Mixofibrosarcoma de partes blandas: a propósito de un caso
Keywords:
TPB- Tumor de partes blandas RA- Resección amplia SPB- sarcoma de partes blandas IRM- Imagen de resonancia magnéticaAbstract
Background: soft tissue sarcomas are frequent lesions today and can affect a large number of patients at any age, their histological types are very varied hence the clinical behavior of these entities.
Objective: to present a patient with myxofibrosarcoma in the anterior region of the right knee.
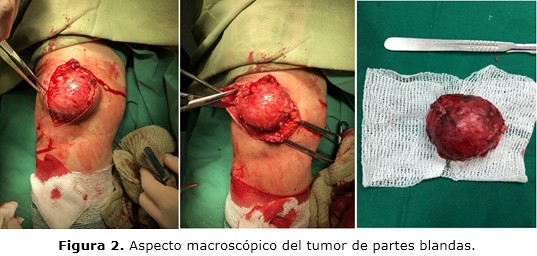
Case report: 56-year-old white woman with a history of essential arterial hypertension, who goes to the outpatient department of Orthopedics and Traumatology for referring to having a tumor in the anterior part of the right knee that is accompanied by slight pain and functional disability. It appeared two years ago, but it has increased its size rapidly in the last three months. Taking into account all the previous elements, it was decided to take the patient to the operating room, for surgical treatment, where the tumor described above was removed surgically through the surrounding healthy tissue with safety margin, the piece was sent to the department of pathological anatomy for histological study, which later reported a tumor of myxofibrosarcoma type.
Conclusions: myxofibrosarcoma is a malignant lesion that is located in the lower limb of slow growth with absence of pain, the imaging means provide very important information for its diagnosis, specifically high resolution ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging. Timely surgical treatment through extensive resection improves the prognosis.
DeCS: KNEE/diagnostic imaging; SOFT TISSUE NEOPLASMS/surgery; SARCOMA/diagnostic imaging; SARCOMA/surgery; CASE REPORT.
Downloads
References
1. Callegaro D, Miceli R, Bonvalot S, Ferguson P, Strauss DC, Levy A, et al. Impact of perioperative chemotherapy and radiotherapy in patients with primary extremity soft tissue sarcoma: retrospective analysis across major histological subtypes and major reference centres. Eur J Cancer [Internet]. 2018 Dec [citado 20 Ene 2020];105:19-27. Disponible en:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0959804918313984?via%3Dihub
2. Widemann BC, Italiano A. Biology and management of undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma, myxofibrosarcoma, and malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors: state of the art and perspectives. J Clin Oncol [Internet]. 2018 [citado 20 Ene 2020];36(2):160-7. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5759316/.
3. Roland CL, Wang WL, Lazar AJ, Torres KE. Myxofibrosarcoma. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2016;25(4):775-88. doi: 10.1016/j.soc.2016.05.008
4. Hu Q, Zhou S, Hu X, Zhang H, Huang S, Wang Y. Systematic screening identifies a 2-gene signature as a high-potential prognostic marker of undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma/myxofibrosarcoma. J Cell Mol Med [Internet]. 2020 [citado 20 Ene 2020];24(1):1010-21. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6933343/. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14814
5. Tjarks BJ, Ko JS, Billings SD. Myxofibrosarcoma of unusual sites. J Cutan Pathol. 2018 Feb;45(2):104-10. doi: 10.1111/cup.13063.
6. Ogura K, Hosoda F, Arai Y, Nakamura H, Hama N, Totoki Y, et al. Integrated genetic and epigenetic analysis of myxofibrosarcoma. Nat Commun. 2018 Jul;9(1):2765. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03891-9
7. Kikuta K, Nakayama R, Yamaguchi S, Nishiwaki Y, Susa M, Nishimoto K, et al.
Wide-spread ignorance on the treatment of subcutaneous malignant tumors; a questionnaire-based study. Jpn J Clin Oncol [Internet]. 2018 Feb [citado 20 Ene 2020];48(2):130-4. Disponible en: https://academic.oup.com/jjco/article/48/2/130/4774981 doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyx184
8. Mizuno T, Susa M, Horiuchi K, Shimazaki H, Nakanishi K, Chiba K. Spontaneous regression of myxofibrosarcoma of the thigh after open biopsy. Case Rep Oncol [Internet]. 2019 [citado 20 Ene 2020];12(2):364-9. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6547297/. doi: 10.1159/000500504
9. Mühlhofer HML, Lenze U, Gersing A, Lallinger V, Burgkart R, Obermeier A, et al. Prognostic factors and outcomes for patients with myxofibrosarcoma: a 13-year
retrospective evaluation. Anticancer Res. 2019 Jun;39(6):2985-92. doi:10.21873/anticanres.13430
10. Song B, Lee K, Lee C, Moon KC. Prognostic significance of microscopic tumor extension in local recurrence of myxofibrosarcoma and undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma. Pathol Int. 2018 Sep;68(9):509-16. doi: 10.1111/pin.12709.
11. Yoshimoto M, Yamada Y, Ishihara S, Kohashi K, Toda Y, Ito Y, et al. Comparative study of myxofibrosarcoma with undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma: histopathologic and clinicopathologic review. Am J Surg Pathol. 2020 Jan;44(1):87-97. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000001389.
12. Sambri A, Spinnato P, Bazzocchi A, Tuzzato GM, Donati D, Bianchi G. Does pre-operative MRI predict the risk of local recurrence in primary myxofibrosarcoma of the extremities? Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2019 Oct;15(5):e181-e186. doi: 10.1111/ajco.13161.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Alejandro Alvarez-López, Rodrigo Fuentes-Véjar, Sergio Ricardo Soto-Carrasco, Yenima de la Caridad García-Lorenzo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025