Tomographic characterization of membranes in patients with chronic subdural hematoma
Abstract
Introduction: Chronic subdural hematoma is a hematoma encapsulated by two internal and external membranes. There are different imaging classifications that include the characteristics of these lesions, but the presence of the membranes and their characteristics is a little described aspect.
Objective: To describe the tomographic characteristics of the membranes of chronic subdural hematomas.
Methods: A descriptive study was carried out in the Neurosurgery service in conjunction with the Imaging service of the Manuel Ascunce Domenech University Hospital during the year 2021. 20 adult patients who underwent surgery with the diagnosis of chronic subdural hematoma were included. The membranes were characterized according to their density, thickness, number of layers, morphology and extension.
Results: Male patients over 65 years of age predominated, with more frequent unilateral hematomas on the left side. The average volume was 150 ml and the diameter was 3 cm. Thin, hyperdense, incomplete, single-layer membranes were more frequent, and the morphology was variable.
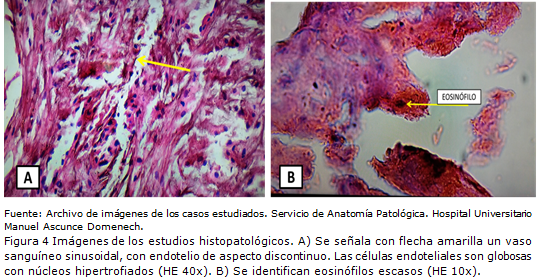
Conclusions: The membranes that make up the chronic subdural hematoma can be seen on computerized axial tomography. Different types of membranes have been found according to their density, thickness, morphology, extension and presence of septa. The presence of a thick or thin membrane with septa may indicate a craniotomy that allows careful resection of the parietal membrane and sufficient opening of the visceral membrane to facilitate brain re-expansion and reduce the incidence of recollections.
DeCS: MEMBRANES/physiopathology; HEMATOMA, SUBDURAL, CHRONIC; TOMOGRAPHY, SPIRAL COMPUTED; HEMATOMA, SUBDURAL, INTRACRANIAL; AGED.
Downloads
References
1. Altaf I, Shams S, Vohra AH. Radiological predictors of recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma. Pak J Med Sci [Internet]. 2018 Ene-Feb [citado 11 Ene 2021];34(1):194-197. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5857011/
2. Shim YW, Lee WH, Lee KS, Kim ST, Paeng SH, Pyo SY. Burr Hole Drainage versus Small Craniotomy of Chronic Subdural Hematomas. Korean J Neurotrauma [Internet]. 2019 Oct [citado 11 Ene 2021];15(2):110-116. Disponible en: https://europepmc.org/article/pmc/6826100
3. Bender MB, Christoff N. Nonsurgical treatment of subdural hematomas. Arch Neurol. 1974 Ago; 31(2): 73-9.
4. Rojas Quiñones MX, Gómez Vega JC. Hematoma subdural crónico. Una actualización y revisión. Universitas Médica [Internet]. 2021 [citado 13 Nov 2020];62(3). Disponible en: https://revistas.javeriana.edu.co/index.php/vnimedica/article/view/33384
5. Wong-Achi X, Cabrera D. Patogénesis y fisiopatología del hematoma subdural crónico. Rev Mex Neurociencia [Internet]. 2016 Jul-Ago [citado 13 Feb 2021];17(4):78-85. Disponible en: https://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/revmexneu/rmn-2016/rmn164i.pdf
6. Vacca VM, Argento I. Hematoma subdural crónico: una complicación frecuente. Nursing. 2019 Ene-Feb; 36(1): 16-23.
7. Zhu F, Wang H, Li W, Han S, Yuan J, Zhang C, et al. Factors correlated with the postoperative recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma: An umbrella study of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Eclinicalmedicine [Internet]. 2021 Dic [citado 13 Nov 2020];43:1011234. Disponible en: https://europepmc.org/article/med/34988412
8. Lee KS. History of Chronic Subdural Hematoma. Korean J Neurotrauma [Internet]. 2015 Oct [citado 14 Mar 2021];11(2):27-34. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4847516/
9. Lee KS. Chronic Subdural Hematoma in the Aged, Trauma or Degeneration? J Korean Neurosurg Soc [Internet]. 2016 Ene [citado 04 Mar 2021];59(1):1-5. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4754581/
10. Prinzo Yamurri H, Wilson E, Aboal C. Complicaciones intracraneanas en la cirugía del hematoma subdural crónico. Arch Inst Neurol. 2006 Ene-Jun; 9(1).
11. Shlobin NA, Kedda J, Wishart D, Garcia RM, Rosseau G. Surgical Management of Chronic Subdural Hematoma in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci [Internet]. 2021 Jul [citado 17 Nov 2020];76(8):1454-62. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33220683/
12. Nakaguchi H, Tanishima T, Yoshimasu N. Factors in the natural history of chronic subdural hematomas that influence their postoperative recurrence. J Neurosurg [Internet]. 2001 Ago [citado 14 Mar 2021];95(2):256-62. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11780895/
13. Petrov A, Ivanov A, Rozhchenko L, Petrova A, Bhogal P, Cimpoca A, et al. Endovascular Treatment of Chronic Subdural Hematomas through Embolization. A Pilot Study with a Non-Adhesive Liquid Embolic Agent of Minimal Viscosity (Squid). J Clin Med [Internet]. 2021 Oct [citado 17 Nov 2020];10(19):4436. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8509410/
14. Russell JBW, Baryoh MBL, Conteh V, Gordon-Harris L, Radcliffe Lisk D. Outcoms of craniotomies for chronic subdural hematoma in Sierra Leone. Pan Afr Med J [Internet]. 2021 [citado 17 Nov 2020];38:80. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8033179/
15. Song P, Li Z, Ke Y, Wang W, Wei H, Ji B, et al. A novel imaging classification system for the neuroendoscopic treatment of chronic subdural hematoma. Am J Transi Res [Internet]. 2021 [citado 12 Nov 2020];13(11):12235-48. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8661176/
16. Castro-Rodríguez C, Román-Pena P, Arán-Echabe E, Gelabert-González M. Hematoma subdural crónico en pacientes muy ancianos. Rev Esp Geriatr Geront [Internet]. 2016 Nov-Dic [citado 14 Mar 2021];51(6):309-316. Disponible en: https://www.elsevier.es/es-revista-revista-espanola-geriatria-gerontologia-124-articulo-hematoma-subdural-cronico-pacientes-muy-S0211139X16300464
17. Shen J, Xin W, Li Q, Gao Y, Zhang J. A Grading System For The Prediction Of Unilateral Chronic Subdural Hematoma Recurrence After Initial Single Burr Hole Evacuation. Risk Manag Healthc Policy [Internet]. 2019 [citado 14 Mar 2021];12:179-88. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6830374/
18. Du B, Xu J, Hu J, Zhong X, Liang J, Lei P, et al. A Clinical Study of the Intra- Neuroendoscopic Technique for the Treatment of Subacute–Chronic and Chronic Septal Subdural Hematoma. Front Neurol [Internet]. 2019 [citado 14 Abr 2021];10:1408. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6979069/
19. Pan Z, Bao J, Wei S, Efficay of the Direct Aspiration-Irrigation Maneuver for the Treatment of Chronic Subdural Hematoma: A Single Hospital´s Experience. Cureus [Internet]. 2021 [citado 12 Nov 2020];13(7):e16231. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8262522/
20. Kung WM, Lin MS. CT Based Quantitative Analysis for Pathological Features Associated With Postoperative Recurrence and Potential Application Upon Artificial Intelligence. A Narrative Review With a Focus on Chronic Subdural Hematomas. Mol Imaging [Internet]. 2020 Ene-Dic [citado 14 Abr 2021];19:1536012120914773. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7290264/
21. Kim HC, Ko JH, Yoo DS, Lee SK. Spontaneous Resolution of Chronic Subdural Hematoma: Close Observation as a Treatment Strategy. J Korean Neurosurg Soc [Internet]. 2016 Nov [citado 14 Abr 2021];59(6):628-36. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27847578/
22. Martínez F, Mañana G, Panuncio A, Laza S. Revisión anatomo-clínica de las meninges y espacios intracraneanos con especial referencia al hematoma subdural crónico. Rev Mex Neurociencia [Internet]. 2008 [citado 14 Abr 2021];9(1):47-60. Disponible en: https://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/revmexneu/rmn-2008/rmn081h.pdf
23. Sahyouni R, Mahboubi H, Tran P, Roufail JS, Chen JW. Membranectomy in Chronic Subdural Hematoma: a Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg [Internet]. 2017 Ago [citado 14 Abr 2021];104:418-29. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5541138/
24. Lizana Toledo JC, Aliaga S? nchez NI, Basurco Carpio A. Hematoma subdural crónico: una patología común de manejo complejo. Rev Argent Neuroc [Internet]. 2021 [citado 10 Ene 2022];35(2):124-39. Disponible en: https://rane.com.ar/index.php/revista article/view/152/230
25. Balevi M. Organized Chronic Subdural Hematomas Treated by Large Craniotomy with Extended Membranectomy as the Initial Treatment. Asian J Neurosurg [Internet]. 2017 Oct-Dic [citado 10 Ene 2022];12(4):598-604. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5652083/
26. Sahyouni R, Goshtasbi K, Mahmoodi A, Tran DK, Chen JW. Chronic Subdural Hematoma: A Perspective on Subdural Membranes and Dementia. World Neurosurg [Internet]. 2017 Dic [citado 10 Ene 2022];108:954-58. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28935547/
27. Algorta M, Spagnuolo E. Hematoma subdural crónico. Modalidades de tratamiento revisión del tema. Propuesta de manejo. Rev argent neurocir [Internet]. 2010 Oct-Dic [citado 10 Ene 2022];24(4). Disponible en: https://aanc.org.ar/ranc/items/show/306
28. Majovsky M, Netuka D, Benes V, Kucera P. Burr-Hole Evacuation of Chronic Subdural Hematoma: Biophysically and Evidence–Based Technique Improvement. J Neurosci Rural Pract [Internet]. 2019 Ene-Mar [citado 10 Ene 2022];10(1):113-118. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6337972/
29. Rovlias A, Theodoropoulos S, Papoutsakis D. Chronic subdural hematoma: Surgical management and outcome in 986 cases: A classification and regression tree approach. Surg Neurol Internat [Internet]. 2015 Jul [citado 10 Ene 2022];6:127. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26257985/
30. Varela Hernández A, Peñones Montero R, Silva Adán S, Pardo Camacho G, Mosquera Betancourt G, Medrano García R. Valor de la membranectomía parietal radical en el tratamiento de hematoma subdural crónico traumático del adulto. Rev cubana neurol neurocir [Internet]. 2011 [citado 10 Ene 2022];1(1):15-20. Disponible en: http://www.revneuro.sld.cu/index.php/neu/article/view/10/7
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Gretel Mosquera-Betancourt, Rogers Téllez-Isla, Jorge Fuentes-Chávez, Elizabet Ramírez-Reyes, Yudenia Toledo-Cabarcos

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025