Botulinum toxin as an alternative treatment in patients with achalasia
Abstract
Background: achalasia is found among the diseases that affect the esophagus. Although there is no curative treatment for this disease, there are several palliative therapeutic strategies; in recent years the use of botulinum toxin has been increasingly discussed.
Objective: to evaluate the effectiveness of botulinum toxin as an alternative treatment in patients with achalasia in Camagüey.
Methods: a descriptive, longitudinal and prospective study was carried out. The study universe increased to a total of 13 patients. The data was recorded in a collection form. For better understanding the information was shown in tables.
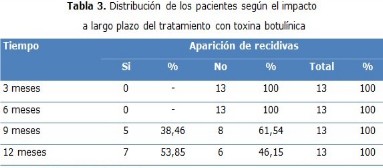
Results: six patients, for 46,15 % refused to receive another treatment. A satisfactory result of this short-term therapeutic option was found in 100 %. There were no recurrences of the disease during the first six months of the treatment, in none of the patients. More than half of the treated cases did not present adverse reactions, with 61,54 %.
Conclusions: the treatment was applied when most of the patients refused to receive another therapeutic option. The short-term evaluation showed that all patients reported being asymptomatic, and recurrences appeared between nine and 12 months. Patients who did not present adverse effects predominated.
DeCS: ESOPHAGEAL ACHALASIA/drug therapy; ESOPHAGEAL ACHALASIA/diagnosis; BOTULINUM TOXINS/therapeutic use; BOTULINUM TOXINS /drug effects; DRUG EVALUATION.
Downloads
References
1.Martín de Argila C, Boixeda D. Trastornos motores de esófago. En: Montoro MA, García Pagan JC, editores. Gastroenterología y hepatología clínica. Problemas comunes en la práctica clínica. 2ª ed. Madrid: Jarpyo Editores SA; 2012. p. 243-50.
2.Orgaz Gallego MP. Achalasia: un trastorno de la motilidad esofágica, no tan raro. Rev Clin Med Fam [Internet]. Feb 2009 [citado 31 Jul 2018];2(6): [aprox. 8 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1699-695X2009000100010&lng=es
3.Hani de Ardila AC. Acalasia. Rev Gastroenterol. 2014;14(2):1-8.
4.Luzardo Silvera E, Eirin J. Cirugía laparoscópica mediante la técnica de Heller-Dor en pacientes con acalasia. MEDISAN [Internet]. Dic 2012 [citado 31 Jul 2018];16(12):[aprox. 7 p.]. Disponible en: http://scieloprueba.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S102930192012001200001
5.Mearin Manrique F, Elizalde Fernández JI. Acalasia. En: Farreras Valentí P, Rozman C, editores. Medicina Interna. 17ª ed. Madrid: Elservier; 2012. p.77-89.
6.Nodarse Pérez P, Pérez Menéndez R, González Torres MJ, Rodríguez Allende MA. Acalasia esofágica: tratamiento endoscópico. Protocolo de Tratamiento del Hospital Docente Universitario Hermanos Ameijeiras [tesis].Ciudad de La Habana: Hospital Docente Universitario Hermanos Ameijeiras; 2012.
7.Braghetto I, Csendes AJ, Burdiles P, Korn OB, Valera JM. Manejo actual de la acalasia del esófago: revisión crítica y experiencia clínica. Rev Méd Chile [Internet]. Sep 2002 [citado 20 May 2016];130:[aprox. 11 p.]. Disponible en:http://www.scielo.cl/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S003498872020900015
8.Restrepo Pardo AJ, Rey Tabares MH, Garzón Oca MA, Farfán Quirol YA, Molano Vázquez JC, Marulanda JC, et al. Acalasia. Controversias del tratamiento. Rev Col Gastroenterol [Internet]. 2007 [citado 31 Jul 2018];22(1):[aprox. 7 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.co/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0120-99572007000100012&lng=es
9.Fuentes Valdés E, González Fernández R. Acalasia de esófago. En: Pardo Gómez G, García Gutiérrez A, editores. Temas de cirugía. La Habana: Editorial Ciencias Médicas;2010. p. 1002-6.
10.Leyden JE, Moss AC, Mac Mathuna P. Dilatación neumática endoscópica versus inyección de toxina botulínica en el tratamiento de la acalasia primaria (Revisión Cochrane traducida) [Internet]. Oxford: Update Software Ltd.; 2008 [citado 20 May 2016]. Disponible en: https://www.cochrane.org/es/CD005046/dilatacion-neumatica-endoscopica-versus-inyeccion-de-toxina-botulinica-en-el-tratamiento-de-la
11.Peñaloza Ramírez A, Suárez Correa J. Acalasia: en defensa del manejo endoscópico. Rev Col Gastroenterol [Internet]. Abr-Jun 2012 [citado 20 May 2016];27(2):[aprox. 7 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.co/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S012099572012000200007
12.Dorado Acuesta EA. Manejo mínimamente invasivo de la acalasia: la cirugía como la opción más efectiva. Rev Col Gastroenterol [Internet]. Jun 2012 [citado 20 May 2016];27(2):[aprox. 3 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.co/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0120-99572012000200006&lng=en
13.Tighe AP, Schiavo G. Botulinum neurotoxins: Mechanism of action. Toxicon. 2012;67(1):2013.
14.Lozano Lanagrán M, Lavín Castejón I, Alcaín Martínez G. Tratamiento de acalasia con inyección de toxina botulínica guiada por ecoendoscopia en paciente con varices esofágicas. Rev Esp Enferm [Internet]. 2011 [citado 20 May 2018];103(12):[aprox. 9 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?pid=113001082011001200016&script=scarttext&tlng
15.Vivancos Matellano F, Pascual Pascual SI, Nardi Vilardaga J, Miquel Rodríguez F, Miguel León I de, Martínez Garre MC. Grupo Español de Espasticidad. Guía del tratamiento integral de la espasticidad. Rev Neurol.2007;45(6):365-75.
16.Sharkey KA, Wallance JL. Tratamiento de los trastornos motores intestinales y del flujo de agua. En: Goodman LS, Gilman A, editores. Goodman & Gilman. Las bases farmacológicas de la terapéutica. 11a ed. México: McGraw-Hill Interamericana;2012. p. 1323-6.
17.Brizuela Quintanilla RA. Acalasia. En: Paniagua Esteves ME, Piñol Jiménez MN, editores. Gastroenterología y hepatología clínica. La Habana: ECIMED;2016. p.670-676.
18.Liu A, Carruthers A, Cohen JL, Coleman WP, Dover JS, Hanke CW, et al. Recommendations and current practices for the reconstitution and storage of botulinum toxin type A. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67(3):373-8.
19.Dressler D, Benecke R. Pharmacology of therapeutic botulinum toxin preparations. Disab Rehab. 2010;29:1761-8.
20.Campos G, Vittinghoff E, Rabl C, Takata M, Gadenstätter M, Lin F, et al. Endoscopic and surgical treatments for achalasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg. 2009 Jan;249(1):45-57.
21.Pasricha PJ, Ravich WJ, Hendrix TR, Sostre S, Jones B, Kalloo AN. Intrasphinteric botulinum toxin for treatment of achalasia. N Engl J Med.1995;332:774-8.
22.Annese V, Bussotti G, Coccia G, Dinelli M, D´Onofrio G, Gatto G, et al. A multicentre randomized study of intraspheric botulinum toxin in patient with oesophageal achalasia. Gut. 2000;46:579-600.
23.Vaezi MF, Pandolfino JE, Vela MF. Nueva Guía para el diagnóstico y tratamiento de la Acalasia. Am J Gastroenterol [Internet]. 2013 [citado 31 Jul 2018];108: [aprox. 11 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.nature.com/ajg/journal v108/n8/full/ajg2013196a.html
24.Zoons E, Dijkgraaf MG, Dijk JM, van Schaik IN, Tijssen MA. Botulinum toxin as treatment for focal dystonia: a systematic review of the pharmaco therapeutic and pharmaco-economic value. J Neurol. 2012;259(12):2519-26.
25.Benecke R, Moore P, Dressler D, Naumann M. Cervical and axial dystonia. In: Moore P, Naumann M, editors. Handbook of botulinum toxin treatment. Oxford UK: Blackwell Publishing Company;2013. p.158-94.
26.Tejedor Cerdeña MA. Estudio clínico y molecular de acalasia esofágica [tesis]. España: Universidad de Salamanca; 2011.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2018 Yosvany Rojas Peláez, Yon Luis Trujillo Pérez, Guillermo Brito Adam, Everto Daniel Menéndez Estrada, Martín Chiong Quesada

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025