Relación entre los condilomas acuminados y lesiones precursoras del cáncer cervicouterino en consulta infanto juvenil
Resumen
Fundamento: el cáncer cervicouterino y los condilomas acuminados comparten el mismo agente causal. El primero es ocasionado por papiloma virus humano de alto riesgo oncogénico, mientras que el segundo generalmente por virus de bajo riesgo, pero son un importante indicador de infección por virus de alto riesgo. La persistencia viral es fundamental para desarrollar cáncer cérvicouterino. Entre los factores que favorecen esta, se señalan edad temprana del primer coito e infecciones de transmisión sexual. Los adolescentes son un grupo vulnerable.Objetivo: relacionar los condilomas acuminados con lesiones precursoras del cáncer cervicouterino en consulta infanto-juvenil.
Métodos: se realizó un estudio descriptivo y transversal. El universo estuvo constituido por todas las pacientes con diagnóstico clínico de condilomas acuminados que asistieron a consulta infanto juvenil del policlínico de especialidades pediátricas de Camagüey, desde el 1ro de enero hasta el 31 de diciembre de 2014. Los métodos empleados fueron estadística descriptiva de distribución de frecuencias absolutas y relativas. La información obtenida fue procesada mediante el programa estadístico SPSS-10. Los resultados del estudio se expusieron en tablas.
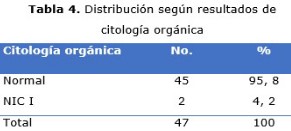
Resultados: el grupo de edad más afectado fue de 15 a 17 años y una sexta parte presentaban infección subclínica. La mayoría tenían conducta sexual de riesgo, y aproximadamente la tercera parte presentaba infecciones de transmisión sexual asociadas. Casi la totalidad de las citologías orgánicas fueron normales. Se encontró neoplasia intraepitelial grado I con presencia de epitelio acetoblanco a la colposcopia en alrededor de la octava parte de las enfermas.
Conclusiones: a toda paciente adolescente con condiloma acuminado se le debe realizar estudio citológico y colposcopia, así como identificar los factores para la persistencia del papiloma virus humano.
DeCS: CONDILOMA ACUMINADO; NEOPLASIAS DEL CUELLO UTERINO; ENFERMEDADES DE TRANSMISIÓN SEXUAL; ADOLESCENTE; EPIDEMIOLOGÍA DESCRIPTIVA.
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2016 Telma Margarita Ferrá Torres, Damarys Florat Gutierrez, Marlon Navarro Vázquez

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 4.0.
La Revista Archivo Medico Camagüey, ofrece de forma inmediata después de ser indexada en el Proyecto SciELO; acceso abierto al texto completo de los artículos bajo el principio de hacer disponible y gratuita la investigación para favorecer el intercambio del conocimiento global y coadyuvar a una mayor extensión, publicación, evaluación y uso extensivo de los artículos que se exponen pudiendo ser utilizados, sin fines comerciales, siempre y cuando se haga referencia a la fuente primaria.
Carta De Declaración De Autoría u Derechos De Autor(a)
Conflictos de intereses: los autores deberán declarar de forma obligatoria la presencia o no de conflictos de intereses en relación con la investigación presentada. (Descargar Plantilla para declarar confictos de intereses)
La Revista Archivo Médico Camagüey se encuentra bajo una
Licencia Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial 4.0 International (CC BY NC 4.0).
Esta licencia permite a otros distribuir, mezclar, ajustar y construir a partir de su obra, incluso con fines comerciales, siempre que le sea reconocida la autoría de la creación original. Esta es la licencia más servicial de las ofrecidas. Recomendada para una máxima difusión y utilización de los materiales sujetos a la licencia. La licencia completa puede consultarse en: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/











