Clinical and epidemiological characterization of bronchiolitis in infants under six months in Santa Clara, Villa Clara
Abstract
Introduction: Bronchiolitis is a lower respiratory infection of generally viral etiology, a frequent cause of infant morbidity and mortality, which caused a high demand for care.
Objective: To characterize the behavior of bronchiolitis in infants under six months of age with hospital admission belonging to the municipality of Santa Clara during the year 2022.
Methods: A descriptive cross-sectional study was carried out in the José Luis Miranda Pediatric Hospital in Villa Clara with infants under six months of age from the municipality of Santa Clara admitted with a diagnosis of bronchiolitis from January to December 2022. The sample consisted of 74 infants under six months of age. The data source was the hospital medical record and a form with the variables under study used to extract the data. The variables under study were: age, sex, gestational age at birth, birth weight, breastfeeding, passive smoker, nutritional status, comorbidities, overcrowding, severity of bronchiolitis and complications.
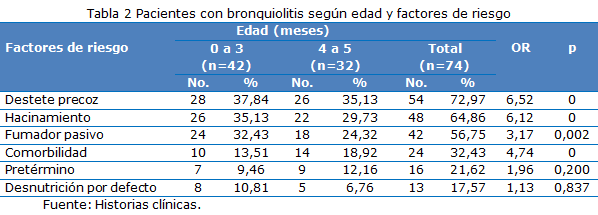
Results: The most frequent ages were those under three months (56.76 %); with mild forms of the disease predominating (46) and few severe forms unrelated to the age of the patients. Among the main risk factors were early weaning, overcrowding, comorbidity, and passive smoking, associated with moderate and severe forms of the disease. The main complications were pneumonia, acute otitis media, and atelectasis.
Conclusions: Bronchiolitis is a more frequent disease in the first months of life with a generally benign evolution and is associated with potentially preventable risk factors.
DeCS: BRONQUIOLITIS/diagnosis; BRONCHIOLITIS/epidemiology; INFANT; RISK FACTORS; COMORBIDITY.
Downloads
References
1. James E, Crowe J. Virus sincitial respiratorio. En: Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, Geme JW, Schor NF, Behrman RE, editores. Nelson. Tratado de Pediatría. España: Elsevier; 2013. p. 1177-81.
2. Barr R, Green CA, Sande CJ, Drysdale SB. Respiratory syncytial virus: diagnosis, prevention and management. Ther Adv Infect Dis [Internet]. 2019 [citado 12 Ene 2023] 6:2049936119865798. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6664627/
3. Watts KD, Goodman DM. Sibilancias, bronquiolitis y bronquitis. En: Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, Geme JW, Schor NF, Behrman RE, editores. Nelson. Tratado de pediatría. España: Elsevier; 2013. p.1514-9.
4. García Quintero F, De la Cruz Rodríguez R. Actualización en la etiopatogenia de la bronquiolitis aguda. Revista 16 de Abril [Internet]. 2018 [citado 07 Ene 2023];57(268):125-34. Disponible en: https://rev16deabril.sld.cu/index.php/16_04/article/view/558
5. Coronel Carvajal C. Factores asociados al desarrollo de la bronquiolitis. Arch méd Camagüey [Internet]. 2019 [citado 07 Ene 2023];23(5):639-647. Disponible en: https://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/medicocamaguey/amc2019/amc195i.pdf
6. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Bronchiolitis in children: diagnosis and management [Internet]. London: NICE; 2020. [citado 08 Ene 2023]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK573086/
7. Martínez FG, Sánchez MI, Pérez Moreno J, del Castillo BT, Fernández RR. ¿Cuál es el flujo inicial idóneo en la oxigenoterapia de alto flujo para el tratamiento de la bronquiolitis en las plantas de hospitalización? Anales de Pediatría [Internet]. 2019 [citado 07 Ene 2023];91(2):112-9. Disponible en: https://www.analesdepediatria.org/es-cual-es-el-flujo-inicial-articulo-S169540331830540X
8. Callén Blecua M, Praena Crespo M, García Merino A, Mora Gandarillas I; Grupo de Vías Respiratorias. Protocolo de bronquiolitis diagnóstico y tratamiento en atención primaria. Protocolo del GVR [Internet]. España: GVR; 2015. [citado 08 Ene 2023]. Disponible en: http://www.respirar.org/images/pdf/grupovias/bronquiolitis pgvr42015.pdf
9. Oliva González Y, Piloto Morejón M, Iglesias Gómez P. Clínica y epidemiología de las infecciones respiratorias agudas en pacientes de 0-14 años. Rev cienc méd Pinar Río [Internet]. 2013 [citado 12 Ene 2023];17(1). Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1561-31942013000100006
10. Bustamante Aponte AO. Factores asociados a evolución desfavorable en pacientes con bronquiolitis hospitalizados en el servicio de pediatría en la Clínica Good Hope en el periodo enero–noviembre en el año 2017 [tesis]. Lima: Universidad Ricardo Palma; 2018 [citado 12 Ene 2023]. Disponible en: https://repositorio.urp.edu.pe/handle/URP/1207
11. Ortega Ramírez ME. Recomendaciones para una lactancia materna exitosa. Acta Pediátrica de México [Internet]. 2015 [citado 12 Ene 2023];36(2). Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.mx/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0186-23912015000200011&lng=es&tlng=es
12. National Collaborating Centre for Women's and Children's Health. Bronchiolitis: diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis in children [Internet]. London: NICE; 2020. [citado 08 Ene 2023]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK299243/
13. Susana Rodríguez M. Bronchiolitis in the year of COVID-19. Arch Argent Pediatr [Internet]. 2020 [citado 08 Ene 2023];118(3):222-223. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32470281/
14. Moreno MG, Sánchez VB, Rivas TG, González NH, Isabel VMM, Ochoa Sangrador C. Effectiveness of high-flow oxygen therapy in a second-level hospital in bronchiolitis. An Pediatr [Internet]. 2022 [citado 08 Ene 2023];96(6):485-491. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35637147/
15. Moreno Carrasco J, Pino Vázquez A. Effect of prenatal and postnatal exposure to tobacco in the development of acute bronchiolitis in the first two years of life. An Pediatr [Internet]. 2021 [citado 08 Ene 2023];94(6):385-395. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34090635/
16. Ramos Fernández JM, Hernández Yuste A, Guitiérrez Bedmar M, Cordón Martínez AM, Moreno Pérez D. Does exposure of pregnant women to epidemic respiratory syncytial virus affect the severity of bronchiolitis? Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin [Internet]. 2019 [citado 08 Ene 2023];37(4):251-255. Disponible en: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0213005X18302337?via%3Dihub
17. Golan Tripto I, Goldbart A, Akel K, Dizitzer Y, Novack V, Tal A. Modified Tal Score: Validated score for prediction of bronchiolitis severity. Pediatric Pulmonol [Internet]. 2018 [citado 18 Ene 2023];53(6):796-801. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29655288/
18. García CG, Bhore R, Soriano Fallas A, Trost M, Chason R, Ramilo O, et al. Risk factors in children hospitalized with RSV bronchiolitis versus non-RSV bronchiolitis. Pediatrics [Internet]. 2012 [citado 12 Ene 2023];126(6). Disponible en: https://www.pediatrics.org/cgi/content/full/126/6/e1453
19. Yanes Macías J, Fonseca Hernandez M, García Rodriguez I, Llul Tombo C, Tio González D, Díaz Ceballos J. Atención al niño con bronquiolitis: consideraciones clínico-terapéuticas generales. Medisur [Internet]. 2022 [citado 05 Ene 2023];20(2):[aprox-175p.]. Disponible en: https://medisur.sld.cu/index.php/medisur/article/view/5208
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Liset Blay-Gómez, Jorge Reinaldo Mondeja-Contino, Margarita Puerto-Díaz, Edward Bediako-Mensah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright: Camagüey Medical Archive Magazine, offers immediately after being indexed in the SciELO Project; Open access to the full text of the articles under the principle of making available and free the research to promote the exchange of global knowledge and contribute to a greater extension, publication, evaluation and extensive use of the articles that can be used without purpose As long as reference is made to the primary source.
Conflicts of interest: authors must declare in a mandatory manner the presence or not of conflicts of interest in relation to the investigation presented.
(Download Statement of potential conflicts of interest)
The Revista Archivo Médico de Camagüey is under a License Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This license allows others to distribute, to mix, to adjust and to build from its work, even for commercial purposes, as long as it is recognized the authorship of the original creation. This is the most helpful license offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials. The full license can be found at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/












 22 julio 2025
22 julio 2025