Baker's cyst
Keywords:
QB- Quiste de Baker IRM- Imagen de resonancia magnética AAP- Aneurisma de la arteria poplíteaAbstract
Background: Baker's cyst is the most common soft tissue popliteal tumor; treatment may be conservative or surgical by arthroscopy or open ways.
Objective: to deep the knowledge about Baker's cyst in the knee joint.
Methods: the search of the information was carried out in a period of three months (from October 1st, 2017 to December 31, 2017) and the following words were used: popliteal cyst and Baker's cyst, from the obtained information it was carried out a bibliographical review of a whole of 316 articles published in the databases PubMed, Hinari, SciELO and Medline by means of the information locator EndNote, of them 50 citations were selected to do the review, 45 of them of last five years, where four books were included.
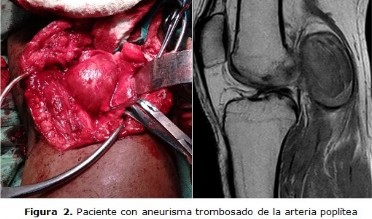
Development: important aspects related to clinical picture and imaging investigations were pointed out. Differential diagnosis between Baker's cyst in children and adults, and Baker's cyst and popliteal aneurysm were described. Treatment modalities were stated as well as surgical indications.
Conclusions: Baker's cyst is the most common soft tissue popliteal tumor affecting children and adults with cardinal differences. Popliteal aneurysm should be always ruled out. Surgical treatment is usually needed in adults by open procedures or arthroscopy, both methods have good results.
DeCS: POPLITEAL CYST/surgery; ARTHROSCOPY/utilization; SOFT TISSUE NEOPLASMS/pathology; MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING; KNEE JOINT/pathology.
Downloads
References
1. Demange MK. Baker's cyst. Rev Bras Ortop. 2015 Nov; 46(6):630-3.
2.Herman AM, Marzo JM. Popliteal cysts: a current review. Orthopedics. 2014 Aug; 37(8):e678-84.
3.Shah A, James SL, Davies AM, Botchu R. A diagnostic approach to popliteal fossa masses. Clin Radiol. 2017 Apr;72(4):323-37.
4.Dodds JA. Arthroscopic treatment of popliteal cyst. En: Sgaglione NA, Lubowitz JH, Provencher MT. The Knee: AANA Advanced Arthroscopic Surgical Techniques. Thorofare: Slack Incorporated; 2016. p.37-53.
5.Papadakis M, Manios A, Trompoukis C. Popliteal cyst before William Baker: first report in the Galenic Corpus. Acta Chir Belg. 2017 Apr;117(2):131-4.
6.Akgul O, Guldeste Z, Ozgocmen S. The reliability of the clinical examination for detecting Baker's cyst in asymptomatic fossa. Int J Rheum Dis. 2014 Feb;17(2):204-9.
7.Wilson PL, Rathjen KE. Disorders of the knee. En: Herring JA. Tachdjian's Pediatric Orthopaedics. 5th ed. Philadelphia:Elsevier;2014.p.698-9.
8.Moyad TF. Massive baker cyst resulting in tibial nerve compression neuropathy secondary to polyethylene wear disease. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ).2015 Apr;44(4):E113-6.
9.Alessi S, Depaoli R, Canepari M, Bartolucci F, Zacchino M, Draghi F. Baker's cyst in pediatric patients: ultrasonographic characteristics. J Ultrasound. 2012 Feb;15(1):76-81.
10.Alves TI, Girish G, Kalume Brigido M, Jacobson JA. US of the knee: scanning techniques, pitfalls, and pathologic conditions. Radiographics. 2016 Oct;36(6):1759-75.
11.Jacobson JA, Ruangchaijatuporn T, Khoury V, Magerkurth O. Ultrasound of the knee: common pathology excluding extensor mechanism. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2017 Apr;21(2):102-12.
12.Billières J, Lascombes P, Peter R. Popliteal cysts: etiologic and therapeutic approach. Rev Med Suisse. 2014 May;10(432):1211-5.
13.Zhou XN, Li B, Wang JS, Bai LH. Surgical treatment of popliteal cyst: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016 Feb;11:22.
14.Crenshaw AH Jr. Soft tissue procedures and corrective osteotomies about the knee. Azar FM, Beaty JH, Canale ST. Campbell's Operative Orthpaedics. 13th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier;2017.p.484-6.
15.Artul S, Jabaly-Habib H, Artoul F, Habib G. The association between Baker's cyst and medial meniscal tear in patients with symptomatic knee using ultrasonography. Clin Imaging. 2015 Jul-Aug;39(4):659-61.
16.Templeton K. Soft tissue tumors of the knee. Scott WN. Insall & Scott Surgery of the Knee. 5 th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier;2012.p.e153-8.
17.Frush TJ, Noyes FR. Baker's cyst: diagnostic and surgical considerations. Sports Health. 2015 Jul;7(4):359-65.
18.Calvisi V, Zoccali C. Arthroscopic patterns of the poster-medial aspect of the knee joint:
classification of the gastrocnemius-semimembranosus gateway and its relationship with Baker's cyst. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2016 Feb;6(4):492-8.
19.Kim TW, Suh JT, Son SM, Moon TY, Lee IS, Choi KU, et al. Baker's cyst with intramuscular extension into vastus medialis muscle. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2012 Dec;24(4):249-53.
20.Wisniewski SJ, Murthy N, Smith J. Ultrasound evaluation of Baker cysts: diagnosis and management. PM R. 2012 Jul;4(7):533-7.
21.Malas FÜ, Kara M, Kaymak B, Akinci A, Özçakar L. Ultrasonographic evaluation in symptomatic knee osteoarthritis: clinical and radiological correlation. Int J Rheum Dis. 2014 Jun;17(5):536-40.
22.Martel Villagrán J, Bueno Horcajadas Á, Agrela Rojas E. Musculoskeletal interventional radiology: ultrasound and CT. Radiologia. 2016 May; 58 Suppl 2:45-57.
23.Hofmann-González F, Hernández-Díaz C, Solano-Ávila C, López-Reyes AG, Peña-Ayala A, Pineda-Villaseñor C. Giant Baker's cyst treated with intralessional methotrexate. Cir Cir. 2013 Jan-Feb;81(1):64-8.
24.Cho JH. Clinical results of direct arthroscopic excision of popliteal cyst using a posteromedial portal. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2012 Dec;24(4):235-40.
25.Vaishya R, Krishnan M, Vijay V, Agarwal AK. Arthroscopic management of popliteal cyst: comments and concerns. Indian J Orthop. 2017 Mar-Apr;51(2):229.
26.Ohishi T, Takahashi M, Suzuki D, Fujita T, Yamamoto K, Ushirozako H, et al. Treatment of popliteal cysts via arthroscopic enlargement of unidirectional valvular slits. Mod Rheumatol. 2015 Sep;25(5):772-8.
27.Harcke HT, Niedzielski A, Thacker MM. Popliteal cysts in children: another look. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2016 Nov;25(6):539-42.
28.Stein D, Cantlon M, Mackay B, Hoelscher C. Cysts about the knee: evaluation and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2013 Aug;21(8):469-79.
29.Leake AE, Segal MA, Chaer RA, Eslami MH, Al-Khoury G, Makaroun MS, et al. Meta-analysis of open and endovascular repair of popliteal artery aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2017 Jan;65(1):246-256.e2.
30.Phair A, Hajibandeh S, Hajibandeh S, Kelleher D, Ibrahim R, Antoniou GA. Meta-analysis of posterior versus medial approach for popliteal artery aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg. 2016 Oct;64(4):1141-50.
31.Balachandran S, Murugesan R, Jayachander K, Muthukkaruppiah S. Popliteal artery aneurysms: role of primary care physicians. J Family Med Prim Care. 2016 Apr-Jun;5(2):482-484.
32.Bandinelli F, Fedi R, Generini S, Porta F, Candelieri A, Mannoni A, et al. Longitudinal ultrasound and clinical follow-up of Baker's cysts injection with steroids in knee osteoarthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2012 Apr;31(4):727-31.
33.Çaglayan G, Özçakar L, Kaymak SU, Kaymak B, Tan AA. Effects of sono-feedback during aspiration of Baker's cysts: a controlledclinical trial. J Rehabil Med. 2016 Apr;48(4):386-9.
34.Chen CK, Lew HL, Liao RI. Ultrasound-guided diagnosis and aspiration of Baker's cyst. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2012 Nov;91(11):1002-4.
35.Baker ND. Evaluation of popliteal cysts. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1991 Aug;17(3):803-4.
36.Hughston JC, Baker CL, Mello W. Popliteal cyst: a surgical approach. Orthopedics. 1991 Feb;14(2):147-50.
37.Kongmalai P, Chernchujit B. Arthroscopic treatment of popliteal cyst: a direct posterior portal by inside-out technique for intracystic debridement. Arthrosc Tech. 2015 Apr;4(2):e143-8.
38.Saylik M, Gökkus K. Treatment of baker cyst, by using open posterior cystectomy and supine arthroscopy on recalcitrant cases (103 knees). BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016 Oct;17(1):435.
39.Ahn JH, Lee SH, Yoo JC, Chang MJ, Park YS. Arthroscopic treatment of popliteal cysts: clinical and magnetic resonance imaging results. Arthroscopy. 2010 Oct;26(10):1340-7.
40.Lie CW, Ng TP. Arthroscopic treatment of popliteal cyst. Hong Kong Med J. 2011 Jun;17(3):180-3.
41.Kim KI, Lee SH, Ahn JH, Kim JS. Arthroscopic anatomic study of posteromedial joint capsule in knee joint associated with popliteal cyst. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014 Jul;134(7):979-84.
42.Liebensteiner MC, Thaler M, Putzer D, Wurm A, Nogler M. Arthroscopic procedure for Baker's cysts: surgical technique. Video article. Orthopade. 2015 Oct; 44(10):803-5.
43.Pankaj A, Chahar D, Pathrot D. Arthroscopic management of popliteal cysts. Indian J Orthop. 2016 Mar-Apr;50(2):154-8.
44.Smith MK, Lesniak B, Baraga MG, Kaplan L, Jose J. Treatment of popliteal (Baker) cysts with ultrasound-guided aspiration, fenestration, and injection: long-term follow-up. Sports Health. 2015 Sep-Oct;7(5):409-14.
45.Stöckli C, Hunziker R, Tamborrini G. Recurrent Baker's cyst. Praxis (Bern 1994). 2011 Jul; 100(15):927-30.
46.Miller TT, Staron RB, Koenigsberg T, Levin TL, Feldman F. MR imaging of Baker cysts: association with internal derangement, effusion, and degenerative arthropathy. Radiology. 1996 Oct;201(1):247-50.
47.Picerno V, Filippou G, Bertoldi I, Adinolfi A, Di Sabatino V, Galeazzi M, et al. Prevalence of Baker's cyst in patients with knee pain: an ultrasonographic study. Reumatismo. 2014 Mar;65(6):264-70.
48.Snir N, Hamula M, Wolfson T, Sherman O, Feldman A. Popliteal cyst excision using open posterior approach after arthroscopic partial medial meniscectomy. Arthrosc Tech. 2013 Aug;2(3):e295-8.
49.Steelman TJ, Wagner SC, Jex JW. Popliteal cyst with positive antinuclear antibodies as the presentation of Lyme disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2015 May;34(5):548.
50.Yavuz F, Kibar S, Balaban B. Hypertonic dextrose injection for the treatment of a Baker's cyst. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016 Feb; 10(2):YD01-2.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2018 Alejandro Álvarez López, Sergio Ricardo Soto Carrasco, Yenima de la Caridad García Lorenzo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025