Prescription patterns characteristics of new antiepileptic drugs
Abstract
Background: epilepsy is one of the most frequent neurological diseases and almost 30 % of patients who suffer from it do not get control with classic antiepileptic drugs.
Objective: to characterize prescription patterns of new antiepileptic drugs.
Methods: a descriptive and cross-section study about use of medicines, of prescription-indication type with elements of therapeutic scheme was conducted. The study universe was composed of 300 patients and all of them were included on the research. The following variables were studied: group of age, associations, indications and interval of administration.
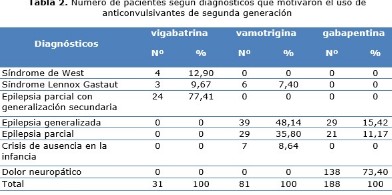
Results: use of vigabatrin and lamotrigine prevailed in children and patients with diagnosis of epilepsy. Use of Gabapentin was more frequent in adults and neuropathic pain. Vigabatrin and lamotrigine were mainly used in associations with classical antiepileptic drugs, being valproate the drug more used on it. Gabapentin was only used alone. There were mistakes on intervals of administration of all studied drugs.
Conclusions: prescription of new antiepileptic drugs was adequate in most cases. Identified mistakes were related to intervals of administration.
DeCS: ANTICONVULSANTS/administration&dosage; MEDICATION ERRORS; PRESCRIPTION DRUGS; EPIDEMIOLOGY, DESCRIPTIVE; EPILEPSY/drug therapy.
Downloads
References
1. Martín Zurro A. Atención primaria. Problemas de salud en la consulta de medicina de familia. 7ma ed [Internet]. España: Elsevier S.L.; 2014 [citado 2 Nov 2018]. Disponible en: https://www.clinicalkey.es/#!/content/book/3-s2.0-B9788490221105000269?scrollTo=%23s0370
2. Wiebe S. Epilepsias. En: Goldman L, Schafer AI. Cecil y Goldman. Tratado de Medicina interna. V. 2. 24 ed. Barcelona: Elsevier; 2013.p. 2287-2298.
3. Daroff R, Jankovic J, Mazziotta J, Pomeroy S, editors. Bradley's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 7a ed [Internet]. Elsevier Inc.; 2016 [citado 2 Nov 2018]. Disponible en: https://www.clinicalkey.es/#!/content/book/3-s2.0-B9780323287838001010?scrollTo=%23s0010
4. Haslam RHA. The nervous system. En: Behrman RE, Kliegman RM, Jenson HB. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 26th ed. Philadelphia: W.B Saunders; 2000. p. 1813-1829.
5. Valdivia Álvarez I, Abadal Borges G. Epilepsia de difícil control en Pediatría: Nuevas drogas antiepilépticas. Rev Cubana Pediatr [Internet]. Dic 2005 [citado 05 Nov 2018];77(3-4):[aprox. 11 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-75312005000300008&lng=es
6. Sosa Sánchez TM. Epilepsia. En: Vicente Peña E, Rodríguez Porto AL, Sánchez Zulueta E, Quintana López L, Riverón González JM, Ledo Grogués D, editores. Diagnóstico y tratamiento en Medicina Interna. La Habana: ECIMED; 2012. p. 660-669.
7. Rimbau Cabrera D. Patrón de reacciones adversas a los anticonvulsivantes en niños en la provincia de Camagüey [tesis]. Camagüey: Universidad de Ciencias Médicas de Camagüey; 2012.
8. Zarranz Imirizaldu JJ. Epilepsias. En: Farreras Valentí P, Rozman C, editores. Farreras. Rozman. Medicina Interna. V.2. 17 ed. Barcelona: Elsevier; 2012.p. 1307-1323.
9. Kros L, Eelkman Rooda OH, De Zeeuw CI, Hoebeek FE. Controlling Cerebellar Output to Treat Refractory Epilepsy. Trends Neurosci [Internet]. 2015 Dec [citado citado 05 Nov 2018];38(12):[aprox. 12 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26602765
10. Auvin S. Antiepilépticos. EMC–Pediatría [Internet]. 2014 [citado 2 Nov 2018]; 49(1):[aprox. 12 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.em-consulte.com/en/article/873593
11. Gómez Betancur L, Vilaplana Domínguez L, Sancho Rieger J. Tratamiento de la epilepsia. Programa de Formación Médica Continuada Acreditado. Medicine [Internet]. Mar 2015 [citado 2 Nov 2018];11(73):[aprox. 10 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.clinicalkey.es/#!/browse/journal/03045412/1-s2.0-S0304541215X70934
12. Pozo Lauzán D, Pozo Alonso A. Antiepilépticos de tercera generación. Rev Cubana Pediatr [Internet]. Ene-Mar 2010 [citado 2 Nov 2018];82(1):[aprox. 3 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S003475312010000100010&lng=es&nrm=iso
13. Pozo Alonso AJ, Pozo Lauzán D. Tratamiento con medicamentos antiepilépticos en el niño. Rev Cubana Pediatr [Internet]. Oct-Dic 2013 [citado 2 Nov 2018];85(4):[aprox. 10 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S003475312013000400010&lng=es&nrm=iso
14. Ministerio de Salud Pública. Cuadro básico de Medicamentos. Medicamentos dispensados por tarjeta control. La Habana: ECIMED; 2014.
15. Ministerio de Salud Pública. Cuadro básico de Medicamentos. Medicamentos por certificado médico. La Habana: ECIMED; 2014.
16. Ministerio de Salud Pública. Formulario Nacional de Medicamentos. 4ta ed. La Habana: ECIMED; 2014.
17. Trevathan E, Kerls SP, Hammer AE, Vuong A, Messenheimer JA. Lamotrigine adjunctive therapy among children and adolescents with primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Pediatrics [Internet]. 2006 Aug [citado 2014 Aug 12];118(2):[aprox. 8 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16847080
18. Hussain K, Walsh TJ, Chazen JL. Brain MRI findings with vigabatrin therapy: case report and literature review. Clin Imaging [Internet]. 2016 Ene-Feb [citado 05 Nov 2018];40(1):[aprox. 3 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26526789
19. Chen L, Mao J. Medicamentos analgésicos no opioides. En: Miller RD, Cohen NH, Eriksson LI, Fleisher LA, Wiener-Kronish JP, Young WL, editores. Miller. Anestesia. Barcelona: Elsevier;2016. p. 1-17.
20. Caminero Rodríguez AB. Dolor neuropático y neuralgias craneofaciales. En: Serra Catafau J, editor. Tratado de dolor neuropático [Internet]. Madrid: Editorial Médica Panamericana;2007 [citado 05 Nov 2018]. Disponible en: https://www.clinicalkey.es/#!/content/book/3-s2.0-B9788445820087500055
21. McNamara JO. Farmacoterapia de las epilepsias. En: Brunton LL, Chabner B, Knollmann BC, editors. Goodman & Gilman. Las bases farmacológicas de la terapéutica. 12a ed. México: McGraw-Hill;2012. p. 583-606.
22. Morales Plaza CD, Machado Alba JE. Patrones de prescripción de antiepilépticos en pacientes colombianos afiliados al Sistema General de Seguridad Social en Salud. Neurología [Internet]. 2014 [citado 05 Nov 2018]:[aprox. 12 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.clinicalkey.es/#!/content/journal/1-s2.0-S0213485314002011
23. Xiao Y, Gan L, Wang J, Luo M, Luo H. Vigabatrin versus carbamazepine monotherapy for epilepsy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev [Internet]. 2015 [citado 05 Nov 2018];11:[aprox. 7 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26580100
24. Marson AG, Al-Kharusi AM, Alwaidh M, Appleton R, Baker GA, Chadwick DW, et al. The SANAD study of effectiveness of carbamazepine, gabapentin, lamotrigine, oxcarbazepine, or topiramate for treatment of partial epilepsy: an unblinded randomised controlled trial. Lancet [Internet]. 2007 Mar [citado 2 Nov 2018];369(9566):[aprox. 15 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.clinicalkey.es/#!/content/medline/2-s2.0-17382827
25. Kwan P, Brodie MJ, Kälviäinen R, Yurkewicz L, Weaver J, Knapp LE. Efficacy and safety of pregabalin versus lamotrigine in patients with newly diagnosed partial seizures: a phase 3, double-blind, randomised, parallel-group trial. Lancet Neurol [Internet]. 2011 Oct [citado 05 Nov 2018];10(10):[aprox. 9 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.clinicalkey.es/#!/content/medline/2-s2.0-21889410
26. Zeng QY, Fan TT, Zhu P, He RQ, Bao YX, Zheng RY, et al. Comparative Long-Term Effectiveness of a Monotherapy with Five Antiepileptic Drugs for Focal Epilepsy in Adult Patients: A Prospective Cohort Study. PLoS One [Internet]. 2015 [citado 05 Nov 2018];10(7):[aprox. 7 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26147937
27. Valdivia Álvarez I, Garnelo Loaeza M, Bonet Quesada E, Odales Ibarra R, García García R, Marrero Martínez P. Eficacia de la vigabatrina en la epilepsia refractaria del niño. Rev Cubana Pediatr [Internet]. Jul-Sep 2007 [citado 2 Nov 2018];79(3):[aprox. 12 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S003475312007000300005&lng=es&nrm=iso&tlng=es
28. Armijo Simon JA, Herranz Fernández JL. Fármacos antiepilépticos y anticonvulsivantes. En: Flórez Beledo J, Armijo Simon JA, Mediavilla Martínez A, editores. Farmacología Humana. 6ta ed. Elsevier Masson; 2014. p. 476-502.
29. Inoue K, Yamamoto Y, Suzuki E, Takahashi T, Umemura A, Takahashi Y, et al. Factors that influence the pharmacokinetics of lamotrigine in Japanese patients with epilepsy. Eur J Clin Pharmacol [Internet]. 2016 Jan [citado 05 Nov 2018]: [aprox. 3 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26790665
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2018 Tania García-Arias, Indira López-Gutiérrez, Emilia Argelia Don-Quirós, Ernesto Sánchez-Rodríguez, Iraida Mederos-Pérez, Marena Morales-Morales

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025