Uso de surfactante porcino en recién nacidos pretérminos con bronconeumonía de inicio temprano
Keywords:
recién nacido, bronconeumonía connatal, surfactante, esteroides prenatalesAbstract
RESUMENFundamento: existen discrepancias con respecto al uso de surfactante en la bronconeumonía del recién nacido.
Objetivo: evaluar el comportamiento de los recién nacidos con bronconeumonía de inicio temprano tratados con surfactante exógeno.
Métodos: se realizó un estudio multicéntricos, abierto, no aleatorizado ni controlado, en 39 recién nacidos pretérminos con bronconeumonía de inicio temprano tratados con surfactante exógeno. Se estudió la edad gestacional, el peso al nacer y el tiempo de estadía en la unidad de cuidados intensivos neonatales, la relación PaO2/FiO2, el tiempo en ventilación mecánica, las complicaciones del soporte ventilatorio y la mortalidad según número de dosis de surfactante exógeno y uso de esteroides prenatales para lo que se calcularon, las frecuencias absolutas y relativas, las medias y ji cuadrado.
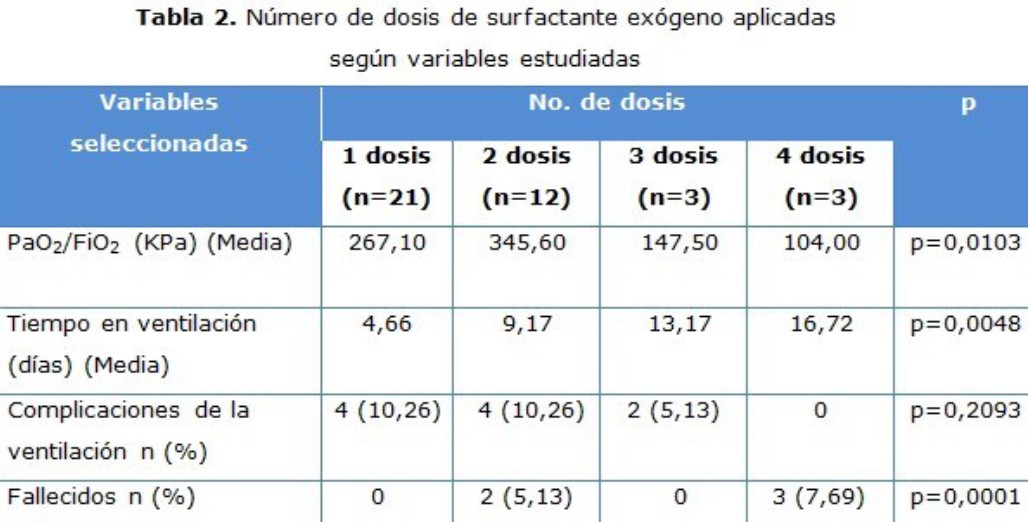
Resultados: la necesidad de administrar un mayor número de dosis se asoció a menor relación PaO2/FiO2 (p=0,0103), se obtuvieron valores adecuados con la primera y segunda dosis. El uso de esteroides prenatales se asoció a un menor tiempo en ventilación mecánica (p=0,0474), a valores mayores de la relación PaO2/FiO2 (p=0,0162) y a una menor mortalidad (p=0,0076). No se halló asociación estadística en las complicaciones relacionadas con la ventilación.
Conclusiones: los pacientes que requirieron mayor número de dosis de surfactante tuvieron una respuesta ventilatoria desfavorable y mayor mortalidad. El uso de esteroides prenatales favoreció una mejor respuesta ventilatoria y menor mortalidad. Puede ser beneficiosa la combinación del uso prenatal de esteroides y surfactante exógeno en pretérminos con bronconeumonía de inicio temprano.
Background: there are disagreements about the use of surfactant in bronchopneumonia in new-borns.
Objective: to evaluate the behaviour of newborns with early bronchopneumonia treated with exogenous surfactant.
Methods: an open, multicentric, non-randomized or controlled study was conducted in 39 preterm new-borns with early bronchopneumonia treated with exogenous surfactant. The gestation age, the birth weight and the stay time in the neonatal intensive care unit, the relation PaO2/FiO2, the mechanical ventilation time, the complications of ventilatory support and the mortality according to the number of doses of exogenous surfactant and the use of prenatal steroids were studied. The absolute and relative frequencies, the average and the chi-squared test were calculated.
Results: the need of administrating a greater number of doses was associated to a lower relation PaO2/FiO2 (p=0,0103). Adequate values were obtained with the first and the second doses. The use of prenatal steroids was associated to a lesser time with mechanical ventilation (p=0,0474), to greater values of the relation PaO2/FiO2 (p=0,0162) and to a lower mortality (p=0,0076). No statistical association was found in the complications related to ventilation.
Conclusions: those patients who required a greater number of doses of surfactant had an unfavorable ventilatory response and a greater mortality. The use of prenatal steroids favoured a better ventilatory response and a lower mortality. The combination of prenatal steroids and exogenous surfactant can be beneficial in preterm newborns with early bronchopneumonia.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2015 Andrés Armando Morilla Guzmán, Elaine Díaz Casañas, Octavio Fernández Limia, Yisel Ávila Albuerne, Yinet Barrese Pérez

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025