Treatment of the mammary ptosis utilizing the technique of Liacyr Ribeiro type I modified
Abstract
Background: the mastopexy aims at repositioning the areole - nipple complex that has descended because of the decrease of the elastic capability of tissues and remodeling the remaining mamma, restructuring the glandular tissue and resecting the cutaneous secondary surplus.
Objective: to determine the mastopexy's esthetic results using Liacyr Ribeiro's technique peduncle type I modified by the author.
Methods: it was carried out a prospective, cross-sectional study about the application of the technique of mastopexy described by the professor Liacyr Ribeiro peduncle type I to which a modification was made by using for its design Wise's pattern, from January, 2014 to December, 2017. The sample was 24 patients with different grade of mammary ptosis, taken in a not-probabilistic form coinciding with the universe.
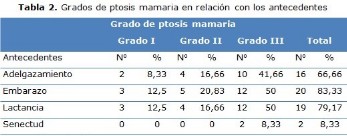
Results: the majority of the patient that underwent surgery had a grade 3 of mammary ptosis. Of the total of patients, the 5.85 % presented different grades of complications related to procedure. The 91.67 % was pleased with the procedure and the obtained results.
Conclusions: the mastopexy is a surgical procedure with high security levels, that achieves an important change in the patients' corporal image and produces great satisfaction in them.
DeCS: NIPPLES/surgery; MAMMAPLASTY; SURGICAL FLAPS; ELASTIC TISSUE/surgery; PROSPECTIVE STUDIES.
Downloads
References
1. Groyecka A, Żelaźniewicz A, Misiak M, Karwowski M, Sorokowski P. Breast shape (ptosis) as a marker of a woman's breast attractiveness and age: Evidence from Poland and Papua. Am J Hum Biol. 2017 Jul;29(4): doi: 10.1002/ajhb.22981
2. Moreno Gallent I, Ribera Pons M. Mastopexia y prótesis. Revisión a los 5 años. Cir plást iberolatinoam [Internet]. 2006 Jun [citado 10 Dic 2018];32(2):[aprox. 10 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sciarttext&pid=S0376-78922006000200005&lng=es
3. Qureshi AA, Myckatyn TM, Tenenbaum MM. Mastopexy and Mastopexy-Augmentation. Aesthet Surg J. 2018;38(4):374-384.
4. Arora G, Arora S. Thread Lift in Breast Ptosis. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2017 Oct-Dec;10(4):228-230.
5. Eyck BM, van Dongen JA, Athanassopoulos T, Martins JB, Stevens HP. Response to Why the Nipple is an Unreliable Marker for Measuring Breast Ptosis. Aesthet Surg J. 2017;37(2):1010-93.
6. Regnault P. Breast reduction and mastopexy, an old love story: B Technique update. Aesth Plast Surg. 1990;14(2):101-106.
7. Regnault P. Breast ptosis. Definition and treatment. Clin Plast Surg. 1976;3(2):193-203.
8. Rodríguez Salazar O. Variaciones al patrón de marcaje Wise en la cirugía estética mamaria por mínima incisión. Arch Med Camagüey [Internet]. 2012 Jun [citado 11 Dic 2018];16(3):[aprox. 4 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sciarttext&pid=S1025-0255201200 0300002&lng=es
9. Ribeiro L, Accorsi J, Buss A, Marcal-Pessoa M. Creation and evolution of 30 years of the inferior pedicle in reduction mammaplasties. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;110(3):960-70.
10. Ribeiro L. Pedículos em mamoplastia: atlas e texto. Rio de Janeiro: Guanabara Koogan;2005.
11. Kono T, Kusano T, Sato N, Yoshimoto S, Nakamura S. Natural mastopexy repositioning based on age-related mean breast shape. Asian J Surg. 2018 Jul;41(4):295-300.
12. de Vita R, Zoccali G, Buccheri EM. The Balcony Technique of Breast Augmentation and Inverted-T Mastopexy With an Inferior Dermoglandular Flap. Aesthet Surg J. 2017;37(10):1114-1123.
13. Cai J, Chen B, Zhou Y, Ma H. Correction of minor breast ptosis by subfascia breast augmentation with periareolar incision and anatomic mammary implant. Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014;30(3):175-8.
14. Wolter A, Scholz T, Pluto N, Diedrichson J, Arens-Landwehr A, Liebau J. Mastopexy in Massive Weight Loss Patients-Extended Ribeiro Technique and Usage of the Lateral Intercostal Artery Perforator Flap (LICAP Flap) for Autoaugmentation. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2017;49(6):380-389.
15. Coombs DM, Srivastava U, Amar D, Rubin JP, Gusenoff JA. The Challenges of Augmentation Mastopexy in the Massive Weight Loss Patient: Technical Considerations. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;139(5):1090-1099.
16. Ors S. Augmentation Mastopexy with a Dermal Encapsulated Round or Anatomic Autoprosthesis. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2018;42(1):88-97.
17. Ibrahim AM, Sinno HH, Izadpanah A, Vorstenbosch J, Dionisopoulos T, Markarian MK, et al. Mastopexy for breast ptosis: Utility outcomes of population preferences. Plast Surg (Oakv). 2015;23(2):103-7.
18. Zavrides H. The Classic Pitanguy Technique and Its Modifications in Mammaplasty: Ten Years of Experiences. Ann Plast Surg. 2017;79(5):433-437.
19. Rubin JP, Gusenoff JA, Coon D. Dermal suspension and parenchymal reshaping mastopexy after massive weight loss: statistical analysis with concomitant procedures from a prospective registry. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;123(3):782-9.
20. Berrocal Revueltas M. Mamoplastia de Aumento secundaria. Evaluación de problemas, resultados insatisfactorios y alternativas de solución. Cir plást iberolatinam. 2012;38(1):9-26.
21. Della Croce FJ, Blum CA, Sullivan SK, Stolier A, Trahan C, Wise MW, et al. Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy and Ptosis: Perforator Flap Breast Reconstruction Allows Full Secondary Mastopexy with Complete Nipple Areolar Repositioning. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;136(1):1-9.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2019 Enrique Joaquín Moya Rosa, Yadira Moya-Corrales

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025