Clinical pathological characteristics of the lupus nephritis
Keywords:
Lupus eritematoso sistémico, nefritis, insuficiencia renal crónica, nefritis lúpica.Abstract
Background: the lupus nephritis is a frequent and serious complication associated to the systemic lupus erythematosus.
Objective: to characterize the lupus nephritis in the nephrology service of the University Hospital Manuel Ascunce Domenech.
Methods: a descriptive, transverse and retrospective study was carried out in the Hospital Manuel Ascunce Domenech of Camagüey from January, 2012 to December, 2017. The universe was constituted for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. As source clinical charts and forms made to empty data were used. The universe was constituted by all the patients with lupus nephritis whose biopsy was useful for the diagnosis. The variables were: age, sex, race, diagnosis criteria, histopathological stage, complications of the illness and noxious effects related with the treatment.
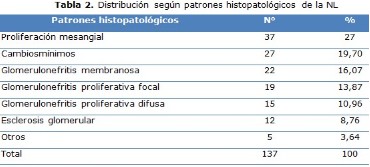
Results: was found that four of each ten patients were between the 30 and the 44 years, while six of each ten were women. The fourth part of the sample was of the white race. The renal, cutaneous and hematologic approaches prevailed in the patients in that order. The histopathological patterns observed were the mesangial proliferation, the minimum changes and the membranous glomerulonephritis. The most frequent complications that were presented were the nephrotic syndrome and the chronic renal failure. The great majority of the studied patients presented as noxious effects of the treatment infections and cardiovascular manifestations.
Conclusions: it is more frequent between 30 to 44 years, in women and in the white race. It is presented more as Nephrotic syndrome and chronic renal failure. The histopathological pattern more observed: the mesangial proliferation, minimum changes and membranous glomerulonephritis.
DeCS: LUPUS NEPHRITIS/pathology; LUPUS NEPHRITIS/complications; NEPHROTIC SYNDROME/complications; RENAL INSUFFICIENCY, CHRONIC/complications; EPIDEMIOLOGY, DESCRIPTIVE.
Downloads
References
1. Bermúdes Marrero WM, Vizcaino Luna Y, Bermúdes Marrero WA. Lupus Eritematosos sistémico. Acta Méd Centro [Internet]. 2017 [citado 13 Dic 2018];11(1):[aprox. 14 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.revactamedicacentro.sld.cu/index.php/amc/article/view/795
2. Vaca Sánchez RM. Prevalencia de la presentación clínico-patológica de la nefropatía lúpica en pacientes que han acudido al servicio de Nefrología del Hospital Carlos Andrade Marín, Quito, de enero 2011 a diciembre 2015 [tesis]. Quito: Universidad Central de Ecuador; 2016 [citado 13 Dic 2018]. Disponible en: http://www.dspace.uce.edu.ec/bitstream/25000/11250/1/T-UCE-0006-011-2016.pdf
3. Polanco Flores NA, Soto Abraham MV, Rodríguez Castellanos FE. Presentación clínico-patológica de la nefropatía lúpica: experiencia de un centro mexicano. Rev Colomb Reumatol [Internet]. 2013 [citado 13 Dic 2018];20(2):[aprox. 3 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.co/scielo.php?pid=S0121-81232013000200002&script=sci_arttext&tlng=pt
4. Basu N, Watts R, Bajema I. EULAR points to consider in the development of classification and diagnostic criteria in systemic vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(10):1744-50.
5. Kallenberg CGM. Pathophysiology of ANCA-associated small vessel vasculitis. CurrRheumatol Rep. 2010;12:399-405.
6. Bacallao Méndez RA, López Marín L, LLerena Ferrer B, Heras Mederos A, Dávalos Iglesias JM, Gutiérrez García F, et al. Experiencia de 20 años en biopsia renal percutánea en adultos del Instituto de Nefrología. Rev Cubana Invest Bioméd [Internet]. Jul-Sept 2015 [citado 13 Dic 2018];34(3):[aprox. 3 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0864-03002015000300002
7. Pinto Peñaranda LF, Castro Mercado IL, Duque Caballero V, Nárquez Hernández JD, Velásquez Franco CJ. Factores de riesgo predictores de falla a la terapia de inducción de nefritis lúpica en una cohorte de pacientes colombianos. Reumatol Clín [Internet]. May-Jun 2014 [citado 13 Dic 2018];10(3):[aprox. 5 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1699258X13002076
8. Rovin BH. Lupus nephritis: Guidelines for lupus nephritis-more recommendations than data? Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012;8:620-1.
9. Grech P, Khamashta M. Targeted therapies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2013;22:978-86.
10. Morris HK, Canetta PA, Appel GB. Impact of the ALMS and MAINTAIN trials on the management of lupus nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013;28(6):1371-1376.
11. Vozmediano C, Rivera F, Lopez-Gomez JM, Hernandez D. Risk factors for renal failure in patients with lupus nephritis: data from the Spanish Registry of Glomerulonephritis. Nephron Extra. 2012;2:269-77.
12. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Glomerulonephritis Work Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Glomerulonephritis. Lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 2012;2(Suppl 2):221-32.
13. Arnaud L, Fagot JP, Mathian A, Paita M, Fagot-Campagna A, Amoura Z. Prevalence and incidence of systemic lupus erythematosus in France: a 2010 nation-wide population-based study. Autoimmun Rev [Internet]. 2014 [citado 13 Dic 2018];13(11):[aprox. 8 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25172239
14. Rúa-Figueroa I, López-Longo FJ, Calvo-Alén J, Galindo-Izquierdo M, Loza E, García deYebenes MJ, et al. Registro nacional de pacientes con lupus eritematoso sistémico dela Sociedad Española de Reumatología: objetivos y metodología. Reumatol Clin [Internet]. 2014 [citado 25 Nov 2016];10(1):[aprox. 8 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.reumatologiaclinica.org/es/registro-nacional-pacientes-con-lupus/articulo/S1699258X13001071/.
15. Hahn BH, McMahon MA, Wilkinson A, Wallace WD, Dasikh DI, Fitzgerald JD, et al. American College of Rheumatology guidelines for screening, treatment, and management of lupus nephritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012;64(6):797-808.
16. Wang J, Kay AB, Fletcher J, Formica MK, McAlindon TE. Is lipstick associated with the development of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)? Clin Rheumatol [Internet]. 2008 [citado 15 Abr 2016];29(9):[aprox. 5 p.]. Disponible en: https://www .ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18523821
17. Grupo Latinoamericano de estudio del lupus (GLADEL). The GLADEL multinational Latin American prospective inception cohort of 1,214 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: ethnic and disease heterogeneity among "Hispanics". Medicine (Baltimore) [Internet]. Ene 2004 [citado 13 Dic 2018];83(1):[aprox. 17 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14747764
18. Seshan SV, Jennette JC. Renal disease in systemic lupus erythematosus with emphasis on classification of lupus glomerulonephritis: advances and implications. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2009;133:233-48.
19. Ruiz-Irastorza G, Espinosa G, Frutos MA, et al. Diagnóstico y tratamiento de la nefritis lúpica. Documento de consenso del Grupos de Enfermedades Autoinmunes Sistémicas de la Sociedad Española de Medicina Interna y de la Sociedad Española de Nefrología. Nephrology. 2012;32(Supl 1):1-35.
20. Mok CC. Epidemiology and survival of systemic lupus erythematosus in Hong Kong Chinese. Lupus. 2011;20:767-71.
21. Sandeep S. A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Presentation of Lupus Nephritis. Am J Med Sciences [Internet]. 2011 Dec [citado 13 Dic 2018];342(6):[aprox. 7 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21681076
22. Rahman A, Isenberg DA. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:929-39.
23. Ward M, Studenski S. Clinical manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Identification of racial and socioeconomic influences. Arch Intern Med [Internet]. 1990 Apr [citado 13 Dic 2018];150(4):[aprox. 5 p.]. Disponible en: https://ww w.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2327845
24. Ward MM. Recent Clinical Trials in Lupus Nephritis. Rheum Dis Clin N Am. 2014 Aug;40(3):519–35.
25. Pinto L, Senior J, Cerón J, Uribe O, Molina J, De la Cruz O, et al. Nefropatía Lúpica. Correlación clínico-patológica y respuesta al tratamiento con pulsos de ciclofosfamida. Acta Méd Colomb [Internet]. 1992 May [citado 13 Dic 2018];18(3):[aprox. 7 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.actamedicacolombiana.com/anexo/articulos/03-1993-07-Nefropatia_lupica.pdf
26. Ramos Casals M, Díaz Lagares C, Soto Cárdenas M, Brito Zeron P. Induction and maintenance therapy for lupus nephritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011 Jun;40(3):159-69.
27. Ruiz Irastorza G, Espinosa G, Frutos MA, Jiménez Alonso J, Praga M, Pallares L, et al. Diagnóstico y tratamiento de la nefritis lúpica. Nefrología [Internet]. 2012 Dec [citado 13 Dic 2018]; 32(Suppl 1) [aprox. 35 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.isciii.es/pdf/nefrologia/v32s1/guias_01.pdf
28. Crow MK. Lupus eritematoso sistémico. En: Goldman L, Schafer AI. Cecil y Goldman Tratado de medicina interna. 24 ed. España: Elsevier; 2012. p. 1701-1709.
29. Villa Blanco I, Calvo Alén J. Lupus Eritematoso Sistémico. En: Sociedad Española de Reumatología. Manual SER de las Enfermedades Reumáticas. 6ta ed. España: Elsevier; 2014. p. 335-347.
30. Lalani S. Clinical features and prognosis of late-onset systemic lupus erythematosus: results from the 1000 faces of lupus study. J Rheumatol. 2010: 37(1):38-44.
31. Vilardell Tarrés M, Ordi Ros J. Lupus eritematoso sistémico. En: Farreras Valentí P, Rozman C, Cardellach López F. Farreras-Rozman. Medicina interna. 17 ed. España: Elsevier;2012;V I. p. 1017-1022.
32. Bruce IN, O’Keeffe AG, Farewell V, Hanly JG, Manzi S, Su L, et al. Factors associated with damage accrual in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Results from the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics (SLICC). Inception Cohort. Ann Rheum Dis [Internet]. 2015 [citado 13 Dic 2018];74(9):[aprox. 8 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24834926
33. Zimmer HR, Scherbarth OL, Rillo JJ, Gomez Reino SM. Lupuzor/P140 peptide in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase iib clinical trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72:1830-5.
34. Wen Y. Renal biopsy findings in new-onset systemic lupus erythematosus with clinical renal disease. Int Urol Nephrol [Internet]. 2011 Sep [citado 13 Dic 2018];43(80):[aprox. 6 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21336956
35. Mosca M, Tani C, Aringer M. European League Against Rheumatism recommendations for monitoring patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in clinical practice and in observational studies. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:1269-1274.
36. Yasdany J, Panopalis P, Gillis J. A Quality Indicator Set for Systemic lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;61:370-377.
37. Ippolito A, Petri M. An update on mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2008;26:S72-79.
38. Hedrich CM. Early onset systemic lupus erythemathosus: differential diagnosis, clinical presentation and treatment options. Clinical Rheumatol. 2011;30(2):275-83.
39. Martínez-Godoy MP, Oliva-Gutiérrez E, Zapata-Zúñiga M, Sánchez-Rodríguez SH. Lupus eritematoso generalizado: características generales, inmunopatogenia y antígenos de relevancia. Arch Med [Internet]. 2012 [citado 15 Abr 2016];8(1:2):[aprox. 7 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.archivosdemedicina.com/medicina-de-familia/lupus-eritematoso-generalizado-caractersticas-generales-inmunopatogenia-y-antgenos-de-relevancia.pdf
40. Starkebaum GA. Lupus eritematoso sistémico [Internet]. 2016 [actualizado 16 Ene 2016; citado 7 Mar 2016]. Disponible en: https://medlineplus.gov/spanish/ency/article/000435.htm
41. Estévez del Toro M, Chico Capote A, Hechavarría R, Jiménez Paneque R, Kokuina E. Daño en pacientes cubanos con lupus eritematoso sistémico. Relación con características de la enfermedad. Reumatol Clin [Internet]. 2010 [citado 3 Dic 2018];6(1):[aprox. 5 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.reumatologiaclinica.org/es/dano- pacientes-cubanos-con-lupus/articulo/S1699258X09001569/.
42. Leyva de la Torres C. Nefritis Lúpica. En: Magrans Buch C, Llerena Ferrer B, Barranco Hernández E, Bacallao Méndez RA, Leyva de la Torres C, editores. Enfermedades Glomerulares. La Habana: Editorial Ciencias Médicas; 2017: p. 244-59.
43. Wallace DJ. Improving the prognosis of SLE without prescribing lupus drugs and the primary care paradox. Lupus. 2008;17(2):91.
44. Smith PP. Systemic lupus erythematosus: clinical presentations. Autoimmun Rev. 2010;10(1):43-5.
45. Bertsias G, Ionnidis JP, Boletis J, Bombardieri S, Cervera R, Dostal C, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Report of a Task Force of the European Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics (ESCISIT). Ann Rheum Dis [Internet]. 2008 [citado 12 Dic 2018];67(2):[aprox. 11 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17504841
46. Muñoz Grajales C, Pinto Peñaranda LF, Velásquez Franco CJ, Márquez Hernández JD, Restrepo Escobar M. Complicaciones infecciosas en lupus eritematoso sistémico. Rev Colomb Reumatol [Internet]. 2013 [citado 12 Dic 2018];20(3):[aprox. 7 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.sciencedirect.Com/science/article/pii/S0121812313701269
47. Vives Iglesias AE, Noda Ortega L. Fallo renal en un paciente con lupus eritematoso sistémico. Rev Cubana Med Gen Integr [Internet]. 2012 [citado 15 Dic 2018];28(3):[aprox. 11 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/pdf/mgi/v28n 3/mgi10312.pdf
48. Lateef A, Petri M. Unmet medical needs in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther [Internet]. 2012 [citado 13 Dic 2018];14(Suppl 4):[aprox. 2 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23281889
49. Izmirly PM, Buyon JP, Saxena A. Neonatal lupus: advances in understanding pathogenesis and identifying treatments of cardiac disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol [Internet]. 2012 [citado 13 Dic 2018];24(5):[aprox. 7 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22832822
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2019 Leonardo Alberto Curbelo-Rodríguez, Taimilkis León-Perón, Yadira Velazco-Oíz, Danay Nápoles-Ramírez

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025