External fixation in Schatzker J´s type VI tibial plateau fracture
Keywords:
FMT- Fractura de meseta tibial FE- Fijación externa FA- Fracturas abiertasAbstract
Background: tibial plateau fractures are common traumatic lesions due to vertical compression in varus and valgus. That is why open fractures associated to skin loss are not so frequent, because they are caused by direct mechanisms.
Objective: to show a patient with an open tibial plateau fractures type VI according to Schatzker J classification system.
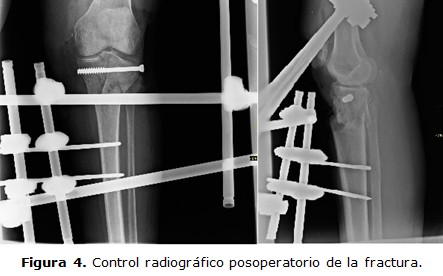
Case report: a 61 year old mixed race, woman without health morbid antecedents, who after having a traffic accident was taken to emergency room of Orthopedics and Traumatology complaining of pain, swelling and limitation of movement of the left knee and leg. Simple imaging examination in antero-posterior and lateral views showed a structural break in the continuity of bone at epiphysis and metaphysis in the left proximal tibia. Definite treatment consisted of an osteosynthesis with cannulated screw and fixation by an external device type Hoffmann 1 with two pins in femur and tibia respectively.
Conclusions: tibial plateau fractures type VI according to Schatzker J classification system are difficult to treat because of associated lesions and complications as open fractures and skin loss. External fixation is a useful and easy method to fix complex fractures as tibial plateau fractures.
DeCS: TIBIAL FRACTURES/surgery; TIBIAL MENISCUS INJURIES/therapy; FRACTURES, COMPRESSION; FRACTURES, OPEN; EXTERNAL FIXATORS.
Downloads
References
1. Egol KA, Koval KJ, Zuckerman JD. Handbook of fractures. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2015.
2. Kateros K, Galanakos SP, Kyriakopoulos G, Papadakis SA, Macheras GA. Complex tibial plateau fractures treated by hybrid external fixation system: a correlation of follow up computed tomography derived quality of reduction with clinical results. Indian J Orthop. 2018 Mar-Apr;52(2):161-9.
3. Prat-Fabregat S, Camacho-Carrasco P. Treatment strategy for tibial plateau fractures: an update. EFORT Open Rev. 2017 Mar;1(5):225-32.
4. Marsh JL, Karam MD. Tibial plateau fractures. En: Court Brown CM, Heckman JD, McQueen MM, Ricci WM, Tornetta P III, editors. Rockwood and Green's Fractures in Adults. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2015.p.2303-67.
5. Ricci WM, Metha S. Tibial plateau fractures and extensor mechanism injuries. En: Cannada LK, editor. Orthopaedic Knowledge Update 11. Rosemont: Am Acad Orthop Surg; 2014.p.521-36.
6. Metcalfe D, Hickson CJ, McKee L, Griffin XL. External versus internal fixation for bicondylar tibial plateau fractures: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Traumatol. 2015 Dec;16(4):275-85.
7. Schatzker J, McBroom R, Bruce D. The tibial plateau fracture. The Toronto experience 1968-1975. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979 Jan-Feb;(138):94-104.
8. Debnath UK, Jha DK, Pujari PK. Results of ring (Ilizarov) fixator in high energy Schatzker type VI fractures of proximal tibia. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2018 Apr-Jun;9(2):186-91.
9. Liskutin T, Bernstein M, Lack W, Perry M, Summers H. Surgical technique: achieving reduction with temporizing, knee-spanning external fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2018 Aug;32 Suppl 1:S32-S33.
10. Gustilo RB, Anderson JT. JSBS classics. Prevention of infection in the treatment of one thousand and twenty-five open fractures of long bones. Retrospective and prospective analyses. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002 Apr;84-A(4):682.
11. Bertrand ML, Pascual-López FJ, Guerado E. Severe tibial plateau fractures (Schatzker V-VI): open reduction and internal fixation versus hybrid external fixation. Injury. 2017 Nov;48 Suppl 6:S81-S85.
12. Perumal VM, Mauffrey C, Roberts CS. External fixators in the treatment of tibial plateau fractures. En: Seligson D, editor. External Fixation In Orthopaedic Traumatology. London: Springer Verlag; 2002.p.121-9.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2020 Alejandro Alvarez-López, Rodrigo Fuentes-Véjar, Sergio Ricardo Soto-Carrasco, Yenima de la Caridad García-Lorenzo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025