Orthodontic surgical treatment in a patient with maxillary impacted canine teeth
Abstract
Introduction: Orthodontic surgical treatment could be a therapy of choice for the impacted canines, as they should be kept in the dental arches for their functional and aesthetic benefits. The bilateral impaction of these in the maxillary bone is less frequent and their treatment is more complex.
Objective: To describe the results of the orthodontic surgical treatment in a female patient with bilateral impaction of upper canines.
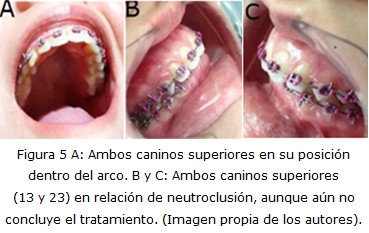
Case report: A 16-year-old female patient with a health history was assisted by a general dentist in the company of the mother, because she was worried about the aspect of her cupids which were whiter and littler. The oral examination showed the presence of a permanent and complete dentition with the exception of the upper canines, in their place, were teeth number 53 and 63. It was also found an abnormal relief in the anterior zone of the hard palate with a slight increase of volume at palpation. It was taken panoramic and periapical X-ray and it was confirmed the presence of both impacted teeth. It was made orthodontic surgical treatment.
Conclusions: Orthodontic surgical treatment gave back the patient the function and aesthetic by means of the correct location of both teeth in the dental arches.
DeCS: CUSPID/surgery; TOOTH MOVEMENT TECHNIQUES; TOOTH; ORTHODONTICS/methods; ESTHETICS, DENTAL.
Downloads
References
1. Noorollahian S, Shirban F. Chair time saving method for treatment of an impacted maxillary central incisor with 15 month follow up. Dent Res J [Internet]. 2018 Mar [citado 10 Jun 2020];15(2): 150-154. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5858075/.
2. Ivanović D, Tomić S, Davidović L, Nogo-Živanović D, Ivanović T. Combined orthodontic-surgical approach in the treatment of impacted upper canines. Serbian Dental Journal [Internet]. 2019 [citado 10 Mar 2020];66(4): 196-200. Disponible en: http://scindeks-clanci.ceon.rs/data/pdf/0039-1743/2019/0039-17431904196I.pdf
3. Corrales León AL, Serrano Corrales A, Martínez Rodríguez M, Serrano Corrales A, Serrano Corrales A. Tratamiento ortodóncico-quirúrgico de caninos retenidos en paciente de 14 años. Rev cienc méd Pinar Rio [Internet]. 2018 [citado 09 Jul 2020];22(5). Disponible en: http://revcmpinar.sld.cu/index.php/publicaciones/article/view/3456/html
4. Mello de Oliveira I, Dal Bello Figueiras R, Faria Ribeiro Castro RC. Simplified treatment for impacted upper canines: a four-year follow-up. Rev Gaúch Odontol [Internet]. 2017 Ene-Mar [citado 09 Jun 2020];65(1). Disponible en: https://www.scielo.br/j/rgo/a/bBsz4HP6WgHhLPqXkkL5jbp/?lang=en
5. Premkumar S, SFs S, Tovani-Palone MR. Management of impacted maxillary canines: a case report. Electron J Gen Med [Internet]. 2019 [citado 09 Jun 2020];16(5):1-10. Disponible en: https://www.ejgm.co.uk/download/management-of-impacted-maxillary-canines-a-case-report-7558.pdf
6. Abu-Hussein M, Watted N, Feştila D, Borbély P. Surgical-Orthodontic Treatment of Impacted Canines. IOSR-JDMS [Internet]. 2015 Oct [citado 20 Jun 2020];14(10):97-104. Disponible en: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/283119259_Surgical-Orthodontic_Treatment_of_Impacted_Canines_Abu-Hussein_Muhamad_68_PUBLICATIONS_2_CITATIONS_Surgical-Orthodontic_Treatment_of_Impacted_Canines
7. Negi A, Murali G. Orthodontic - surgical management of impacted maxillary canines using tunnel traction technique. Annals Dental Specialty [Internet]. 2018 Oct-Dic [citado 09 Abr 2020]; 6(4): 455-458. Disponible en: https://annalsofdentalspecialty.net.in/storage/models/article/nDbxiBnrmmTD1hfQIpCSuFmN3AQ1LUjWs0Cdj4UwLSFL2t2Hg5JE7c9eGkLn/orthodontic-surgical-management-of-impacted-maxillary-canines-using-tunnel-traction-technique.pdf
8. Spuntarelli M, Cecchetti F, Arcuri L, Testi D, Melone P, Bigelli E, et al. Combined orthodontic-surgical approach in the treatment of impacted maxillary canines: three clinical cases. Oral Implantol (Rome) [Internet]. 2015 Abr-Sep [citado 23 Jun 2020];8(2-3): 63-67. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4969730/.
9. Estrada Manilla A, Katagiri Katagiri M. Tratamiento ortodóntico-quirúrgico de incisivo central impactado. Rev Mex Ortod [Internet]. 2017 Jul-Sep [citado 09 Jul 2020];5(3). Disponible en: http://revistas.unam.mx/index.php/rmo/article/view/62360
10. Cavuoti S, Matarese G, Isola G, Abdolreza J, Femiano F, Perillo L. Combined orthodontic –surgical management of a transmigrated mandibular canine. Angle Othod [Internet]. 2016 Jul [citado 01 Jul 2020];86(4):681-691. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8601488/.
11. Peña Raza CP, Estrada Macías AL, Ortiz Sánchez D. Métodos para tracción de dientes incluidos. Reporte de casos. Rev Latinoam Ortod Odontoped [Internet]. 2017 [citado 01 Jul 2020]. Disponible en: https://www.ortodoncia.ws/publicaciones/2017/art-43/.
12. Mummolo S, Nota A, De Felice ME, Marcattili D, Tecco S, Marzo G. Periodontal status of buccally and palatally impacted maxillary canines after surgical-orthodontic treatment with open technique. J Oral Sci. 2018 Dic;60(4):552-556. doi: 10.2334/josnusd.17-0394.
13. Ferguson DJ, AL Rossais D, Wilcko MT, Makki L, Stapelberg R. Forced-eruption time for palatally impacted canines treated with and without ostectomy-decortication technique. Angle Orthod [Internet]. 2019 Sep [citado 17 Jul 2020];89(5):697-704. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8111832/.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Yojander López-Gómez, Mariley Rodríguez-Acosta, Bárbara Liliet León-Arteaga, María Teresa Velázquez-Méndez

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025