Risky factors associated with acute respiratory infection in children less than five years
Abstract
Background: acute respiratory infections are a group of diseases that are produced in the respiratory system, caused by different microorganisms like virus and bacteria, which begin very suddenly and last less than two weeks.
Objective: to identify the risky factors associated with acute respiratory infections in children less than five years old.
Methods: an analytic observational retrospective study was carried out with 88 children: 44 cases and 44 controls at Armando Cardoso hospital from June 2015 to May 2017. The information was obtained from the clinical history of the children and the interviews applied to children's parents.
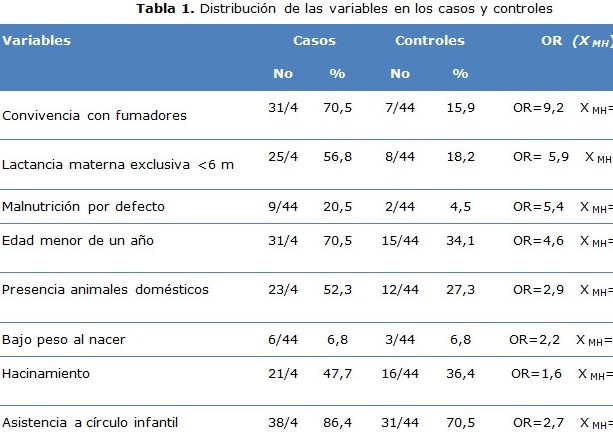
Results: the following risk factors for acute respiratory infections were found: exposure to the smoke of tobacco (OR=9,2 XMH= 5,1), breast feeding for at least 6 months age (OR=5,9 XMH=3,7), malnutrition by defect (OR=5,4 XMH= 2,2), age under one year, (OR=4,6 XMH=3,4) and presence of domestic animals at home (OR=2,9 X MH= 2,4).
Conclusions: the identified risk factors associated with acute respiratory infection were: exposure to the smoke of tobacco, breast feeding for at least 6 months age, malnutrition by defect, age under 1 year old and presence of domestic animals.
DeCS: RISK FACTORS; RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS; MALNUTRITION; CHILD; OBSERVATIONAL STUDY.
Downloads
References
1.Arredondo García JL, Méndez Herrera A. Infección de vías respiratorias agudas en población pediátrica. Rev Enf Infec Pediatr [Internet]. Oct-Dic 2015 [citado 24 Jul 2017];XXIX(114):[aprox. 6 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.materiamedica.ru/news/1Garcia_Herrera.pdf
2.García Corzo JR, Niederbacher Velásquez J, González Rugéles CI, Rodríguez Villamizar LA, Machuca Pérez M, Torres Prieto A, et al. Etiología viral de Infecciones Respiratorias Agudas en niños menores de 5 años en las provincias Comunera y García Rovira de Santander. Rev Univ Ind Santander Salud [Internet]. Abr-Jun 2016 [citado 2 Ago 2017];48(2):[aprox. 5 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.co/scielo.php?script= sci_ arttext&pid= S012108 072016000200011&lng=en
3. González Valdés JA. Las infecciones respiratorias agudas en el niño. Rev Cubana Pediat. 2013;85(2):147-148.
4.Cruz Moreno AP, Porras Molina JJ. Alteraciones y Signos Identificados por los Cuidadores de Niños de Dos a Cinco Años con Infección Respiratoria Aguda que los Llevan a Consultar al Servicio de Urgencias de 2014 [tesis]. Bogotá, Colombia: Pontificia Universidad Javeriana; 2014 [citado 2 Ago 2017]. Disponible en: http://hdl.handle.net/10554/16393
5.Zavaleta Rodríguez RM. Nivel de información materna sobre Infecciones Respiratorias Agudas y capacidad de cuidado dependiente en niños de uno a cinco años. Servicio de Pediatría Hospital Belén de Trujillo [tesis]. Trujillo, Perú: Universidad Católica Los Ángeles de Chimbote; 2015 [citado 2 Ago 2017]. Disponible en: http://tesis.uladech.edu.pe/handle/ULADECH_CATOLICA/121
6.Ladines Canales A, Merejildo Domínguez DE. Conocimiento del manejo de las Infecciones Respiratorias Agudas en madres con niños menores de 5 años de la comunidad de Puerto Hondo [tesis]. Guayaquil, Ecuador: Universidad de Guayaquil; 2014 [citado 2 Ago 2017]. Disponible en. http://repositorio.ug.edu.ec/handle/redug/9010#sthash.5rYsdlVb.dpuf
7.Oliva González Y, Piloto Morejón M, Iglesias Gómez R. Clínica y epidemiología de las Infecciones Respiratorias Agudas en pacientes de 0-14 años. Rev Ciencias Medicas [Internet]. Ene-Feb 2013 [citado 26 Jul 2017];17(1):[aprox. 13 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_ arttext&pid=S1561-31942013000100006
8.Tamayo Reus CM, Bastart Ortiz EA. Morbilidad por Infecciones Respiratorias Agudas en pacientes menores de 5 años. MEDISAN [Internet]. Dic 2013 [citado 14 Jul 2017];17(12):[aprox. 5 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1029-30192013001200007&lng=es
9.Juy Aguirre E, Céspedes FE, Rubal Wong A de la C, Maza González AM, Terán Guardia CA. Morbilidad por Infecciones Respiratorias Agudas en menores de 5 años. MEDISAN [Internet]. Nov 2014 [citado 14 Jul 2017];18(11):[aprox. 8 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld. cu/ scielo.php?script=sci_ arttext&pid=S1029-30192014001100002&lng=es
10.Martínez Urrea H, Alzate Gómez DF, Ríos Ballesteros MJ, Aguilar Marín IC, Archila Quiceno JV, Calvo Betancur VD. Factores de riesgo a enfermedades respiratorias agudas en los menores de cinco años. Rev Mex Ped. Nov-Dic 2009;76(6): 251-255.
11.García Rosique RM. Factores de riesgo de morbilidad y mortalidad por Infecciones Respiratorias Agudas en niños menores de 5 años. Rev Méd Electrón [Internet]. May-Jun 2010 [citado 2 Ago 2017];32(3):[aprox. 5 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.revmatanzas.sld.cu/revista %20medica/ ano% 202010/vol3%202010/ tema10.htm
12.Collantes Mendoza A. Infecciones Respiratorias Agudas en niños menores de 10 años que llegan a la emergencia del hospital Federico Bolaños Moreira y sus factores de riesgo clínico epidemiológicos 2014-2015 [tesis]. Ecuador: Universidad de GuayaquiL; 2015. Disponible en: http://repositorio.ug.edu.ec/handle/redug/10512#sthash.GdKsT9yN.dpuf
13.Ticona-Rendón M, Huanco-Apaza D, Ticona Vildoso M. Incidencia y factores de riesgo de bajo peso al nacer en población atendida en hospitales del Ministerio de Salud del Perú. Ginecol Obstet Mex. Feb 2012;80(2):51-60.
14.López Campos X, Massip Nicot J, Massip Nicot T, Domínguez Y. Factores de riesgo de infecciones respiratorias altas recurrentes en menores de cinco años. Rev Panam Infectol. 2014;16(1):7-16.
15.Corcho Quintero A, Delgado Díaz Olga L, Cruz Martínez G, Verdasquera Corcho D, Díaz Fuentes C, Carbó Riverón M. Factores de riesgo de las Infecciones Respiratorias Agudas en pacientes menores de un año. Rev Cubana Med Gen Integr [Internet]. Dic 2010 [citado 20 Jul 2017];26(4):[aprox. 8 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0864-21252010000400010&lng=es
16.Chia-Gil A, Pariona R, Soto V, Cuipal J, Romaní D, Díaz W, et al. Lactancia materna exclusiva y enfermedades prevalentes de la infancia en menores de seis meses. Rev Peruana Epidemiol [Internet]. Ago 2013 [citado15 Jul 2017];17(2):[aprox.7 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.redalyc.org/articulo .oa?id=203129458009
17.Duchitanga Sangurima JL, Cumbe Minchalo SM. Conocimientos, actitudes y prácticas sobre prevención de Infecciones Respiratorias Agudas en los cuidadores de niños menores de 5 años atendidos en el Subcentro de Salud Parque Iberia [tesis]. Ecuador, Cuenca: Universidad de Cuenca; 2015 [citado 20 Jul 2017]. Disponible en: http://dspace.ucuenca.edu.ec/bitstream/123456789/23054/1/TESIS.pdf
18.Pérez Sánchez M, Fundora Hernández H, Notario Rodríguez M, Rabaza Pérez J, Hernández Sánchez MA, Rodríguez Bertheau A. Factores de riesgo inmunoepidemiológicos en niños con infecciones respiratorias recurrentes. Rev Cuban Ped. 2011;83(3):225-235.
19.de Granda-Orive JI, Alonso-Arroyo A, García-Río F, Villanueva-Serrano S, Pandiella A, Aleixandre-Benavent R. Literatura científica en el ámbito del tabaquismo y el sistema respiratorio: repercusión y colaboración. Arch Bronconeum. 2013;49(4):131-175.
20.MacIntyre EA, Gehring U, Mölter A, Fuertes E, Klümper C, Krämer U, et al. Air pollution and respiratory infections during early childhood: An analysis of 10 European birth cohorts within the ESCAPE Project. Environ Health Perspect. 2014 Jun;122:107–13.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2018 Carlos Coronel Carvajal, Yanet Huerta Montaña, Odelmis Ramos Téllez

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025