Didactic alternative to stimulate the creative thinking of teachers and students
Keywords:
INFERENCIA ESTADÍSTICA, PENSAMIENTO CREATIVO, APRENDIZAJEAbstract
Background: constantly update the methods, procedures and ways to solve problems, whose solutions constitute stereotypes of the inferential statistics, which do not stimulate the creative thinking of teachers and students in general.
Objective: to illustrate, through the resolution of problems of inferential statistics, how to stimulate the creative thinking of the Biostatistics professors and the students of the Medicine degree.
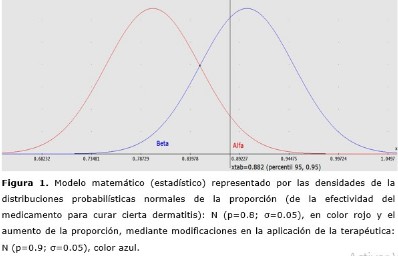
Methods: the theoretical methods used are analysis-synthesis, induction-deduction and abstraction-concretion. Construction of curves of the normal distribution, comprehension processes, explanation and interpretation. Mathematical and statistical methods, procedures and algorithms are applied.
Results: a didactic alternative is elaborated to stimulate the creative thought of the professors and students of the Medicine degree, which illustrates the importance of the topic: Introduction to the statistical inference. Concepts of random variable, normal distribution, probability, acceptance domain, rejection domain, point estimates, among others, are integrated and systematized.
Conclusions: health situations are created to be faced by the General Practitioner in his professional work that evidences the needs to interpret the errors of first and second gender: α and β. The knowledge and skills related to the concepts addressed in the subject are consolidated: Introduction to Inferential Statistics, through professional computer programs visualize the results achieved, according to modeling and mathematical simulation.
DeCS: CREATIVITY; STUDENTS, MEDICAL; FACULTY; HEALTH STATISTICS; TEACHING MATERIALS.
Downloads
References
1. MINSAP. Perfeccionamiento del plan de estudio D de la Carrera de Medicina. La Habana: MINSAP; 2016.
2. Centro de Cibernética Aplicada a la Medicina. Informática Médica: Bioestatística. T. II. La Habana: Ciencias Médicas; 2004.
3. De la Horra J. Estadística Aplicada [Internet]. Madrid, España: Editorial Díaz de Santos S.A; 2012 [citado 28 Mar 2018]. Disponible en: https://estadisticaunicaes.files.wordpress.com/2012/05/uned-estadc3adstica-aplicada-julic3a1n-de-la-horra.pdf
4. Efímov A, Korakulin P, Pospélov P, Teréschenko A, Vokólov E, Zemskov V, et al. Problemas de las Matemáticas Superiores. Moscú: Editorial Mir; 2014.
5. Koroliuk V. Manual de la teoría de probabilidades y estadística matemática. Moscú: Editorial Mir; 2016.
6. Fardales Macías V, Diéguez Batista R, Puga García A. Una aproximación a las concepciones que prevalecen en la formación estadística del profesional médico. MediSur [Internet]. 2014 [citado 16 Jun 2016];12(1):[aprox. 9 p.]. Disponible en:
http://www.medisur.sld.cu/index.php/medisur/article/view/2270/1439
7. Calero Hechavarría M, Rodríguez Corona O, Armas Pupo YR, Núñez Rojas Y. Propuesta de tareas docentes para fortalecer el proceso de enseñanza-aprendizaje de la Metodología de la Investigación. CCM [Internet]. 2013 [citado 16 Jun 2016];(1)Supl 1:[aprox. 11 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.revcocmed.sld.cu/index.php/cocmed/article/view/1265/306
8. Swift L, Miles S, Price GM, Shepstone L, Leinster SJ. Do doctors need statistics? Doctors´ use of and attitudes to probability and statistics. Stat Med. 2009;28(15):1969-81.
9. Tavares Paes A. Teaching statistics to physicians: a five-years experience. ICOTS 8. Brasil: Universidade Federal de São Paulo, Instituto Israelita de Ensino e Pesquisa Albert Einstein; 2010 [citado 16 Jun 2016]. Disponible en:
http://iase-web.org/documents/papers/icots8/ICOTS8_10F4_PAES.pdf
10. Herman A, Notzer N, Libman Z, Braunstein R, Steinberg DM. Author ́s Reply: Statistical education for medical students-Concepts are what remain when the details are forgotten. Stat Med. 2008;27(12):2267-72.
11. Numa M, Martín A, Diéguez R, Sánchez A. La formación estadística universitaria orientada a la solución de problemas profesionales. Pedag Univ [Internet]. 2014 [citado 22 Feb 2018];19(1):[aprox. 17 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.cvi.mes.edu/peduniv /index.php/pedu niv
12. Infante Y, Bayés E. Propuesta de un folleto de ejercicios de Bioestadística. Medisan [Internet]. 2016 [citado 2018 Sep 3];20(12):[aprox. 7 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.medisan.sld.cu/index.php/san/article/view/167
13. Zimmermann W, Cunningham S. Visualization in Teaching and Learning Mathematics. Washington: Mathematical Association of America Washington; 1991.
14. Olmedo Canchola VH, Ariza Andraca R. Matemáticas en medicina: una necesidad de capacitación. Med Int Méx [Internet]. 2012 [citado 22 Feb 2018];28(3):[aprox. 4 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/medintmex/mim-2012/mim123l.pdf
15. Lipkus IM, Peters E. Understanding the role of numeracy in health: proposed theoretical framework and practical insights. Health Educ Behav. 2009;36(6):1065-1081.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2019 Luis Alberto Escalona-Fernández, Silvia María Pérez-Pérez

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025