlay [Internet]. 2016 [citado 27 Oct 2021];6(4):281-9. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2221-24342016000400005&lng=es
22. Leyva T, Masmout M, Carbonel IC, Gámez D, Dueñas O. Caracterización clínico epidemiológica de pacientes con diabetes mellitus de tipo 2. MEDISAN [Internet]. 2017 [citado 04 Nov 2021];17(21):5032. Disponible en: https://www.medisan.sld.cu/index.php/san/article/view/2215
23. Arnold Y, Castelo E, Licea M, Medina I. Comportamiento de indicadores epidemiológicos de morbilidad por diabetes mellitus en Cuba, 1998-2009. Rev Perú epidemiol [Internet]. 2017 [citado 26 Nov 2021];16(1):[aprox. 8p]. Disponible en: http://sisbib.unmsm.edu.pe/BVRevistas/epidemiologia/v16_n1/pdf/a04v16n1.pdf
24. Asenjo JA. Relación entre estilo de vida y control metabólico en pacientes con Diabetes Mellitus Tipo 2 de Chota, Perú. Rev Med Hered [Internet]. 2019 [citado 29 Dic 2021];31(2):101-7. Disponible en: https://www.redalyc.org/journal/3380/338063808004/
25. Aloudah NM, Scott NW, Aljadhey HS, Araujo-Soares V, Alrubeaan KA, Watson MC. Medication adherence among patients with Type 2 diabetes: A mixed methods study. PloS one [Internet]. 2018 [citado 15 May 2021];13(12):e0207583. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30533042/
26. Medina G, Carbajales EB, Carbajales AI. Características clínicas epidemiológicas de la diabetes mellitus en pacientes de un consultorio médico. RMIJ [Internet]. 2020 [citado 12 Dic 2021];21(2):1-13. Disponible en: http://www.remij.sld.cu/index.php/remij/article/view/291/502
27. Ramos-Rangel Y, Morejón-Suárez R, Gómez-Valdivia M, Reina-Suárez M, Rangel-Díaz C, Cabrera-Macías Y. Adherencia terapéutica en pacientes con diabetes mellitus tipo 2. Revista Finlay [Internet]. 2017 [citado 28 Jul 2022];7(2):[aprox. 9 p.]. Disponible en: http://revfinlay.sld.cu/index.php/finlay/article/view/474
28. Mora JF. Adherencia al tratamiento en personas con diabetes mellitus tipo 2 en México: Estudio de meta-análisis. Psicumex [Internet]. 2022 [citado 23 Jul 2022];12:493. Disponible en: https://psicumex.unison.mx/index.php/psicumex/article/view/493
29. Cordero C, Alba C, Muñoz M, Guzmán E, Ramírez N. Características sociodemográficas asociadas a la adherencia del tratamiento en adultos con Diabetes Tipo 2. Rev Horizonte sanitario [Internet]. 2022 [citado 03 Jun 2022];21(2):276-81. Disponible en: https://revistas.ujat.mx/index.php/horizonte/article/view/3885/3734
30. Alfaro Mauricio JG. Calidad de la Atención Farmacéutica y adherencia al tratamiento en pacientes diabéticos. Hospital I La Esperanza EsSalud. Trujillo, 2021 [tesis]. Trujillo: Universidad Cesar Vallejo; 2022 [citado 03 Jun 2022]. Disponible en: https://repositorio.ucv.edu.pe/bitstream/handle/20.500.12692/86966/Alfaro_MJG-SD.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Alfredo Hernández-Magdariaga, Naifi Hierrezuelo-Rojas, Suniel Johnson-Valenciano, Lourdes Marbelys Ferrera-Velázquez, Marileydis Avila-Vazquez

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025